Best Practices for DNS Configuration with Static IP Assignment
Overview
This article describes best practices for configuring DNS servers on the WAN interfaces of all Cisco Meraki products. One of the most common DNS configurations when assigning a static IP address to a Meraki device is to use one ISP-provided DNS server and one well-known public DNS service such as Google (8.8.8.8). Many ISPs use their own hosted DNS server and may not have all records or have lookups to many publicly accessible servers.
Configuration
One of the most common DNS configurations when assigning a static IP address (see Static IP Assignment) is to use one ISP-provided DNS server and one well-known public DNS service such as Google (8.8.8.8) or Level3 (4.2.2.1). Many ISPs maintain their own hosted DNS server and may not have all records or have lookups to many publicly-accessible servers. In practice, it is good to configure two different DNS servers, as demonstrated in the image below (taken on the local status page of an MX appliance):
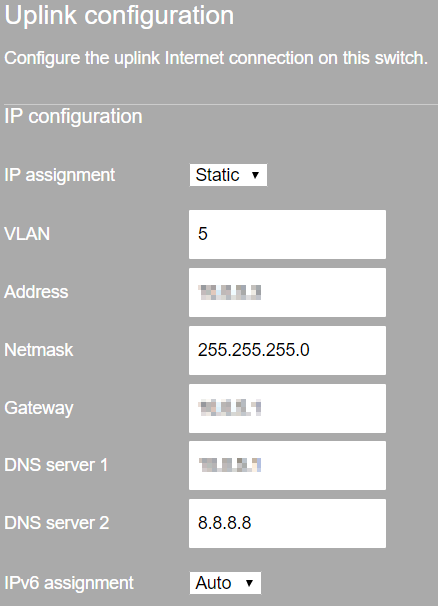
These DNS servers are used by the Meraki device to check Internet connectivity, check into Dashboard, load content lists, and register VPN connections, among other services. Therefore, DNS servers are a critical component for the correct operation of the device, and it is strongly recommended that both DNS server fields be populated.
Note: These DNS servers are only used by the Meraki device for its management traffic and connectivity tests. Downstream clients will not use these servers unless configured within DHCP settings (for more, see: DHCP Services).
Additional resources
For other information on static IP assignment, please refer to Static IP Assignment article.
For information on internet connectivity testing, please refer to Connection Monitoring for WAN Failover article.

