Adaptive Policy for MX/Z Platforms
Overview
This document will cover only the WAN Appliance aspects of the feature enablement process. For more details on the Adaptive Policy feature and its supportability with other platforms, please review this documentation article.
Companies are looking for more granular security and control over segmentation across their network infrastructure. The most challenging part when it comes to network administration and compliance management is monitoring, scaling, and proper security policy of a user/device regardless of where and how the device connects. A security breach can occur with any organization that has to manage many different security policies that are not using the same policy constructs and allow for the same controls.
Traditional segmentation is based on subnets, VLANs and ACL rules. The rule sets are limited to the network which it resides in and is not meant to be globally scalable. Moreover, maintaining ACL based rules can become an operation challenge in sizable deployments with thousands of rules to maintain. Modification of any rule set requires removal/addition/resequencing which brings administrative overhead and complexity. This is a big operational challenge and oftentimes, administrators prefer to add more rules instead of optimizing existing ones.
Cisco’s solution to this challenging problem is Cisco TrustSec (CTS). CTS simplifies policy management by segregating endpoint traffic into groups. Each group is assigned to a Security Group Tag (SGT) and all user traffic associated with the group inherits the tag and its associated enforcement policy (decentralized policy enforcement). The policy should be applied locally and across infrastructures for better security and administration. When a user connects to the network, the assigned tag to the user becomes the identity, and the networking devices use this tag to enforce policies and to make forwarding decisions regardless of where and how the end device connects to the network. In addition, policies can be managed centrally using Cisco ISE and are provisioned dynamically on demand.
Adaptive Policy Architecture
Adaptive Policy has three key components:
-
Identity classification and propagation
-
A tag that is applied to frames from a source device and acts as an identity or grouping for a user/device
-
-
Security policy definition
-
A policy comprised of a source tag, destination tag, and the permissions between them
-
-
Policy deployment and orchestration
-
An engine that implements the policy on supported network devices
-
Enforcement is done on the destination networking device for scalability
-
Destination networking device will deny or allow the flow on the egress based on the policy rules
-
Functionality Breakdown
To enable Adaptive Policy on a MX/Z network the following conditions must be met:
Supported models include all Models that can upgrade to firmware 18.1, except MX84.
| Type | SGT Functionalities | Minimum Firmware | Minimum License |
| SGT Transport | Intra-VLAN transport | TBD | Advanced Security |
| SGT Transport | Inter-VLAN transport | MX 18.1 | Advanced Security |
| SGT Transport | AutoVPN transport | MX 18.1 | Advanced Security |
| SGT Transport | WAN transport for VPN concentrator mode | MX 18.2 | Advanced Security |
| SGT Assignment | Per port assignment | MX 18.2 | Secure SD-WAN Plus |
| SGT Assignment | VLAN assignment and Inter-VLAN transport | MX 18.2 | Secure SD-WAN Plus |
| SGT Assignment | Group Policy assignment | MX 26.1.2 | Advanced Security |
| SGT Assignment | Intra-VLAN transport | TBD | Secure SD-WAN Plus |
| SGT Assignment | IP to SGT assignment | TBD | Secure SD-WAN Plus |
| SGT Assignment | Client VPN assignment and transport (AnyConnect support required) | TBD | Secure SD-WAN Plus |
| SGT Assignment | WAN assignment and transport for VPN concentrator mode (includes vMX) | TBD | Secure SD-WAN Plus |
| SGT Assignment | RADIUS/NAC assignment | TBD | Secure SD-WAN Plus |
| SGT Enforcement | SGACL | TBD | Secure SD-WAN Plus |
Prerequisites
- Verify the MX/Z is running the latest MX18.x and above firmware
- Verify the minimum license support
- SGT Transport requires an Advanced Security license
- SGT Assignment and Transport requires the Secure SD-WAN Plus license
- SGT Enforcement, Assignment, and Transport requires the Secure SD-WAN Plus license
- For license details, please refer to the MX licensing page.
Configuration
Inter-VLAN transport
- Verify and confirm all the prerequisites are met
- Enable adaptive policy for the network
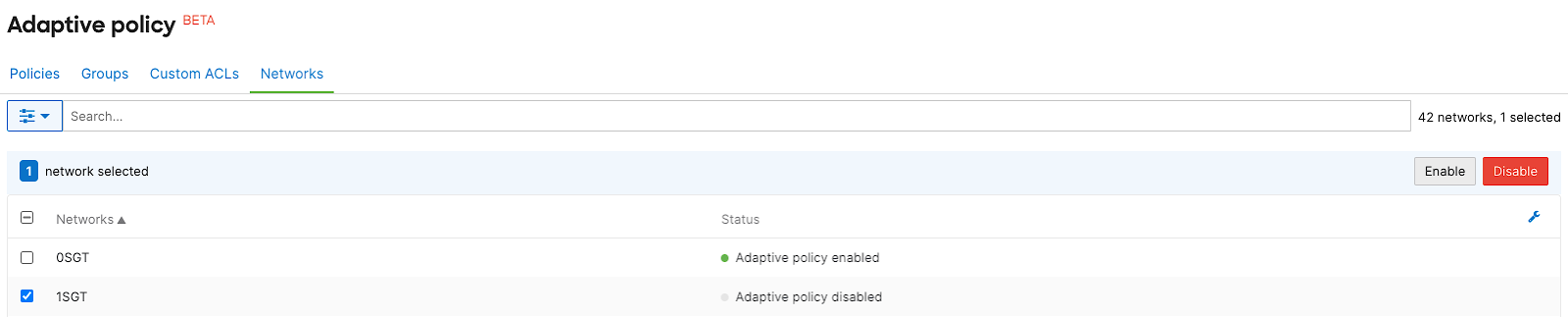
- Navigate to Organization > Configure > Adaptive policy. Select the Networks tab, then select the desired network and Enable adaptive policy for the network
Note: Ensure you have a combined network with SGT compatible devices. For more details, refer to this documentation.
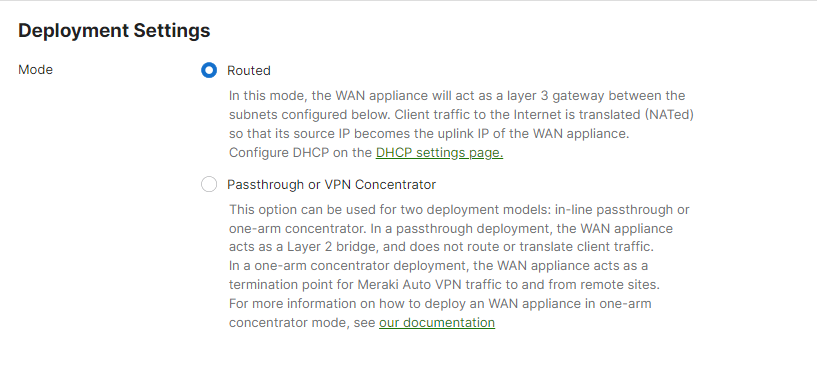
3. Go to the adaptive policy enabled network and select Routed mode in deployment settings
- Under Security & SD-WAN > Configure > Addressing & VLANs, select Routed mode at Deployment Settings
4. Trusting incoming SGT is enabled only via trunk ports and hence requires selecting VLANs for LAN settings. For MX18.2 and beyond, SGT Assignment can be configured on trunk or access ports.
- Under Security & SD-WAN > Configure > Addressing & VLANs, enable VLANs under Routing > LAN settings section

5. Enabling peer SGT capable requires a trunk port. As a result, the WAN Appliance will trust incoming SGT packets via the directly connected peer, and will not override the incoming SGT value. When trunk mode is selected, you will see the option to configure peer SGT capable on the LAN.
- Under Security & SD-WAN > Configure > Addressing & VLANs page, select Routing > Per-port VLAN settings > Trunk > Peer SGT capable, then select Enable
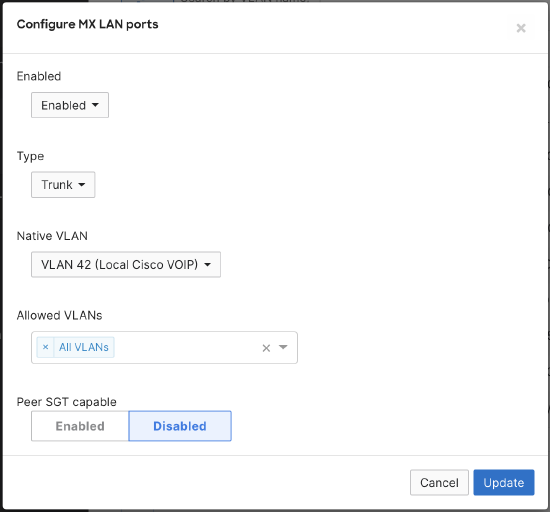
- With the introduction of peer SGT capable configuration, you will now see an additional column in the Per-port VLAN Settings table:
Note: Template, API, and logging support are TBD. SGT Assignment and Policy enforcement is currently done by MS and MR.
Static VLAN Assignment
-
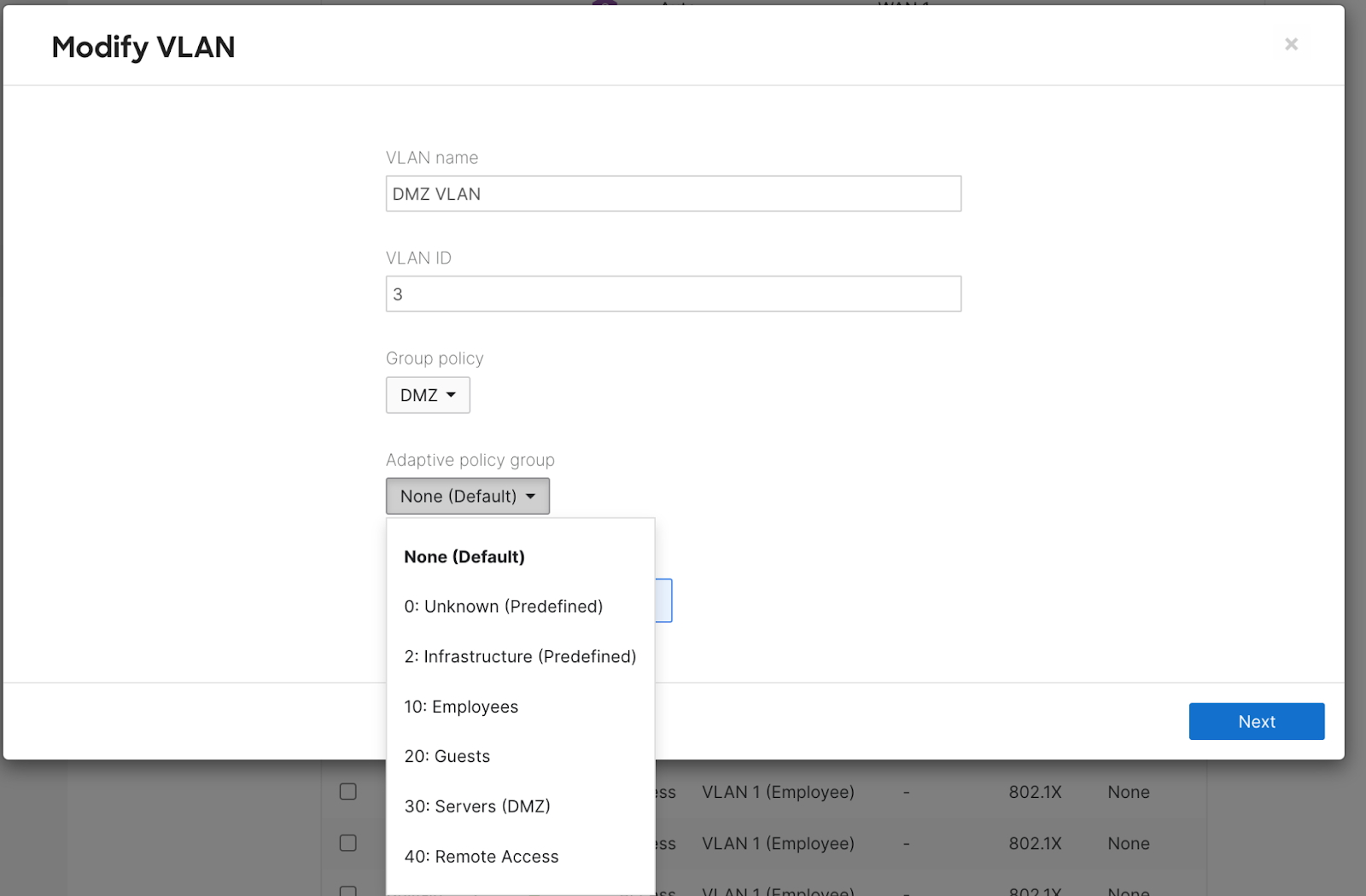
Navigate to Security & SD-WAN > Configure > Addressing & VLANs
-
Select the VLAN you would like to statically tag
-
Set the Adaptive policy to the desired group. This will tag the traffic with the SGT identified for the group.
-
Click Next
-
Click Preview
-
Click Update
-
Save
Static LAN Port Assignment
-
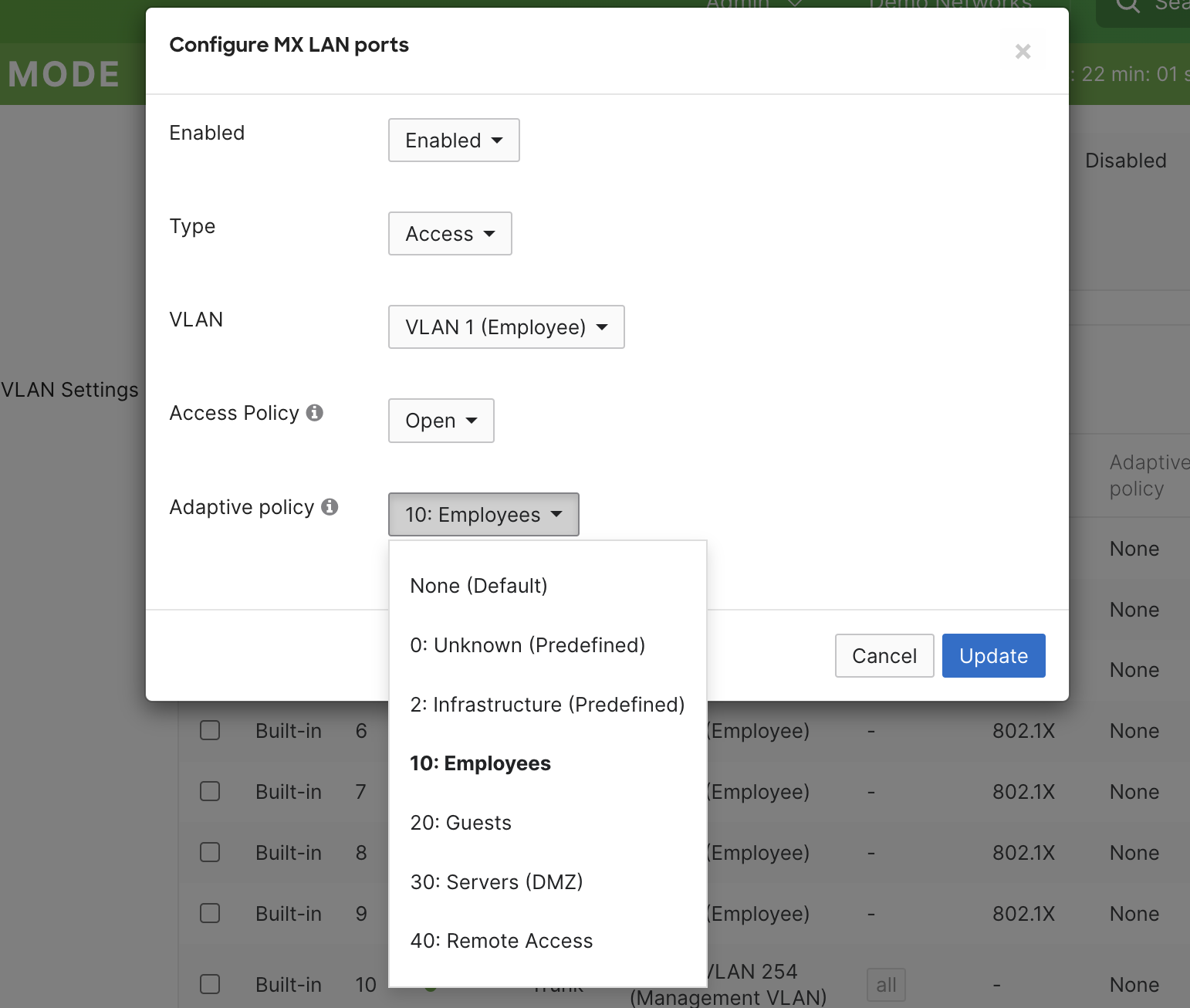
Navigate to Security & SD-WAN > Configure > Addressing & VLANs
-
Select the port(s) you would like to statically tag
-
Set the “Adaptive policy” to the desired group. This will tag the traffic with the SGT identified for the group.
-
Save
Assignment via Group Policy
To assign a Security Group Tag (SGT) using Adaptive Policy through Group Policy, follow these steps:
-
Navigate to Group Policies
Go to Network-wide > Group policies in the Meraki Dashboard. -
Select or Create a Group Policy
- To create a new Group Policy, click Add a group and configure the desired settings.
- To use an existing Group Policy, select it from the list.
-
Assign an SGT
- Scroll down to the Adaptive Policy SGT section.
- Enable the option to Assign SGT.
- From the dropdown menu, choose the Security Group Tag (SGT) you wish to assign to this policy.
-
Save Your Changes
Click Save to apply the SGT assignment to the selected Group Policy.

Note: An MX on 26.1.2 will also match an SGT to a Group Policy and enforce the Group Policy settings. Please see this article for more details.
Enable SGT Peer on WAN interface (Concentrator Only)
-
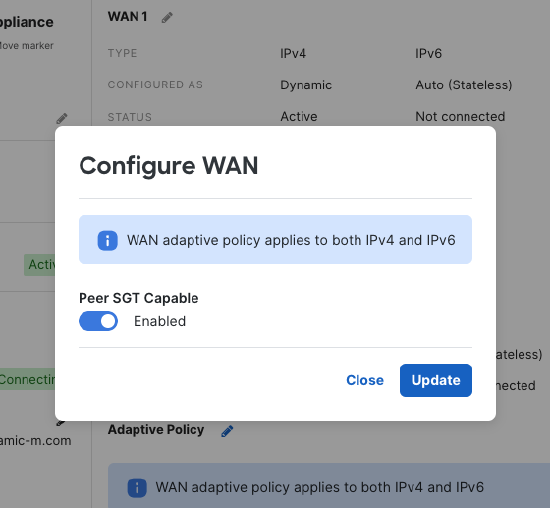
Navigate to Security & SD-WAN > Monitor > Appliance Status. Click on the “Uplink” tab.
-
Click the pencil next to “Adaptive Policy”
-
Set Peer SGT Capable to “Enabled”
-
Click “Update” to save
Expected Behavior
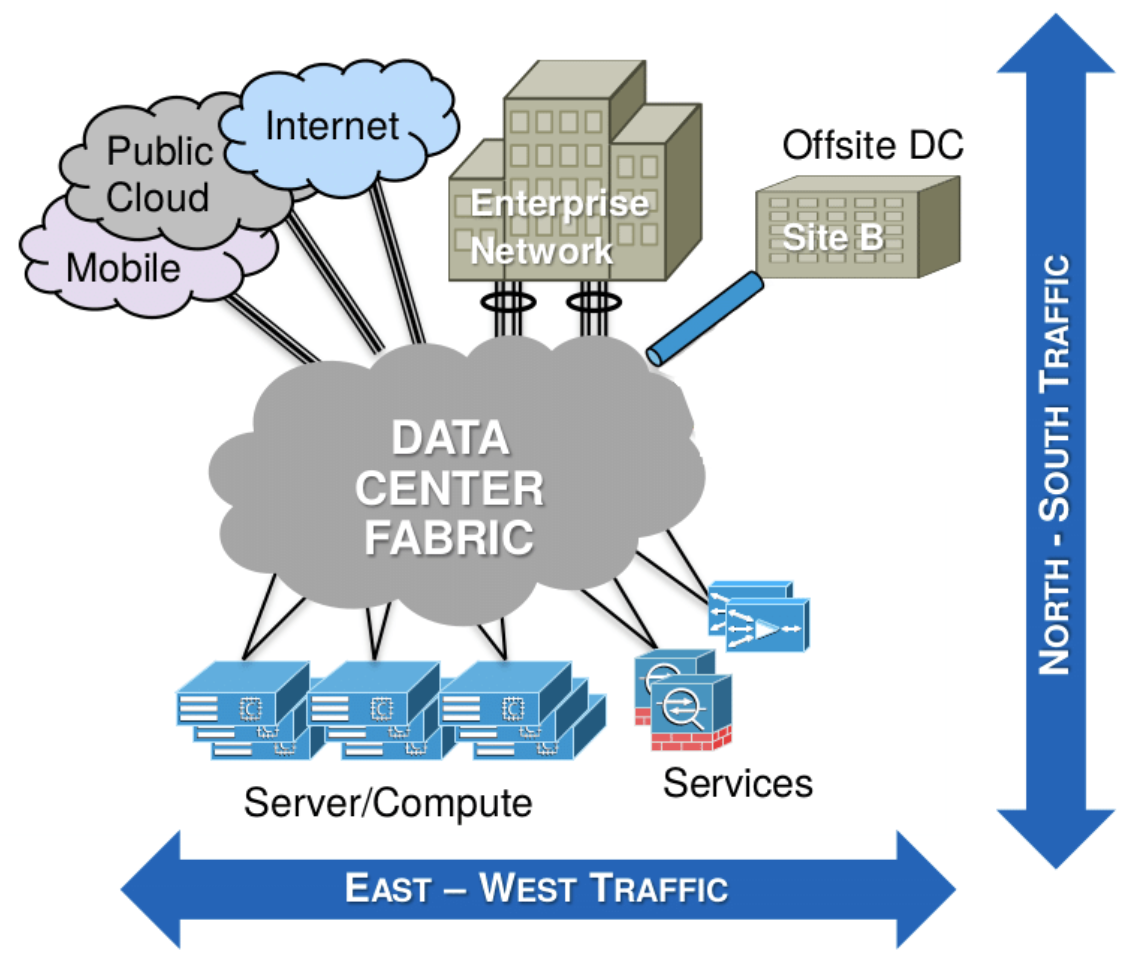
Test conditions are broken down to East-West and North-South traffic. Let's compare the difference between East-West and North-South traffic:
- East-West traffic usually refers to the traffic enclosed within the same network. North-south on the hand refers to the traffic traversing different networks.
- For Inter-VLAN functionality, our test conditions are restricted to East-West traffic as shown below:
|
Port_1 Peer SGT Capable [Enable/Disable] |
What's the ingress packet type? [SGT/non-SGT packet] |
What's the ingress behavior? |
Port_2 Peer SGT Capable [Enable/Disable] |
What's the egress packet type? [SGT/non-SGT packet] |
What's the egress behavior? |
| Enable | SGT packet | Preserve and forward the SGT packet | Enable | SGT packet | Forward the SGT packet |
| Disable | SGT packet | Strip the SGT tag and forward the non-SGT packet | Enable | Add SGT tag =0 and forward the SGT packet | Forward the SGT packet |
| Enable | Non-SGT packet | Add SGT tag=0 and forward the SGT packet | Enable | SGT packet | Forward the SGT packet |
| Disable | Non-SGT packet | Forward the non-SGT packet | Enable | Add SGT tag=0 and forward the SGT packet | Forward the SGT packet |
| Enable | SGT packet | Preserve and forward the SGT packet | Disable | Strip the SGT tag and forward the non-SGT packet | Forward the non-SGT packet |
| Disable | SGT packet | Strip the SGT tag and forward the non-SGT packet | Disable | Non-SGT packet | Forward the non-SGT packet |
| Enable | Non-SGT packet | Add SGT tag=0 and forward the SGT packet | Disable | Strip the SGT tag and forward the non-SGT packet | Forward the non-SGT packet |
|
Disable |
Non-SGT packet |
Forward the non-SGT packet | Disable | Non-SGT packet | Forward the non-SGT packet |
AutoVPN transport
- Verify and confirm all the prerequisites are met
- Enable adaptive policy for the network
- Navigate to Organization > Configure > Adaptive policy, click on the Networks tab, then select the desired network and click Enable adaptive policy for the network
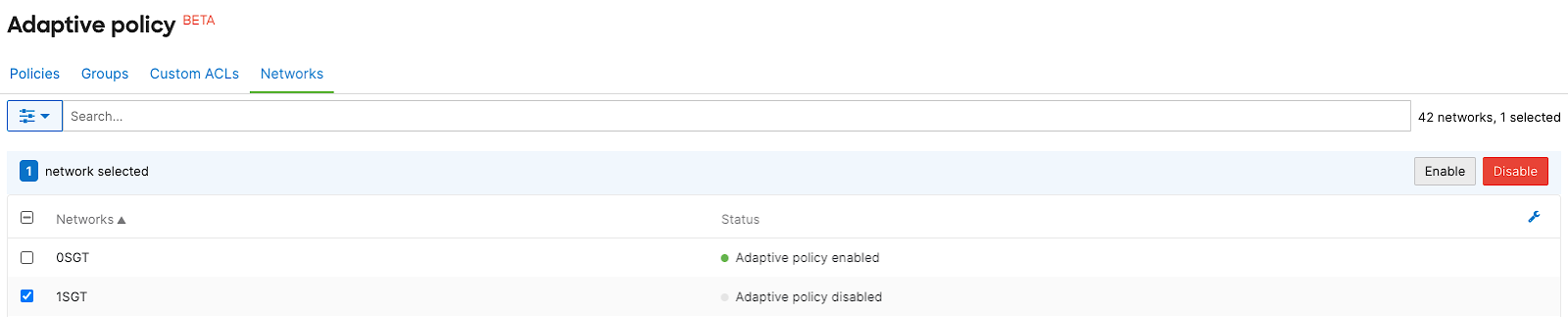
3. Navigate to VPN settings to enable SGT transport for AutoVPN peering.
- Navigate to Security & SD-WAN > Configure >Site-to-site VPN, under VPN settings > Peer SGT Capable > Select Enable
- Enable for both WAN Appliance peers to preserve and transport SGT packets across the AutoVPN fabric.
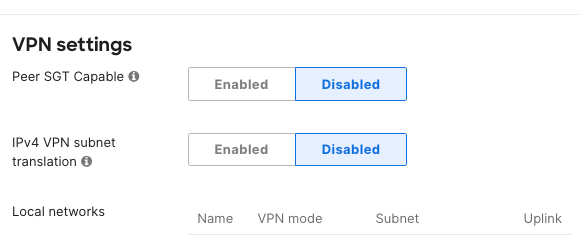
Keep in mind you must enable "Peer SGT Capable" for both peers to preserve and carry SGT packets across the AutoVPN fabric. If either WAN Appliance peer have "Peer SGT Capable" disabled, then SGT packets will not be preserved and transported across the AutoVPN network.
Note: Template, API, and logging support are TBD. SGT Assignment and Policy enforcement is currently done by MS and MR.
Expected Behavior
- For AutoVPN transport functionality, our test conditions are restricted to North-South traffic as shown below:
|
Local MX: VPN Peer SGT Capable [Enable/Disable] |
What's the ingress packet type? [SGT/non-SGT packet] |
What's the ingress behavior for AutoVPN transport (including AutoVPN transport)? |
Remote MX: VPN Peer SGT Capable [Enable/Disable] |
What's the egress packet type when exiting AutoVPN? [SGT/non-SGT packet] |
What's the egress behavior? |
| Enable | SGT packet | Preserve and forward the SGT packet | Enable | SGT packet | Forward the SGT packet |
| Disable | SGT packet | Strip the SGT tag and forward the non-SGT packet | Enable | Non-SGT packet | Forward the non-SGT packet |
| Enable | Non-SGT packet | Add SGT tag=0 and forward the SGT packet | Enable | SGT packet | Forward the SGT packet |
| Disable | Non-SGT packet | Forward the non-SGT packet | Enable | Non-SGT packet | Forward the non-SGT packet |
| Enable | SGT packet | Strip the SGT tag and forward the non-SGT packet | Disable | Non-SGT packet | Forward the non-SGT packet |
| Disable | SGT packet | Strip the SGT tag and forward the non-SGT packet | Disable | Non-SGT packet | Forward the non-SGT packet |
| Enable | Non-SGT packet | Forward the non-SGT packet | Disable | Non-SGT packet | Forward the non-SGT packet |
|
Disable |
Non-SGT packet |
Forward the non-SGT packet | Disable | Non-SGT packet | Forward the non-SGT packet |
Compatibility With Other Cisco Technologies
With adaptive policy utilizing Cisco’s inline SGT functionality the feature is compatible across a number of solutions including but not limited to:
-
Catalyst switching and routing (3k, 4k, 6k, 9k, ISR)
-
ASR and CSR
-
Sourcefire Next Generation Firewalls (FTD)
-
Adaptive Security Appliances (ASA)
-
Application Centric Infrastructure (ACI)
-
Datacenter switching (Nexus)
-
Software Defined Access (SD-Access)
For more information on which Cisco platforms support inline SGTs please see: Cisco Trustsec Compatibility Matrix
For Documentation on interoperability with Catalyst please see: Adaptive Policy and Catalyst Interoperability
For Documentation on interoperability with Cisco Identity Services Engine please see: Adaptive Policy and Cisco ISE
Additional Adaptive Policy Resources
For additional information on Adaptive Policy, refer to the following links:
Adaptive Policy Overview
Adaptive Policy Configuration Guide
Adaptive Policy MS Configuration Guide
Adaptive Policy MR Configuration Guide
Adaptive Policy Telemetry