MI VoIP Health Overview
VoIP Health Overview
The VoIP Health feature is designed to monitor network links for the performance of the uplink for VoIP. This feature will monitor the path from each ISP uplink to the VoIP servers (i.e. PBX or SIP server) and the path to your VoIP on-prem servers configured by the admin. Monitoring occurs via ICMP Probes every second to the endpoint. The admin can use this information to estimate the call quality along each path. VoIP Health is an active monitoring tool utilizing probes from the WAN appliance to measure VoIP performance parameters and provide results based on the MOS (mean opinion score) of the link.
VoIP Health solves two use cases for users:
-
Is the link causing poor call quality?
-
If the link is not causing poor call quality, what is the issue and who should I reach out to, to fix the problem?
Activate VoIP Health
VoIP Health is a part of the Meraki Insight product line. If your organization has Meraki Insight licenses added to the dashboard, VoIP Health should be enabled by default. For more information about Meraki Insight please refer to our Introduction to Meraki Insight article.
Configuration
To get the most out of VoIP Health, you will require the IP address of the servers from your service providers.
Note: h.323 is not supported.
Note: IP addresses may be available on your service provider’s portal or you can find out the address by contacting your service provider's support.
Support for URL/FQDN Monitoring has been deprecated and is not longer enabled.
Once you have the IP address available, try pinging it by using the ping tool on Security Appliance > Monitor > Appliance Status > Tools to make sure it is reachable. After the successful ping responses, you can navigate to the Insight > Monitor > VoIP Health page.
For the first time configuration, the landing page will direct you to the configuration wizard:
To configure your servers, click on “Configure VoIP Servers” and it will lead you to the Add VoIP Servers screen as shown below:

Here you can add the provider’s name for your reference and the corresponding IP address of the provider’s SIP servers. If your provider has multiple SIP servers, you can add them under the same provider by clicking on Add more VoIP servers. If you use multiple providers and would like to track all of them, you can add them by clicking Add more VoIP providers. Once all the providers and servers are added, hit Save. After adding the servers, it may take up to 15 minutes for VoIP performance to populate in the dashboard.
Best Effort Monitoring
There are some VoIP servers that do not allow or drop the ICMP pings used for monitoring VoIP statistics such as MOS, loss, latency, and jitter. However, as VoIP services are critical, we have integrated Best Effort Monitoring to MI VoIP Health to give a “nearest” best estimation on VoIP performance for a given link.
This tool will measure the performance of the hop nearest to the server that responds to ICMP. By enabling 'Ping Nearest Hop' under the Configure VoIP server option, you can get a good approximation of the VoIP behavior on the given link to the given VoIP server if the server does not respond to ICMP directly.
If you try pinging the VoIP server by using the ping tool on Security Appliance > Monitor > Appliance Status > Tools and if it fails, the BEM feature in VoIP Health will look at the nearest available hop to the server and start monitoring VoIP statistics. MOS, Loss, Latency, and Jitter are the statistics that are monitored to reflect the behavior of the "Nearest Hop" to the VoIP server.
While using the "Configure Server option" to add a VoIP server you will notice "Ping nearest Hop" option is available under the Best Effort Monitoring column. (See above screenshot)
1. If left unchecked and the VoIP server is pingable, then the box will turn into a green checkmark,  indicating the end VoIP server is reachable and BEM is not needed.
indicating the end VoIP server is reachable and BEM is not needed.
2. If you identify that the VoIP server is non-pingable, then you can check the box for the BEM tool to identify the nearest hop to the end VoIP server and start monitoring VoIP statistics to that hop.
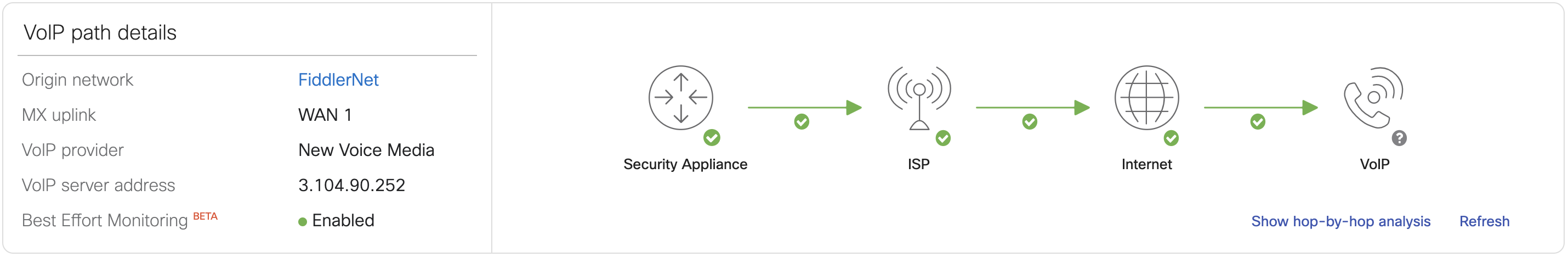
The Drill-down page will indicate if Best Effort Monitoring is enabled by the green radio button. Running "Show Traceroute" will run it to the nearest pingable hop and give you a hop-by-hop analysis for the same.
Overview Page
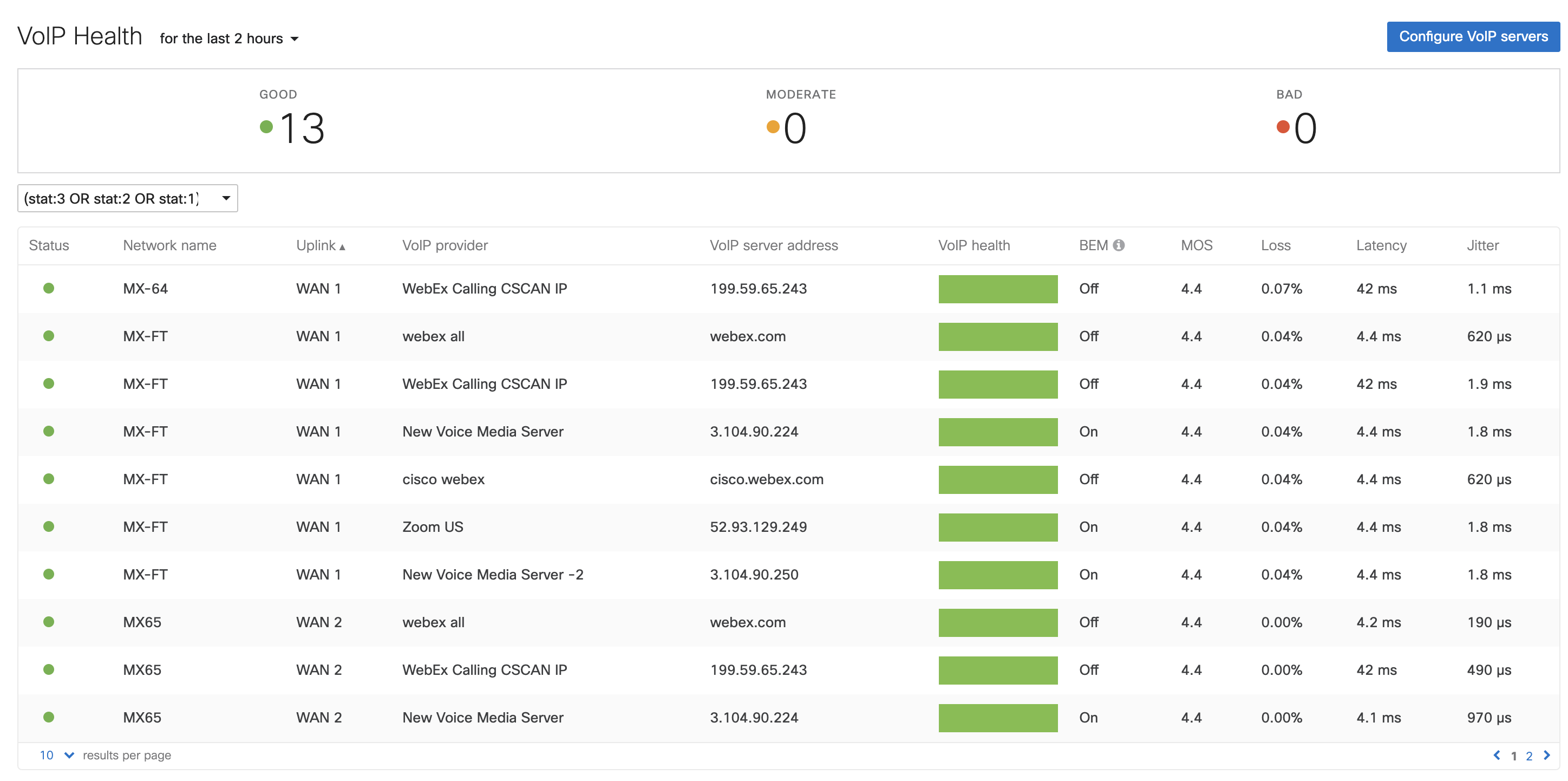
Once MI starts collecting the data, it will show an overview of your organization links and the performance of the links for the provider’s SIP server. VoIP Health measures Loss, Latency, Jitter and MOS (mean opinion score) based on the provider's responses to the probes sent to the provider's SIP servers. Each uplink will send probes to each SIP server and give the performance analysis of the link. Depending on the MOS threshold, VoIP health will highlight the uplink in 3 different categories. The category and corresponding MOS thresholds are listed below:
|
MOS |
Uplink |
|
> 4 |
Good |
|
3.5 - 4 |
Moderate |
|
< 3.5 |
Bad |
The BEM column will show the status as being "ON" or "OFF" against networks that have the "Ping Nearest Hop" enabled or disabled.
Note: We probe with ICMP pings to the server from the WAN appliance interfaces.
Detailed View
By clicking on the individual link, it will show a detailed view of each of the four parameters. The graphs can be expanded for the last 2 hours, the last day, and last week. The MOS graph highlights time periods during which MOS dipped below the acceptable threshold, indicating that call quality may have been impacted during that time.
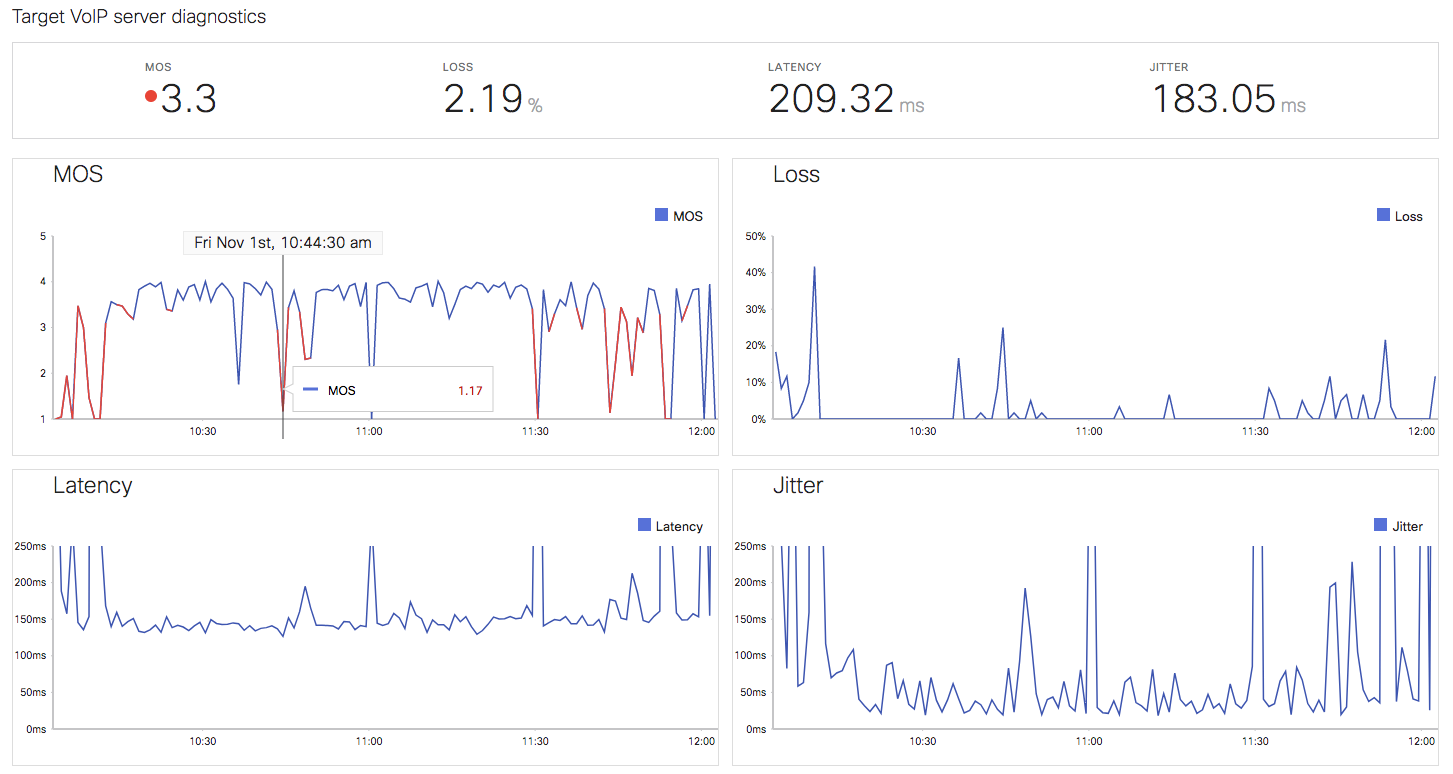
The detailed view also provides a network name, SIP server details, link details, and a traceroute tool to confirm the behavior and find the root cause. By clicking on hop-by-hop analysis, it will show details of each hop.
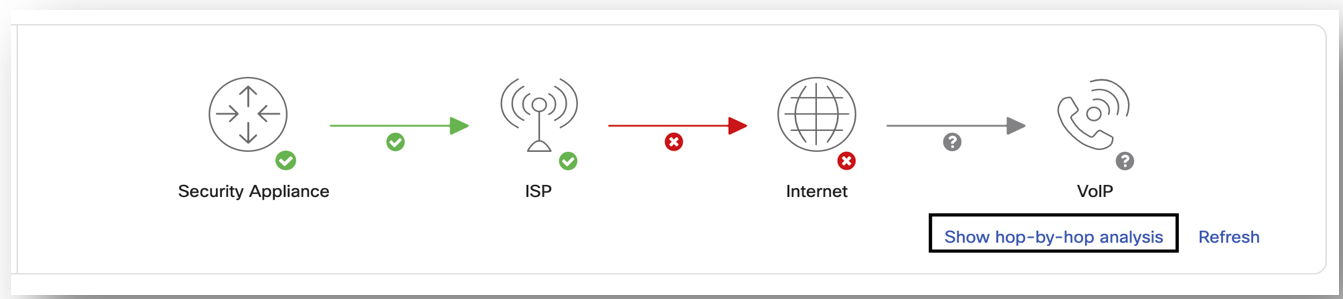
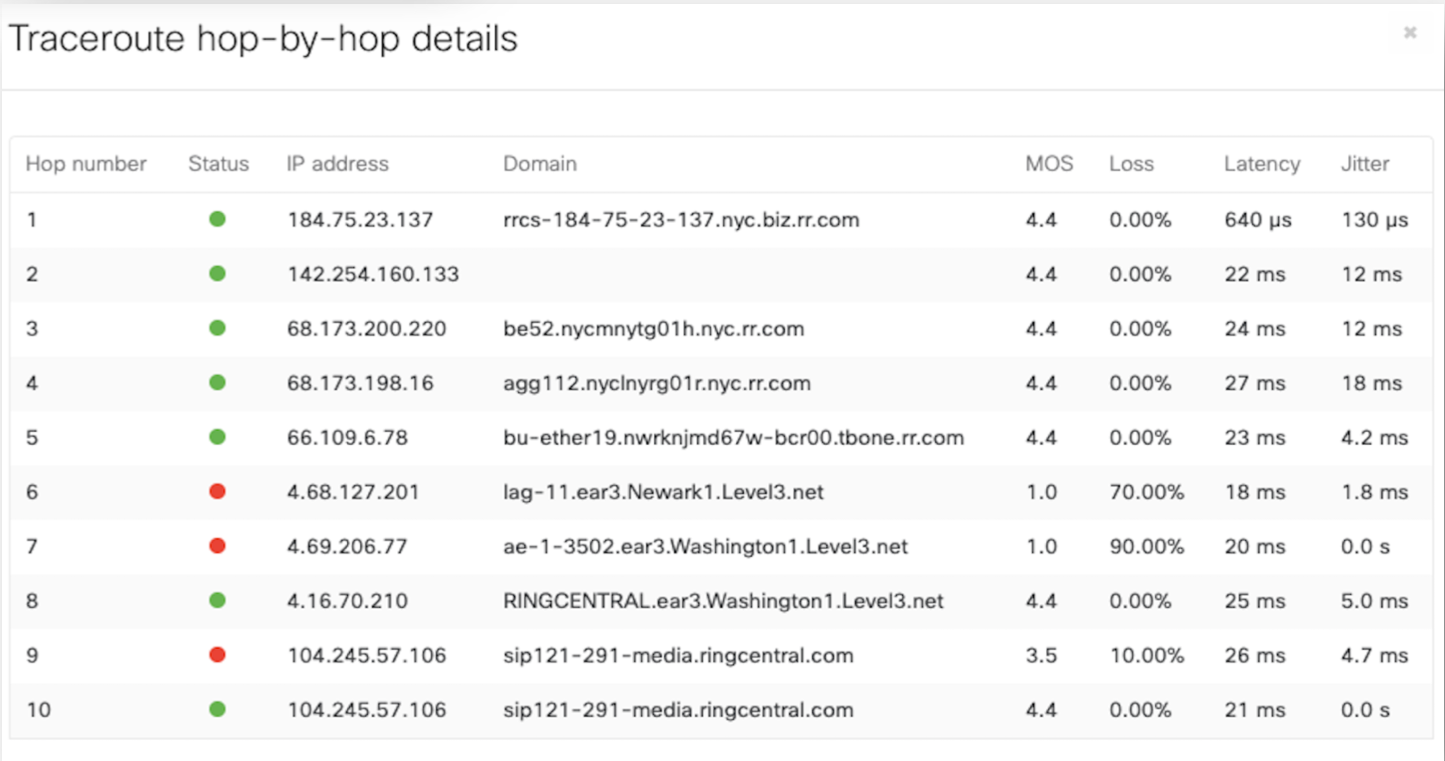
BEM status is indicated under the VoIP path details and the traceroute diagram will indicate a "?" against the VoIP server icon showing that it is unreachable and is pinging the "nearest hop" to the VoIP server configured. The Show hop-by-hop analysis will show all the hops till the configured VoIP server but will only show MOS, loss, latency, and jitter scores till the last pingable hop. The rest of the hops from the last pingable hop to the configured VoIP server will be grayed out with no stats on MOS, loss, latency, or jitter.
How the traceroute Tool Works
VoIP Health will use traceroute to repeatedly probe each hop along the path between the WAN appliance and the VoIP server. The tool uses these probes to calculate the MOS at each hop. If the MOS meets the threshold defined above, it will mark the hop as ‘Good’. If it violates the thresholds, it will mark the hop as ‘Bad’.
Limitations
-
VoIP Health gives performance details between two endpoints (i.e. WAN appliance and SIP server)
-
It does proactive monitoring only - it does not monitor the call quality of any calls themselves
-
VoIP Health does have metrics between WAN appliance and SIP servers. It does not have metrics between WAN appliance and any particular phones
-
-
VoIP Health can only be configured with IPs and domains. Subnets are not currently supported
-
VoIP On-Prem (Servers with private IP addresses) will not show the hops between the WAN appliance in the Traceroute diagram on the detailed page

