Troubleshooting Client VPN with Packet Captures
Click 日本語 for Japanese
This article provides best practices for using packet captures to troubleshoot client VPN connection issues, including expected behavior and troubleshooting steps.
NOTE: This article assumes IKEv1 is using Main Mode and not Aggressive Mode. Aggressive Mode is not recommended on MX 14 and earlier firmware versions due to known security flaws in the protocol. Aggressive Mode is not supported for client VPN on MX 15 and later firmware versions.
Negotiation Process
Client VPN connections are negotiated with the following process:
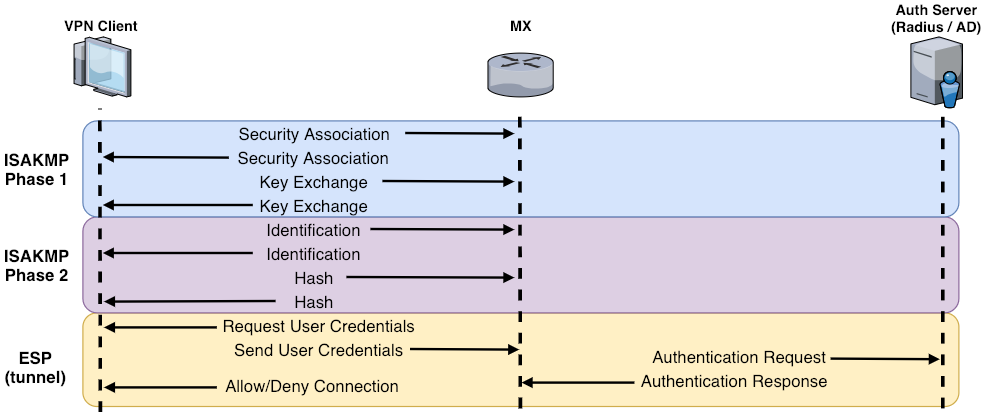
The guide below provides guidance on using a WAN packet capture to troubleshoot failures in this process.
Understanding the WAN Packet Capture
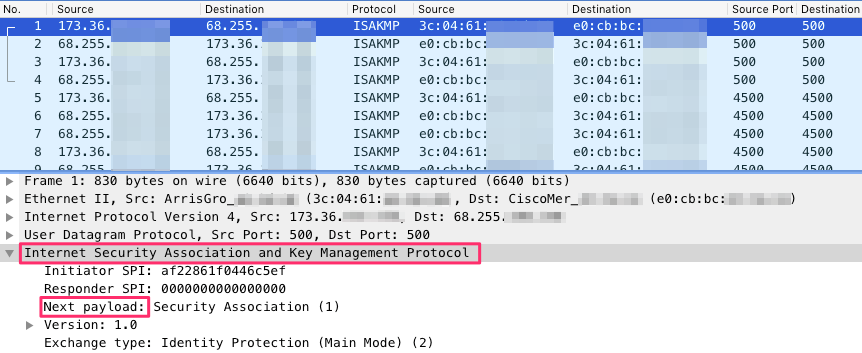
Filter the WAN pcap for the client’s public IP and ISAKMP/ESP, if necessary. Look for the ISAKMP “Next payload” field, which identifies the negotiation step. Start at the first “Security Association” from the client.
Troubleshooting Tips
If there is no ISAMKP traffic from the client:
- Verify client is connecting to the primary MX WAN IP (VIP for warm spare)
- Verify inbound UDP 500 traffic is not being blocked/dropped upstream
- If the MX is behind a NAT, port forwarding on UDP ports 500 and 4500 might need to be configured on the upstream device
- Test the connection on a different device type (e.g. a different OS or smart phone) to rule out OS-specific causes
ISAKMP Phase 1
1. Security Association
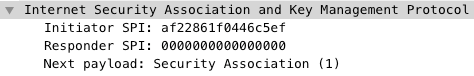
The initiator sends a Security Association and the responder sends a Security Association response.
2. Key Exchange
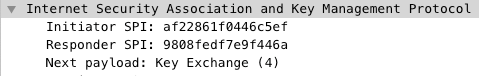
The initiator sends a Key Exchange and the responder sends a Key Exchange response.
Troubleshooting Tips
Phase 1 uses UDP 500, phase 2 uses UDP 500 or UDP 4500 (NAT-T)
- If the MX doesn’t respond to the client, verify:
- The destination IP and MAC addresses (or VIP for warm spare) are correct
- Port forwarding is not configured on the MX for port 500
- Client is not trying to connect from behind the same MX
- Client public IP does not match any non-Meraki VPN peer IPs or another currently connected VPN client
- Any extra configuration options manually applied to the MX that would override default client VPN settings
- If both sides are continually sending Security Association, this could indicate port 500 traffic isn’t being received at the client
- If one side is continually sending Key Exchange, this could indicate one of the following problems:
- Incorrect pre-shared key
- Port 4500 traffic to initiate phase 2 is being dropped or filtered and not reaching the client
ISAKMP Phase 2
3. Identification
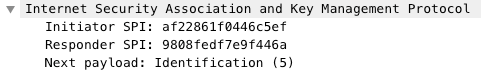
The initiator sends an Identification, and the responder sends an Identification response.
4. Hash
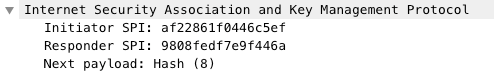
The initiator sends a Hash, and the responder sends a Hash response.
Troubleshooting Tips
Phase 2 uses UDP 4500 (NAT-T) or sometimes UDP 500
- If both sides are continually sending phase 2 packets, this might indicate one of the following problems:
- Incorrect encryption or authentication settings
- Incorrect subnet definition (site-to-site only)
- Verify VPN settings on the client device, for more information see Client VPN OS Configuration
ESP
If bidirectional ESP traffic is seen, the tunnel is up.
- User authentication happens at this step
- The WAN packet capture will no longer be helpful, since everything is encrypted past this point
- Verify if the authentication is successful between the MX and the authentication server
Troubleshooting Tips
For Meraki Cloud authentication, verify:
- The MX WAN port can resolve meraki.com via DNS, and all required cloud connections are allowed on upstream equipment; for additional explanation of what Meraki requires for cloud communication, see Upstream Firewall Rules for Cloud Connectivity
- The account is "Authorized for client VPN" in dashboard and the password is correct
For RADIUS authentication, verify:
- RADIUS authentication packets sent between MX and server must result in ACCESS-ACCEPT for successful connection
- RADIUS server event log, for more information, see RADIUS Issue Resolution Guide
For Active Directory authentication, verify:
- Active Directory packets sent between MX and server show a successful TLS connection
- Active Directory server event log
For all authentication types:
- If no authentication logs or packets are seen, the client may not be sending credentials
- The client may need to verify their VPN settings, for more information, see Client VPN OS Configuration
- If the problem exists for only one client, troubleshooting might be required at the client machine (e.g. reboot, check for conflicting software)
- If authentication is successful but client still fails to connect, ensure the IP pool for the client VPN subnet is not exhausted

