NAT Exceptions with Manual Inbound Firewall on MX Security Appliances
Overview
In some circumstances, network administrators may have topologies that require network traffic to egress the WAN interface while maintaining its private source IP address. While it is recommended to rewrite all internal source addresses to protect the internal network and prevent IPv4 exhaustion, some use cases require internal traffic to maintain the same internal source IP. A typical use case is a layer 3 MPLS VPNs terminating on a WAN uplink of the WAN appliance. The NAT Exceptions with Manual Inbound Firewall feature allows for WAN appliances to fulfill these use cases.
NAT Exceptions
NAT Exceptions (AKA No NAT) offer the ability to configure NAT exemptions on some or all configured VLANs. This exempts the source IP address of a packet received on the LAN of the WAN appliance from being rewritten as it transverses the WAN uplink.
As of 16+ firmware, changes were required that prevent the concurrent use of Client VPN, (either via AnyConnect or IPsec) and No NAT.
The MX will still be able to establish IPsec tunnels if initiated from the MX. However, incoming ISAKMP requests will be dropped when NAT Exceptions is enabled.
WARNING: Allowing Inbound traffic on VLANs with NAT Override
When an MX is running MX 18.x, inbound traffic is not allowed through the WAN interface of VLANs with the No-NAT Exceptions override.
Workaround: To allow traffic inbound on these VLANs, a 1:1 NAT rule corresponding with the IP(s) you need inbound connectivity towards is required alongside the appropriate inbound firewall rules.
For example, if No-NAT is enabled on a VLAN configured with 192.168.0.0/24 and you wanted to allow externally sourced traffic inbound to 192.168.0.100, then a 1:1 NAT rule must be configured mapping 192.168.0.100 LAN to 192.168.0.100 WAN. This would also require a corresponding inbound firewall rule allowing remote sources to 192.168.0.0/24.
Use Cases
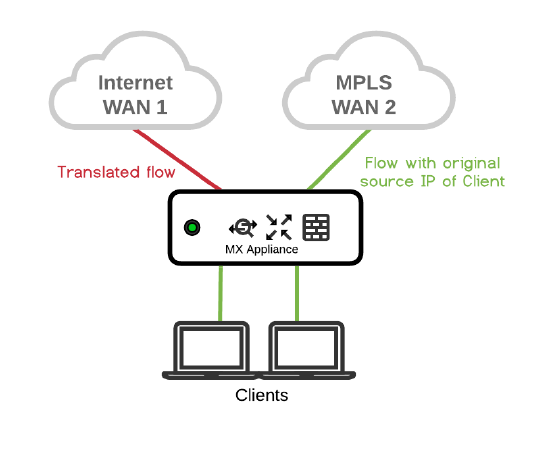
Direct Internet Access with MPLS failover
|
|
Problem: Client needs to access MPLS network with original source IP. Solution: This problem can be solved with NAT Exceptions enabled on WAN2. Traffic is NATed on the Internet link and not NATed over MPLS link. |
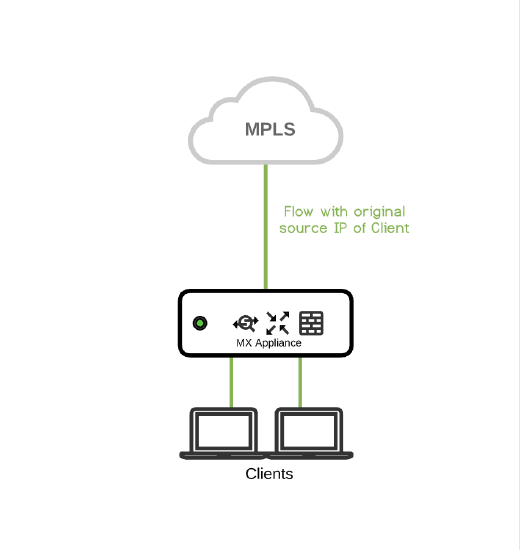
MPLS-only branches
|
|
Problem: Only MPLS at branch with Internet access at Data Center. Clients needs to access MPLS network with original source IP. Solution: This problem can be solved with NAT Exceptions enabled on the WAN interface. Traffic will not be NATed on the WAN. The WAN appliance needs to be online via MPLS for cloud management. |
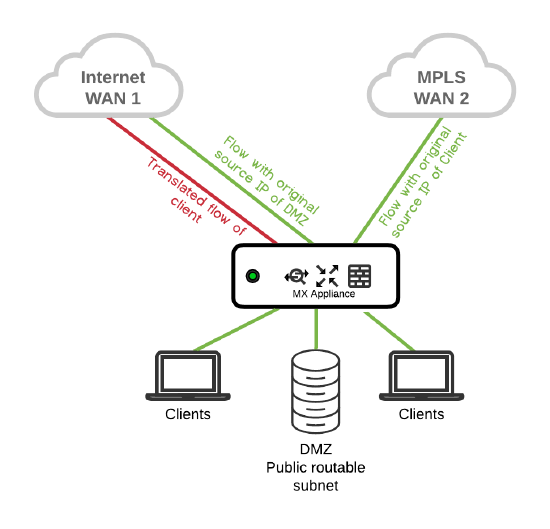
Publicly routable LAN subnets and DMZs
|
|
Problem: Ability to configure publicly routable DMZ subnet. Solution: With NAT Exceptions enabled on the DMZ VLAN, public routable subnets can be used in the DMZ. Public routable subnet is not NATed, MPLS is not NATed while traffic over Internet link is NATed. |
Caution
Inbound Firewall
When you opt into using NAT Exceptions, the inbound firewall configuration interface will be enabled as well. The inbound firewall will be used to police traffic sourced from outside the network. This includes inbound connections for 1:1 NAT, 1:Many NAT, port forwards, and client VPN connections. You will risk unauthorized access to your network if you do not configure the inbound firewall correctly.
The WAN appliance Firewall will remain stateful for traffic initiated from inside the network (behind the WAN appliance). Only traffic initiated from outside the network (on the WAN side) will be affected by the inbound firewall.
Requirement: Inbound traffic requires a NAT override at the uplink level.
Behavior: When inbound traffic is allowed on a 'No-NAT' uplink, it is granted to all VLANs. This includes VLANs configured with a local NAT override.
What you need to do
A Deny Any Any rule is automatically configured as the default rule for the inbound firewall. Any externally sourced traffic that you would like to allow through can be configured as Allow Rules. Please note that a Deny Any Any rule will not take the Security Appliance offline or affect cloud management traffic.
These rules can be created by navigating to the Security & SD-WAN > Configure > Firewall page. Permit inbound connections as needed.
The default Deny Any Any rule for the inbound firewall is the default Routed Mode behavior when this feature is enabled via the Early Access page. If you previously had this feature enabled by support as part of Beta, the behavior will not have changed until the feature override is removed via a support request.
If your MX is configured for Passthrough mode, the default firewall rule is Allow Any Any.
1:1/ 1:Many NATs, Port forwards, Firewall Services
The inbound firewall overrides the “allowed inbound connections” field for NATs, port forwards, and firewall host services, etc.
The inbound firewall also affects inbound services such as Web Local Status Page, Port Forwarding, or Client VPN(assuming No NAT is disabled) and rules must be configured towards the MX's uplink IP (or virtual IP, if in a warm-spare configuration using one) in order for those connections to be allowed.
What you need to do
Use inbound firewall to accommodate allowed inbound connections for NATs, port forwards and firewall services on the inbound firewall on the Security & SD-WAN > Configure > Firewall page.
Inbound firewall rules must use the MX WAN interface IP address in the destination, not the LAN IP configured under NAT/port forwarding rules. Ensure to specify destination port in the rule as well.
Prerequisites
- This feature requires MX 15.4 firmware or higher
- This feature can be enabled on your network via the Organization > Early Access page
- Overriding NAT per-VLAN option is only available when VLANs are enabled and NAT Exceptions is disabled on either uplink. As seen in the image above and below.

Configuration
To configure NAT Exceptions, once enabled, navigate to Security & SD-WAN > Configure > Addressing & VLANs.
Below are configuration examples and expected behavior.
Configuration Example 1 - NAT disabled on Uplink 1

Override NAT per VLAN option is only available when VLANs are enabled and NAT Exceptions is disabled on either Uplink. As seen in the image above and below.

Expected Behavior
All traffic flowing out of the WAN appliance through uplink 1/WAN 1 will not be NATed (LAN sourced traffic will maintain the source IP address). While all traffic flowing out via uplink 2/WAN2 will be NATed.
Configuration Example 2 - NAT disabled on Uplink 1 and Uplink 2, with VLAN 100 set to override NAT Exceptions
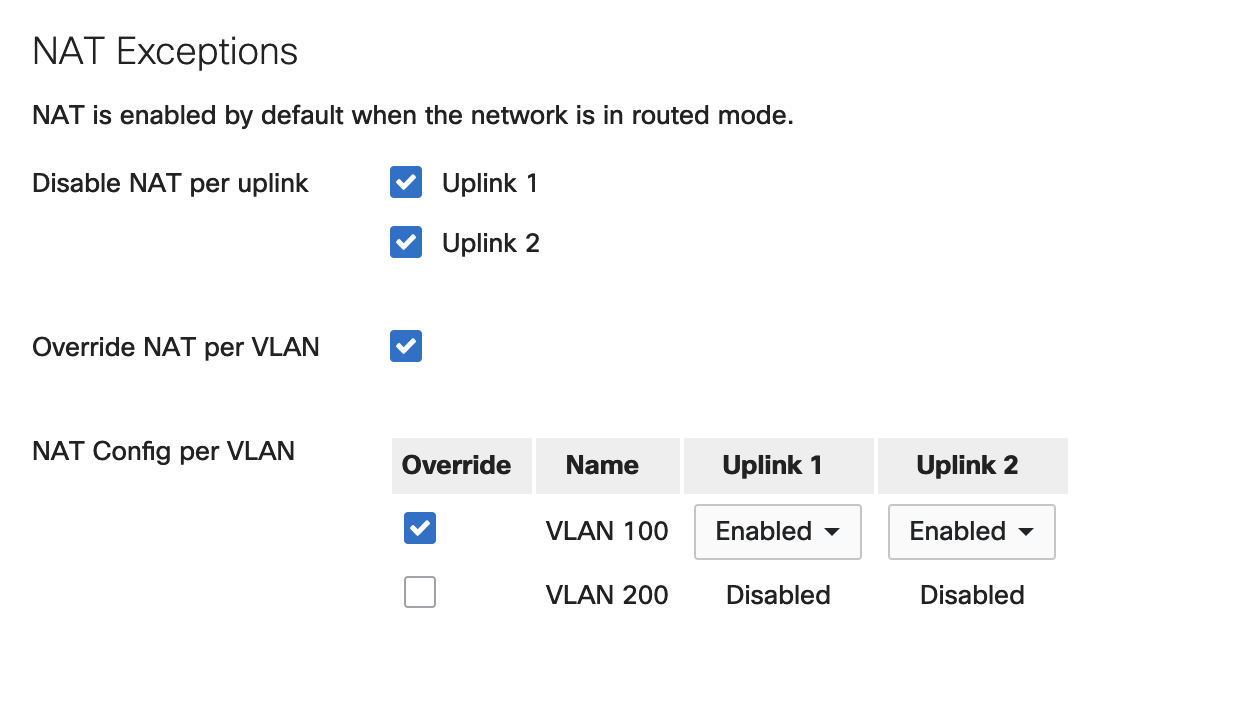
Expected behavior
Traffic from VLAN 100 will be NATed on both uplinks, Traffic from VLAN 200 will not be NATed on both uplinks.
Troubleshooting
The easiest way to verify NAT Exceptions is working will be to: generate traffic from the LAN of the security appliance and use the packet capture tool available on dashboard to sniff traffic on the uplink that has NAT Exceptions enabled. Observe source IP of the traffic flowing through the uplink. If traffic is still being NATed, verify your configuration and ensure the security appliance's configuration is up to date.
Duplicate subnets
Please ensure you do not have duplicate subnets on the LAN and WAN. This usually occurs when the WAN appliance is sitting behind a NAT device, ISP modem, etc. This can cause NAT Exceptions to not function as expected.
Unidirectional traffic flow outbound
If you have unidirectional traffic flow,
- Ensure you have a return route pointing to the right next hop (WAN appliance uplink IP, Virtual IP if you have one configured).
- Ensure that you are permitting the right subnets on your inbound firewall
- Take simultaneous packet captures on the LAN and WAN of the MX security appliance and identify where the traffic is being dropped
Unidirectional traffic flow inbound
- Ensure you are permitting the right traffic on the outbound firewall (Security & SD-WAN > Configure > Firewall)
- Ensure the device on the LAN is reachable (ping, check ARP with live tools on dashboard, ensure the device is on the right VLAN)
- Take simultaneous packet captures on the LAN and WAN of the WAN appliance and identify where the traffic is being dropped