Configuring DHCP Services on the MX and MS
Click 日本語 for Japanese
Introduction
The MX Series Security Appliances and MS Series Switches (with layer 3 routing enabled) have a built-in DHCP service. When enabled, it can provide DHCP to all configured subnets/VLANs, or relay DHCP messages to designated DHCP servers.
Configuration Steps
To configure, navigate to...
- For security appliance networks: Security & SD-WAN > Configure > DHCP, and refer to the section for the desired VLAN/subnet.
- For switch networks: Switching > Configure > Routing & DHCP, and select the desired interface.
Once there, the Client addressing setting will determine how DHCP messages are handled on that VLAN/subnet.
- Run a DHCP server - The MX/MS will use its internal DHCP server to provide addressing and other information to clients. If selected, the other options below will become available.
- Relay DHCP to another server - The MX/MS will forward DHCP messages to a server on a different VLAN or over the site-to-site VPN. The DHCP server IP field will appear and is used to indicate where DHCP messages should be forwarded to.
Note: On an MX, the DHCP server cannot be over a 3rd party VPN peer connection.
Note: If there are multiple DHCP relay server IPs configured for a single subnet, the MX/MS will send the DHCP discover message to all servers. Whichever server responds back first is where the communication will continue.
- Do not respond to DHCP requests - The MX/MS will not process or forward DHCP messages on this subnet. This disables the DHCP service for this subnet. If DHCP is still desired, another server must exist to handle the requests.
Note: Please ensure that Mandatory DHCP is disabled before disabling DHCP on MX otherwise all traffic to VLAN may be blocked.
"Run a DHCP Server" Options
If set to 'Run a DHCP server', the following options will become available:
- Gateway IP - (Only for Static routes) Indicates what default gateway IP address should be given to clients in this subnet. This address must be in the same subnet as the clients.
- Lease time - How long clients will have an address allocated to them, before the lease expires and the client must renew.
- DNS nameservers - Which addresses are provided to clients requesting DNS servers. These are used to resolve names (such as google.com) to IP addresses.
- Proxy to upstream DNS - (MX only) The MX will provide clients with its LAN IP as the DNS server, then proxy any DNS queries to the server(s) it has been configured to use on its Internet port(s).
- Use Google Public DNS - Clients will be instructed to send DNS queries to Google's Public DNS servers.
- Use Umbrella - Clients will be instructed to send DNS queries to Cisco Umbrella DNS Servers.
- Specify nameservers... - Clients will be given a list of DNS servers configured by the administrator. These servers are listed in the Custom nameservers box that will appear, with a single address per line.
- Boot options - Used to provide necessary information to clients booting from TFTP.
- Boot next-server - The address of the server to load the boot file from.
- Boot filename - The name of the file to load from the server and use to boot. Please note that forward slashes ("/") should be used in place of back slashes ("\"), otherwise Dashboard may report an "invalid path" error.
- DHCP options - These can be used to provide additional information to clients, as desired by the administrator. Choose Add a DHCP option to bring up additional fields. Several typical options are available in the Option field, or custom codes can be used for additional options.
Note: Starting with firmware version 17.15.1 , there has been a change in functionality for MS390 series switches when using Option 61 for Fixed Ip Addressing. The hardware address will be used to match and assign IP addresses and not the client identifier.
Note: On MS, if an NTP server (option 42) is not configured, by default, the switch will use its SVI IP address as the NTP server option. This can cause problems for legacy devices that do not have hardcoded NTP servers since the MS does not respond to NTP requests.
- Reserved IP ranges - Ranges of IP addresses within the subnet that should not be provided to clients via DHCP. Typically used if the subnet contains some statically assigned addresses, such as for printers and servers. By default, the MX/MS will use the entire subnet for the DHCP pool, besides its own LAN IP.
- Choose Add a reserved IP address range.
- Enter the First IP and Last IP of the range that should be excluded. Both of these addresses will be excluded, as well as any addresses between them. The Comment field is optional and for reference purposes.
Ex. The screenshot below shows two reserved ranges, covering 192.168.100.2 - 192.168.100.49 and 192.168.100.101 - 192.168.100.254. Addresses in these ranges will never be allocated to clients unless specified in the Fixed IP assignments section.
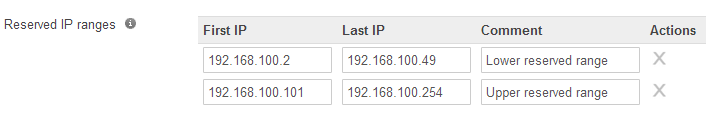
- Note: optionally use import CSV option to import several reserved IP ranges. This feature is only available on MX and not MS.
- If a range must be deleted, select the X in the Actions column.
- Fixed IP assignments - Allows specific MAC addresses to always be assigned the same IP address. These addresses will not be allocated to other devices on the network.
- Choose Add a fixed IP assignment.
- Enter the MAC address of the client device and the IP address it should be assigned. The Client name address is optional and for reference purposes.

- Note: optionally use import CSV option to import several fixed IP assignments. This feature is only available on MX and not MS.
- If an assignment must be deleted, select the X in the Actions column.
- Mandatory DHCP (only applicable for security appliances) - Clients on VLANs with Mandatory DHCP enabled must request for a DHCP address prior to gaining access to the network. If the device is configured for a static IP and the MX does not detect full DORA per client MAC, then the client device is denied access to the network.
- To recap:
- If you have mandatory DHCP enabled, fixed IP assignments may not function properly. If the WAN appliance is rebooted, those clients won't be able to pass traffic until a new full DORA transaction is detected.
- When DHCP reservations are in place, devices with static IP assignments won’t be able to communicate on the network until they request a DHCP address.
- When you set up DHCP relay, the DHCP leases are not stored in the MX table (DHCP relay server is an external device). Consequently, clients with DHCP assignments from a DHCP relay server won’t be able to pass traffic once their lease time expires. To regain network access, the client device must flush the DHCP lease and request for a new DHCP address. In summary, configuring DHCP relay may result in client devices losing connectivity to the network.
- In the event of a device reboot (including MX HA failover), the client device should request for a DHCP address before it can connect to the network (DHCP lease table is flushed during a device reboot).
- This feature is identical to the MR implementation found in Access Control article.
- To recap:
-
Once complete with any changes, choose Save Changes to have them go into effect.
Note: MX acts as a NTP Server on each one of its VLAN Interfaces.
Note that if an MX security appliance has been rebooted, clients will not be able to pass traffic until they obtain a new lease or until mandatory DHCP is disabled.

