MR Meraki RADIUS 2.0
RADIUS Configuration
On the Access Control page, make sure "View new version" has been selected in the upper right corner. Once this has been done, click on the RADIUS option to show configuration options for RADIUS authentication and accounting servers.

You can add up to 3 servers for authentication and 3 for accounting. It is required to have an IP Address for the server, the port to be used, and the secret phrase to be configured on each one.
Note: RADIUS accounting is only available by default with 802.1X authentication. To enable RADIUS accounting for splash pages as well, please contact Cisco Meraki support.
Accounting interim interval: If an accounting server is added and saved, the option Accounting interim interval will be available to control how often accounting messages are sent to the server.
For the use of Accounting interim interval, all APs must support firmware MR28 and be updated, this means all access points must be WiFi 5 Wave 2 or higher.
RADIUS Accounting Device Profiling
Firmware: MR 31.2+
Hardware: MR28,30H, MR33, MR42, MR42E, MR52, MR53, MR53E, MR74, MR84, MR36, MR36H, MR36, MR44, MR45, MR46, MR46E, MR55, MR56, MR57, MR76, MR78, MR86. CW916X APs, CW917X APs
As of MR 31.2+, device sensor functionality provides enhanced client attributes for device profiling from AP to ISE over RADIUS Accounting-Request messages. Device Profiling now shares client's DHCP IPv4, HTTP, mDNS with the ISE server to profile the client's OS.
RADIUS Accounting Start Delay:
By default, APs send RADIUS accounting-start messages immediately when a client associates. This results in accounting-start messages lacking the Framed-IP-Address, which is required to apply IP-based access control policies
RADIUS Accounting Start Delay allows a DHCP address to be assigned to clients on association before RADIUS accounting messages are sent from the access points to the RADIUS server. This is done whenever a client successfully connects to the SSID.
Configuration
-
Navigate to Wireless > Configure > Access Control
-
Configure RADIUS accounting servers
-
Set that RADIUS Accounting start delay
Note: The radius accounting delay can be set to a value of 0 to 60 seconds before accounting messages will be sent.
Note: If downgrading firmware from MR 28 the RADIUS Accounting Start delay previously set will default to 0.
API Configuration
The RADIUS accounting start delay in a valid range 0-60 seconds using the dedicated API:
PUT /api/v1/networks/{networkId}/wireless/ssids/{number}
{ "radiusAccountingStartDelay": 11 }
RADIUS testing: If enabled, Meraki devices will periodically send Access-Request messages to these RADIUS servers using identity 'meraki_8021x_test' to ensure that the RADIUS servers are reachable.
RADIUS CoA support: If enabled, Meraki devices will act as a RADIUS Dynamic Authorization Server and will respond to RADIUS Change-of-Authorization and Disconnect messages sent by the RADIUS servers.
RADIUS proxy: Meraki devices can send RADIUS Access-Request and Accounting messages via a Meraki proxy, which will forward these messages to the specified RADIUS servers.
RADIUS attribute specifying group policy name: Specify the RADIUS attribute used to look up group policies. Access points must receive this attribute in the RADIUS Access-Accept message. The value of the attribute must match the group policy name configured on this page. Four different attributes can be used to achieve this:
- Filter-ID
- Reply-Message
- Airespace-ACL-Name
- Aruba-User-Role
Note: Adding or removing tags to an AP will cause the RADIUS SSID(s) to restart, resulting in wireless clients being disconnected.
Advanced Settings
For the use of the new features, all APs must support firmware MR28 + (WiFi 5 Wave 2 or higher) and be updated.
Called Station ID
The ability to configure the called-station-ID attribute that it is sent from the Access Point to the RADIUS server provides flexibility to network administrators when creating rules.
Once upgraded to firmware MR28, all Access points will automatically update the default setting for both Called-Station-Id and NAS-ID as "AP MAC address:SSID Name" and "AP MAC address:SSID Number" respectively.
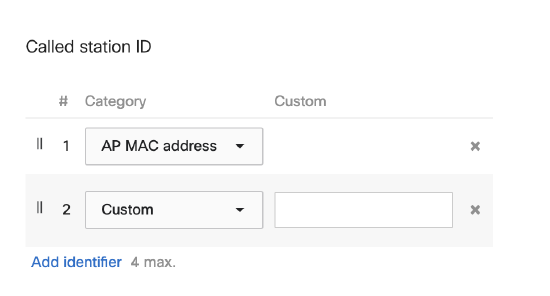
A maximum of 4 attributes can be configured including a custom phrase that can be set in the dashboard. Each setting will be appended with ":" as a separator in the called-station-ID attribute. The attributes that can be configured are:
- AP MAC address
- SSID name
- SSID number
- AP name
- RF profile
- AP VLAN ID
- AP tags
- AP LAN IP
- AP Public IP
- Custom (input by the administrator)
For example, in the following packet capture, it was selected:

And the result in the packet capture is:

Called-station-id will be set to MAC:SSID_NAME automatically if using radius proxy feature, and the customization will not take place.
NAS ID
Similar to called-station-ID, Meraki offers a variety of attributes that can be configured when using the NAS-ID option, including:
- AP MAC address
- SSID name
- SSID number
- AP name
- RF profile
- AP VLAN ID
- AP tags
- AP LAN IP
- AP Public IP
- Custom (input by the administrator)
A maximum of 4 attributes can be configured and there will be a ":" between each attribute.
Note: When 802.11r is enabled, the available NAS-ID options will be limited to specific attributes to ensure the network remains stable.
On a packet capture it will show as the following:

Device IP set as NAS-ID
The NAS-ID value can be set as the AP’s Public or LAN IPv4 address.
Configuration

Please note that only IPv4 addresses are supported as part of this feature enhancement dashboard and API component.
Server Timeout and Retry Count
Two settings can be used to configure how long the Meraki dashboard should wait before it classifies a RADIUS server as inactive/unreachable:
- Server timeout specifies how long to wait for a response from a RADIUS server in seconds (before being marked inactive/unreachable) from 1 to 10 secs.
- Retry count specifies how many retries should be made before moving to the next server, from 1 to 5 retries.

RADIUS Fallback

The fallback behavior depends on the order the servers are listed on the dashboard will dictate the priority of each one, For example:
- Server 1 = priority 1
- Server 2 = priority 2
- Server 3 = priority 3
Where the available server with higher priority will be used (priority 1 is the highest). If Server 1 were to become unreachable, Server 2 would become active, and so on.
If the fallback option is enabled, once the server with higher priority recovers, the AP will switch back to using that preferred (higher priority) server.
The fallback mechanism relies on the server's implementation of the RFC-5997
EAP Timers
The Meraki dashboard provides the ability to customize the EAP timers for communication over wireless between the access point and the client.
It is not recommended to change these values without oversight from an expert technician.

RADIUS VLAN Override
RADIUS VLAN Override offers the option to override the VLAN with the attributes coming from a RADIUS server with the option "RADIUS override." It is disabled by default.

For a VLAN override to be successful, the RADIUS server must send:
-
IETF 64 (Tunnel Type) — Set this to VLAN.
-
IETF 65 (Tunnel Medium Type) — Set this to 802
-
IETF 81 (Tunnel Private Group ID) — Set this to VLAN ID.
Behavior as of R31.1
RADSec Keep Alives

In order to not have to reestablish a TLS tunnel between the MR and RADIUS sever APs can be configured to send "keep-alive" messages to RADSec servers. This feature helps to maintain the TLS connection, preventing devices like load balancers or the RADIUS server from closing the connection in case authentications or accounting updates aren't sent.
Configuration:
-
Within the Radius server settings, specify the TLS idle timeout.

Note: The idle timeout can be set to 1- 32767 minutes.
API Configuration
PUT /networks/{networkId}/wireless/ssids/{number}
- Optional property radiusRadsecTlsIdleTimeout Added
{
"radiusRadsecTlsIdleTimeout": 900
}
RADSec with Tunneled SSIDs
With R31, all RADSec traffic to and from the AP is securely encrypted as it passes through the IPSec tunnel that terminates at the MX security appliance located back in the physical premises.


Accounting
- Test to ensure a TLS connection can be made to any RADSec server configured in the SSID access control.
- Check accounting packets are sent as regular to the SSID tunnel to the MX
- Take a pcap and verify the packets are sent frequently using the same socket(4) Found Auth-Type = Accept
Change of Authorization with RADSec
Configuration:

Navigate to the RADIUS server settings and select the check box to enable RADIUS CoA support.
When enabled, MR APs will act as a RADIUS Dynamic Authorization Server and will respond to RADIUS Change-of-Authorization and disconnect messages sent by the RADIUS servers.

