Campus Gateway Installation Guide
About this Guide
This guide provides instruction on how to install your Cisco Campus Gateway.
Introduction
The Cisco Campus Gateway (CG) is the cloud-native solution from Cisco for centralized wireless deployments. Similar to a wireless LAN controller (WLC), data plane traffic is tunneled from the APs to the CG, where it is terminated and switched to the rest of the network. By terminating traffic centrally, client VLANs only have to exist in the core. This allows for seamless roaming across layer 3 (L3) domains of the APs.
Campus Gateway leverages the same hardware as a CW9800H1 WLC, but it will leverage a different architecture. It's a cloud-native managed architecture. In this, each device, Campus Gateway and APs, will be directly managed by Dashboard. They will each maintain their own individual Meraki Tunnel to Dashboard.

Additionally, only certain aspects of the wireless networks need to be brought back to a centralized box on-premises in order to meet the large-scale roaming needs for customers. Things like data plane aggregation, RADIUS proxy and Mobility database need to exist on the CG. Otherwise, unless the control plane and management plane tasks need to be centralized, Dashboard and the APs will continue to serve those functions. Management plane tasks, like configuration management and software management, and non-real time control plane tasks, like AutoRF, Air Marshal, and Rogues, do not need to be done by the CG. It can be kept on the cloud.
The following image illustrates the breakdown of these functions.
.png?revision=1)
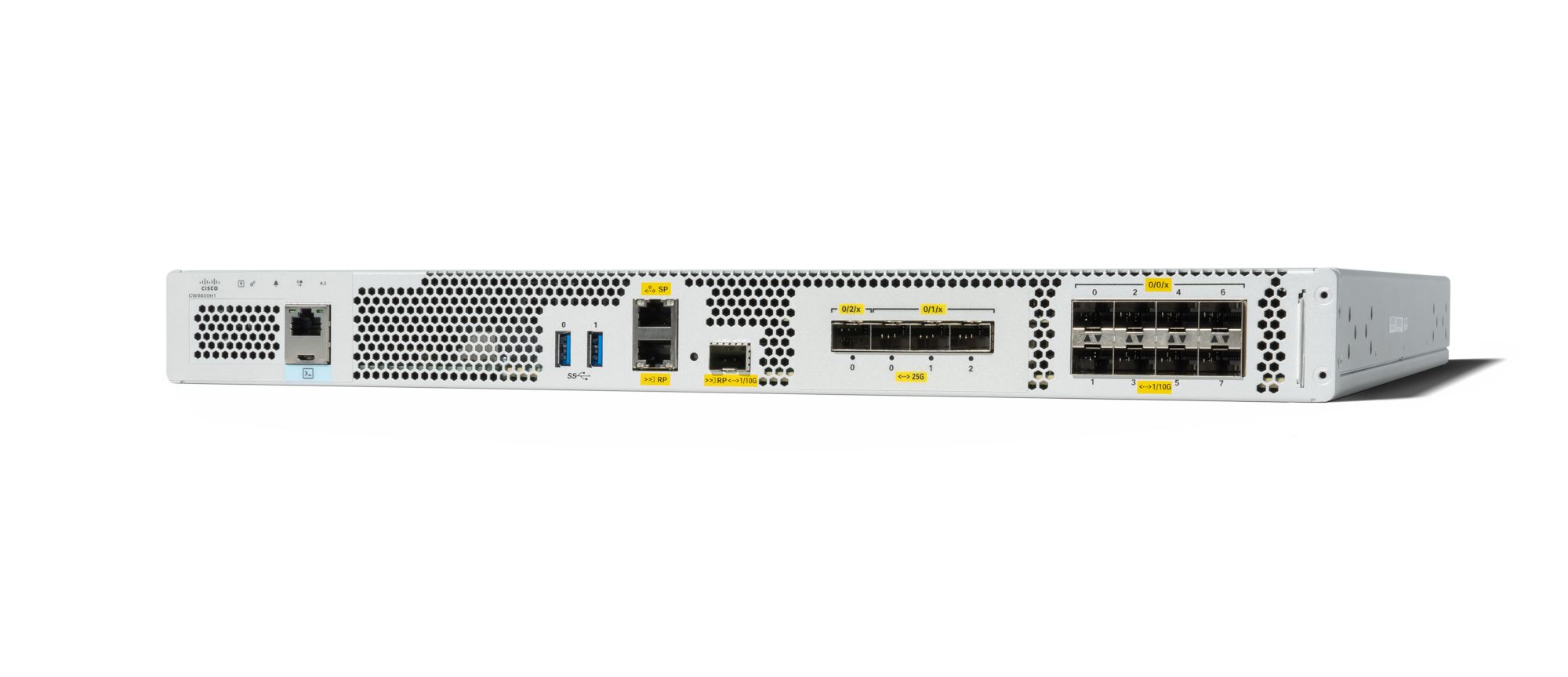
Product View and Physical Features
Front View

|
1 |
PWR—Power LED |
|---|---|
|
2 |
SYS—System LED |
|
3 |
ALM—Alarm LED |
|
4 |
HA—High-Availability LED |
|
5 |
M.2 SSD |
|
6 |
RJ-45 compatible console port (Not available for use on Campus Gateway) |
|
7 |
USB Port 0 (Not available for use on Campus Gateway) |
|
8 |
USB Port 1 (Not available for use on Campus Gateway) |
|
9 |
SP— RJ-45 1-GE management port |
|
10 |
RP— 1/10-GE SFP+ port |
|
11 |
TwentyFiveGigE0/2/0 - 25-GE SFP28 EPA2 Port 0 |
|
12 |
TwentyFiveGigE0/1/0 - 25-GE SFP28 EPA1 Port 0 |
|
13 |
TwentyFiveGigE0/1/1 - 25-GE SFP28 EPA1 Port 1 |
|
14 |
TwentyFiveGigE0/1/2 - 25-GE SFP28 EPA1 Port 2 |
|
15 |
Te0/0/0—1-GE SFP/ 10-GE SFP+ Port 0 |
|
16 |
Te0/0/2—1-GE SFP/ 10-GE SFP+ Port 2 |
|
17 |
Te0/0/4—1-GE SFP/ 10-GE SFP+ Port 4 |
|
18 |
Te0/0/6—1-GE SFP/ 10-GE SFP+ Port 6 |
|
19 |
Carrier Label Tray |
|
20 |
Te0/0/7—1-GE SFP/ 10-GE SFP+ Port 7 |
|
21 |
Te0/0/5—1-GE SFP/ 10-GE SFP+ Port 5 |
|
22 |
Te0/0/3—1-GE SFP/ 10-GE SFP+ Port 3 |
|
23 |
Te0/0/1—1-GE SFP/ 10-GE SFP+ Port 1 |
|
24 |
RP— RJ-45 1-GE redundancy port |
|
25 |
CON— 5-pin Micro-B USB console port (Not available for use on Campus Gateway) |
LED Indicators
|
System Status |
Power LED |
Dashboard Status LED |
System LED |
Alarm LED |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
CG is powered off or not receiving power. |
Off |
Off |
Off |
Off |
|
2 |
CG if powered on and is loading the bootstrap firmware. |
Solid Green |
No change in LED state |
No change in LED state |
Solid Amber: ROMMON boot |
|
3 |
ROMMON Boot complete |
No change in LED state |
No change in LED state |
No change in LED state |
Solid Green |
|
4 |
CG is loading the operating system. |
No change in LED state |
No change in LED state |
Slow Blinking Green |
Solid Amber: SYSTEM bootup |
|
5 |
Boot up fails; device in ROMMON |
No change in LED state |
No change in LED state |
Solid Amber - Crash Slow Blinking Amber - Secure boot failure |
Slow Blinking Amber - Temperature Error & Secure boot failure |
|
6 |
System error: CG failed to load operating system or bootstrap firmware. |
No change in LED state |
No change in LED state |
Solid Amber - Crash Slow Blinking Amber - Secure boot failure |
Slow Blinking Amber - Temperature Error & Secure boot failure |
|
7 |
Setting up local management and cloud-connectivity requirements. Note: If the CG has not been assigned a static management IP previously, it will try to obtain an IP via DHCP in this stage. |
No change in LED state |
Slow blinking Amber |
No change in LED state |
No change in LED state |
|
8 |
System error: CG failed to complete local provisioning. |
No change in LED state |
Solid Amber |
No change in LED state |
No change in LED state |
|
9 |
CG is completely provisioned but unable to connect to Meraki cloud |
No change in LED state |
Solid Amber |
No change in LED state |
No change in LED state |
|
10 |
Firmware download / upgrade in progress |
No change in LED state |
Blinking Green: System upgrade in progress |
No change in LED state |
No change in LED state |
|
12 |
CG is fully operational and connected to the Meraki cloud |
Solid Green |
Solid Green |
No change in LED state |
No change in LED state |
|
13 |
Operating System boot complete |
No change in LED state |
No change in LED state |
Solid Green |
No change in LED state |
|
14 |
Factory Reset via the Local Status Page |
No change in LED state |
No change in LED state |
Slow Blinking Red |
No change in LED state |
|
15 |
Blink LED Feature |
No change in LED state |
Fast Blinking Red |
Fast Blinking Red |
Fast Blinking Red |
Built-In SFP and SFP+ Ports
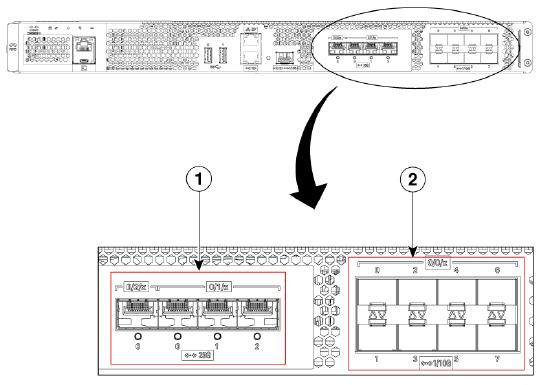
| 1 |
Bay 1 - 3 X 25-GE SFP28 ports.
Bay 2—1 X25-GE SFP port.
|
|---|---|
| 2 | Bay 0—8 X 1-GE/10-GE SFP+ ports.
|
Supported SFP Modules
Data Port SFP Modules
| Type |
Modules supported |
|---|---|
|
Small Form-Factor Pluggable (SFP) |
GLC-LH-SMD |
|
GLC-SX-MMD |
|
|
GLC-TE |
|
|
GLC-ZX-SMD |
|
|
GLC-BX-U |
|
|
GLC-BX-D |
|
|
GLC-EX-SMD |
|
|
Enhanced SFP (SFP+ / SFP28) |
SFP-10G-SR |
|
SFP-10G-SR-S |
|
|
SFP-10G-LR |
|
|
SFP-10G-LR-X |
|
|
SFP-10G-ER |
|
|
SFP-H10GB-ACU10M |
|
|
SFP-H10GB-CU5M |
|
|
SFP-10G-AOC10M |
|
|
Finisar-LR (FTLX1471D3BCL) |
|
|
Finisar-SR (FTLX8574D3BC) |
|
|
SFP-H10GB-CU1M |
|
|
SFP-H10GB-CU1-5M |
|
|
SFP-H10GB-CU2M |
|
|
SFP-H10GB-CU2-5M |
|
|
SFP-H10GB-CU3M |
|
|
SFP-H10GB-ACU7M |
|
|
SFP-10G-AOC1M |
|
|
SFP-10G-AOC2M |
|
|
SFP-10G-AOC3M |
|
|
SFP-10G-AOC5M |
|
|
SFP-10G-AOC7M |
|
|
SFP-10/25G-CSR-S (Only supported in the 25-GE ports) |
|
|
SFP-10/25G-LR-S (Only supported in the 25-GE ports) |
|
|
SFP-25G-SR-S |
|
|
SFP-25G-AOC2M |
|
|
SFP-25G-AOC10M |
|
|
SFP-25G-AOC5M |
|
|
SFP-H25G-CU1M |
|
|
SFP-H25G-CU5M |
|
|
SFP-25G-AOC3M |
|
|
SFP-25G-AOC7M |
|
|
SFP-25G-AOC1M |
Supported Redundancy Port SFP Modules
| Type |
Modules supported |
|---|---|
|
SFP/SFP+ Modules |
GLC-LH-SMD |
|
GLC-SX-MMD |
|
|
SFP-10G-SR |
|
|
SFP-10G-SR-S |
|
|
SFP-10G-LR |
|
|
SFP-10G-LR-S |
Installation Instructions
Physical Mounting
To mount the Campus Gateway chassis, please see the CW9800H1 installation instructions here: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/wireless/controller/9800/9800-h/installation-guide/b-wlc-ig-9800-h/installing-the-controller.html
Initial Connection Dashboard
Configure your Dashboard Network
To add devices to your Dashboard network please refer to the Creating a Dashboard Account and Organization document.
Check and Configure Upstream Firewall Settings
If a firewall is in place, it must allow outgoing connections on particular ports to particular IP addresses. The most current list of outbound ports and IP addresses for your particular organization can be found under Help → Firewall info. The help button is located on the top right corner of any dashboard page. For more information refer to Upstream Firewall Rules for Cloud Connectivity.
Additionally, if there is a firewall in place between Campus Gateway and APs, please ensure that UDP port 16674 for QUIC and UDP port 16675 for VXLAN are open.
Note: If the VXLAN port needs to be changed, please contact Meraki support.
Uplink Switchport Connections
For the initial boot and for Dashboard registration, it’s critical to connect the Campus Gateway to a switch via at least one port configured with a 802.1Q trunk connection that has at least one active VLAN. The VLAN needs to provide an IPv4 DHCP address to CG with related DNS servers so that it can automatically reach Dashboard. This VLAN with active DHCP can be a 802.1Q tagged VLAN or the native VLAN on the trunk port. Once the CG is configured via the cluster onboarding flow, the user can change the CG’s IP address to a static IP in the same or different VLAN. It is recommended to use a 802.1Q tagged VLAN to carry the management and client traffic.
Note: IPv6 for the Campus Gateway interfaces is not supported at MVP, so it’s important to provide an IPv4 address.
By default, when the Campus Gateway boots up, all ports (4x25G and 8x10G) will be configured to be in a single port-channel. This means that before wiring up the CG to the rest of the network, the ports on the upstream switch will need to be configured in a port-channel to allow the CG to come up. At least 2 ports are recommended for CG to upstream switch connections.
Note: It’s important that you use only ports of the same speed and type to connect to the switch etherchannel, so either all 10GE or all 25GE ports.
Port-Channel Configuration
The default port-channel configuration on Campus Gateway, which is applied to all the ports, is shown below for the port TwentyFiveGigE0/1/0. By default, all VLANs will be allowed on the ports with a native VLAN ID of 1.
port-channel load-balance src-dst-mixed-ip-port ! interface TwentyFiveGigE0/1/0 switchport mode trunk channel-group 1 mode active interface TwentyFiveGigE0/1/1 switchport mode trunk channel-group 1 mode active interface Port-channel1 switchport mode trunk end
The default load balancing algorithm for Cisco Catalyst switches is either src-mac or src-dst-mixed-ip-port (the latter used on high end switches). The load balancing algorithm used for the etherchannel on Campus Gateway is src-dst-mixed-ip-port, so it is recommended to match it on the switch side as well. If non-Cisco switches are used, please consult the vendor documentation to make sure that this load balancing algorithm is used.
An example of a port-channel configuration for a customer-managed, Catalyst switch is below.
port-channel load-balance src-dst-mixed-ip-port ! interface TwentyFiveGigE 1/0/19 channel-group 1 mode active switchport mode trunk switchport trunk allowed vlan 2,3-10 interface TwentyFiveGigE 1/0/20 channel-group 1 mode active switchport mode trunk switchport trunk allowed vlan 2,3-10 interface PortChannel 1 switchport mode trunk switchport trunk allowed vlan 2,3-10
Similarly if you connect to a Catalyst switch monitored by Dashboard or a Meraki MS switch, use Dashboard to configure a port-channel on the ports connected to CG.
Note: While the default CG and cloud-managed switch configurations allow all VLANs, the best practice is to prune to include only required VLANs. In the example above, the VLANs are pruned to only include VLANs 2 and 3-10 as those are VLANs required for the CG cluster.
For more detailed info on how to configure port-channel on cloud-managed, Cisco switches, please see here: https://documentation.meraki.com/General_Administration/Tools_and_Troubleshooting/Link_Aggregation_and_Load_Balancing
What if you connect the Campus Gateway with only one link?
This is not recommended in production, but it can happen in the lab during testing. Even if only one port on Campus Gateway is connected, on the switch side you must create a port-channel with one port. If you don’t, the CG port will not be UP and will not pass traffic as it fails to negotiate LACP packets.
To configure a port-channel with just one physical port:
- In IOS-XE, create the port-channel interface as shown in the example above and add the channel-group command on the connected physical port.
- In Dashboard for MS or cloud-managed Catalyst switch, you need at least to select two ports to be able to aggregate them in a port-channel; select the connected port and another port that is not connected and click on the Aggregate tab as shown below:
Assigning an IP address
Uplink Auto Configuration
After initial boot up, Campus Gateway will leverage the Meraki auto-uplink logic to determine one active VLAN which it can use to connect to Dashboard. The CG will detect the available VLANs which are on the trunk port and choose one with internet connectivity. Campus Gateway leverages DHCP on the selected VLAN to get and IP address and automatically connect to Dashboard
In order for Campus Gateway and the auto-uplink to work, the user needs to make sure:
- The uplink switch is configured accordingly (port-channel and trunk)
- DHCP is active on at least one VLAN and with a default gateway and DNS server provider
- Connectivity to dashboard is allowed on the active VLAN
Once Campus Gateway is connected to Dashboard and configured with the required connectivity information, Campus Gateway fetches the onboarding configuration and will use the IP address information pushed from Dashboard to connect to Dashboard from now on.
Manually Configuring the Uplink
If connectivity between Campus Gateway and Dashboard is lost and/or cannot be established, the Local Status Page (LSP) can be used to manually configure parameters like the uplink ports’ VLAN, IP address or DNS settings to restore the connectivity.
This can happen for multiple reasons:
-
DHCP is not available on the active VLAN
-
Info provided by DHCP are not correct (missing DNS, wrong default gateway, etc.)
-
Connectivity to Meraki Dashboard is not there, etc.
There is no console access on Campus Gateway, so the LSP is used to connect to the box. This is mainly used for out-of-band uplink configuration and overall system health check.
If Campus Gateway is unable to reach out to Dashboard, even if LSP is used, please reach out to Meraki Support.
Connecting to the Local Status Page

Step 1: Plug in the computer to the Service Port (SP port). This will assign an IP address in the range 198.18.0.X.
Note: Please refer to the Front View section for where to find the SP port.
Step 2: Navigate to https://mcg.meraki.com or directly to https://198.18.0.1 and enter the credentials.
The credentials for Campus Gateway devices that have never connected to a Meraki network or that went through a factory reset are:
-
Username: admin
-
Password: Cloud ID (Meraki Serial Number) of the CG
Note: The cloud ID can be found in the shipment email from Cisco as well as physically on the chassis of the CG.
After the CGs devices connect for the first time to a Meraki network, they automatically get their LSP credentials updated to a strong password. Please see the Changing Log-In Credentials section in the Using the Cisco Meraki Device Local Status Page guide for more details.
After deploying Campus Gateway in a cluster, the LSP can be accessed using the IP address of the Management or AP Tunnel Interface of Campus Gateway.
Uplink Configuration

The user can configure the following uplink settings:
-
VLAN
-
IP Address
-
Gateway
-
DNS server(s)
Campus Gateway will use these to connect to the Meraki Dashboard if DHCP does not work or is not configured. As all the ports are configured in a single L2 port-channel, this will configure the L3 VLAN interface (SVI) for management connectivity.
Note: If Campus Gateway is already provisioned and is using the single interface deployment, where both the Management and AP Tunnel Interface share the same IP address, the Uplink Configuration will not be able to be changed as this would also change the AP Tunnel Interface. This would lead to downtime in the wireless network as the APs would no longer be able to tunnel to the Campus Gateway's AP Tunnel Interface.

Adaptive Policy

In the event the Adaptive Policy is configured in the network and Campus Gateway is unable to connect to the upstream network and Dashboard due to Campus Gateway not having infrastructure Adaptive Policy enabled (uplink port is not configured with the correct SGT), the LSP can be used to enable uplink traffic to be tagged with the correct SGT, typically a value of 2.
Note: The SGT value can be found in either the upstream switch port configurations or, for Cisco cloud-managed devices, in Organization > Adaptive policy > Groups page under Infrastructure.
Reset and Reload Campus Gateway

Campus Gateway can quickly be reloaded or completely factory reset using the LSP. Click on the respective button to do so.
Deploying Campus Gateway and Adding to a Network
For the best practices on deploying Cisco Campus Gateway, please refer to the deployment guide.
Warranty
Campus Gateway Warranty coverage periods are as follows:
| Time Period | Comments | |
| CW9800H1-MCG | 1 year |
1 Year Warranty with next-day replacement included. |
|
Campus Gateway Accessories |
1 Year |
The following are considered accessories: SFP Modules, twinax/SFP+ cables, all mounting kits and stands, additional power cords |
Note: The above table is a general guideline for warranty terms and is not final. Warranty terms are subject to printed warranty information on the online Meraki Returns and Policy section.
Support and Additional Information
If issues are encountered with device installation or additional help is required, contact Meraki Support by logging in to dashboard.meraki.com and opening a case by visiting the Get Help section.
- The equipment is intended for industrial or other commercial activities.
- The equipment is used in areas without exposure to harmful and dangerous production factors, unless otherwise specified in the operational documentation and/or on the equipment labeling.
- The equipment is not for domestic use. The equipment is intended for operation without the constant presence of maintenance personnel.
- The equipment is subject to installation and maintenance by specialists with the appropriate qualifications, sufficient specialized knowledge, and skills.
- Rules and conditions for the sale of equipment are determined by the terms of contracts concluded by Cisco or authorized Cisco partners with equipment buyers.
- Disposal of a technical device at the end of its service life should be carried out in accordance with the requirements of all state regulations and laws.
- Do not throw in the device with household waste. The technical equipment is subject to storage and disposal in accordance with the organization's disposal procedure.
- The equipment should be stored in its original packaging in a room protected from atmospheric precipitation. The permissible temperature and humidity ranges during storage are specified in the Operation (Installation) Manual.
- Transportation of equipment should be carried out in the original packaging in covered vehicles by any means of transport. The temperature and humidity during transportation must comply with the permissible established ranges of temperature and humidity during storage (in the off state) specified in the Operation Manual (Installation)
For additional information on Meraki hardware and for other installation guides, please refer to documentation.meraki.com.



