Client VPN Load Sharing
As the need for remote access continues to grow, administrators may need to look at ways to scale large amounts of users or spread Client VPN load between multiple firewalls. Highlighted below are two ways to scale users and load share Client VPN connections.
For Loading Sharing with AnyConnect VPN see AnyConnect Load Sharing
Distributed Load Across Physical Sites
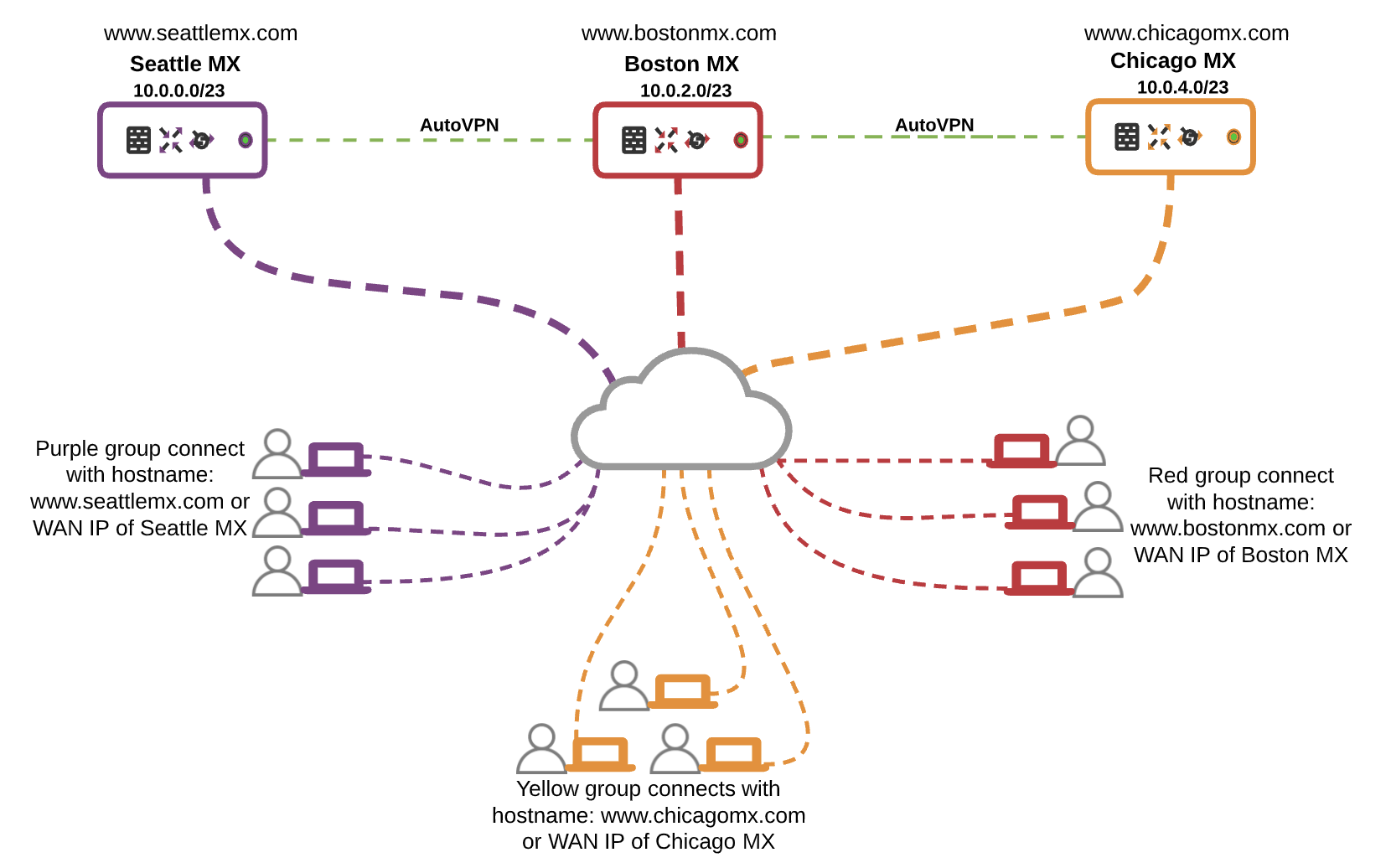
If you have multiple MX appliances in your Organization, you can spread users across different physical locations. Users simply connect to different physical locations to access the corporate network. This allows for load sharing across multiple MX appliances rather than the traditional connection to one VPN Server/ MX Appliance, however, each end device will need to be configured to point to the MX appliance they will be connecting to.
Please note that you may need to address possible bottlenecks at the "main site" if all users eventually need access resources at the "main site" e.g. Datacenter or Head Office.
Distributed Load With Multiple Hubs
This is more traditional but with a twist. This requires implementing a DNS load balancer to load share Client VPN requests between different MX appliances. There are numerous DNS load balancers available today, e.g. AWS Route 53, Azure Traffic Manager, StackPath, etc. The aforementioned are just a few examples, but please use whichever load balancing service you prefer.
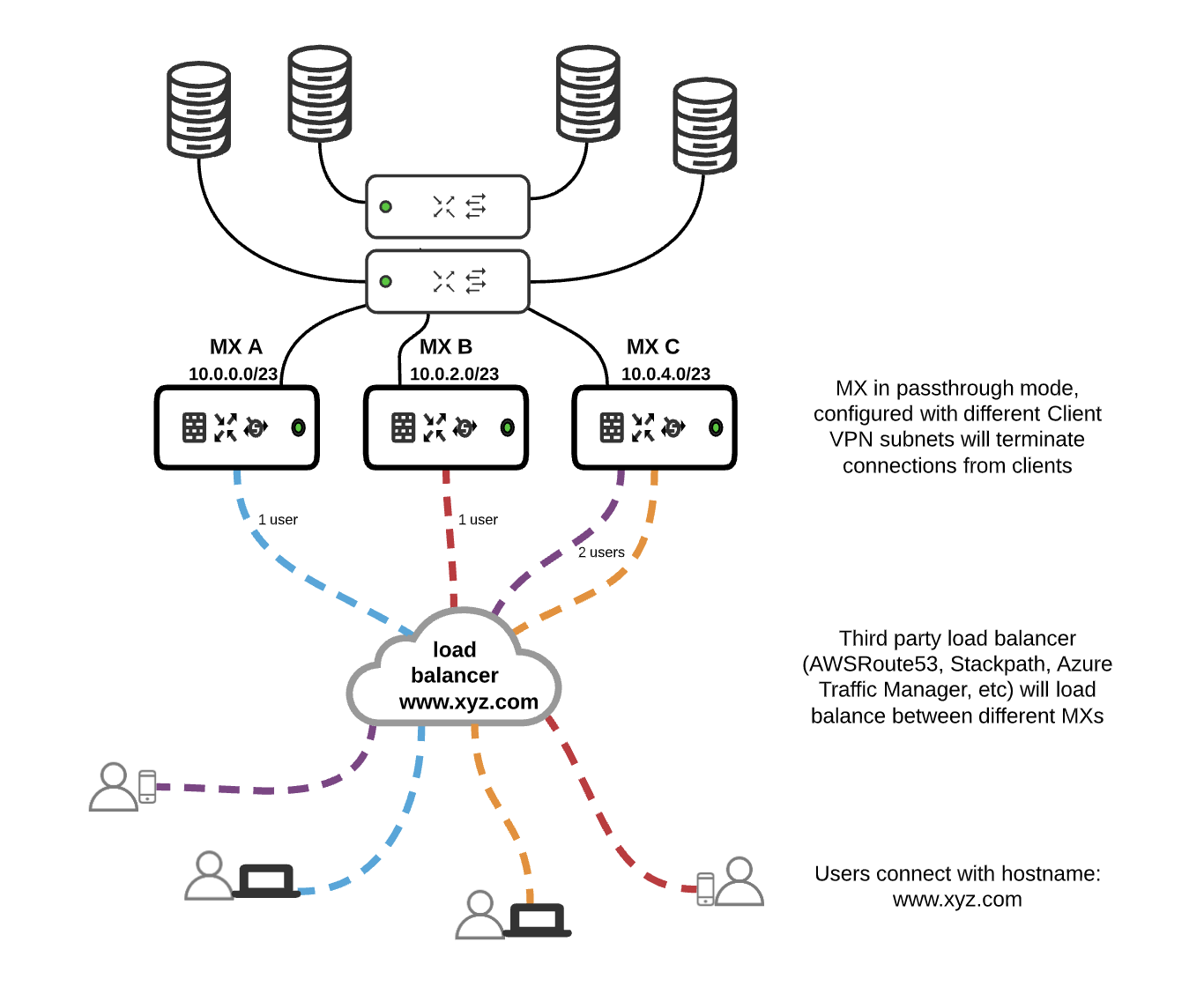
End devices will be configured to connect to Client VPN with the hostname configured on the DNS load balancer, which will need to know the IPs of each MX. When users connect to Client VPN, the load balancer will shuffle requests between MX A, MX B, and MX C, making this ideal for large deployments with a lot of users.

