Using the Ping Live Tool
Overview
When troubleshooting a network, ping can be a useful tool for verifying client/network reachability. All Cisco Meraki devices provide a ping live tool, however the behavior of that tool varies by platform. This article will identify those differences.
There is also a tool to ping the device located next the live ping tool used for testing client reachability. The ping device tool will ping the selected device from Meraki Dashboard services and report back results.
Learn more with these free online training courses on the Meraki Learning Hub:
Ping Tool Location by Platform
- MX - Security & SD-WAN > Monitor > Appliance Status > Tools
- MS - Switching > Monitor > Switches > (Select a switch) > Tools
- MR - Wireless > Monitor > Access points > (Select an AP) > Tools
- MG - Cellular Gateway > Monitor >Cellular Gateways > (Select an MG) > Tools
- MV - Cameras > Monitor > Cameras > (Select a Camera) > Network
Pinging from Live Tools
To perform a ping from a specific device, navigate to the status page for that device and find Ping under Tools.

Enter a destination value, such as an IP address or DNS hostname, then click Ping to begin the test. The section that appears will include information on the percentage of packets lost, average latency, and provide a graph of the latency to the device while the test is running.

If the ping tool shows 100% loss, the outgoing request either wasn't able to reach the destination or the reply wasn't received by the Meraki device.

MX Ping Tool
The MX ping tool will accept the following values
- IP address
- DNS hostname
- Client MAC address
Note: Entering a Client MAC address does not trigger the WAN Appliance to perform an ARPing. When a MAC address is entered, the WAN Appliance will attempt to map the client MAC address to a known IP address using its ARP table, then will initiate an IP ping.
Behavior - Firmware MX 15.11 or Lower
For WAN Appliances running firmware MX15.11 or below, the source IP that WAN Appliance uses while pinging a destination is the VLAN Interface IP of highest VLAN ID. If the destination is across a VPN, the WAN Appliance uses the VLAN interface IP of highest VLAN ID participating in VPN.
Behavior - Firmware MX 15.12 or Higher
For WAN Appliances running firmware MX 15.12+, additional ping options have been added to the live tool. The ping tool now has a drop down to select the source IP address for pinging destinations from the WAN Appliance.
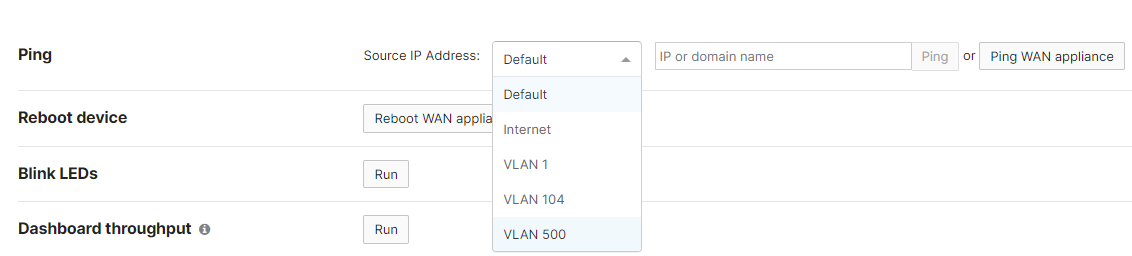
Source IP Address Options:
Default. The WAN Appliance uses the route table to dynamically choose the ping source IP address closest to the destination IP entered.
- LAN example: If you input a destination IP that is in VLAN A, the WAN Appliance will source the ping from its VLAN A interface IP
- Site-to-site VPN example: If you input a destination IP that resides across a site-to-site VPN, the WAN Appliance will source the ping from the WAN Appliance VLAN interface IP of the highest VLAN ID that is participating in the VPN
- Internet example: If you input a destination IP that resides on the WAN/internet, the WAN Appliance will source the ping from the configured WAN Appliance primary uplink (as configured on SD-WAN and traffic shaping)
Internet #. The source IP address will be the WAN IP address selected. The ping will continue to follow the same routing as clients connected on the LAN of the WAN Appliance.
VLAN #. The source IP address will be the VLAN IP address selected. The ping will continue to follow the same routing as clients connected on the LAN of the WAN Appliance.
Note:
If a VLAN source interface is selected for the ping tool, the ping traffic will not be able to traverse through the WAN Appliance NAT.
- Example: If a VLAN source interface is selected, pings to destination IPs on the WAN, such as 8.8.8.8 or google.com, will always show 100% loss
If VLANs are disabled on the WAN Appliance while in routed mode, the LAN source interface will be named "VLAN 0"
Behavior - WAN Appliance in Passthrough Mode
If the WAN Appliance is operating in passthrough mode (e.g. one-armed VPN concentrator), the source IP will generally be the MX WAN interface IP.
MS Ping Tool
The MS switches ping tool will accept the following values
- IP address
- DNS hostname
MS switches will source pings from either the management interface or the configured layer 3 interface.
- If the MS switch/stack is only configured for layer 2 switching, pings will be sourced from the MS management interface
-
If the MS switch/stack has a layer 3 routing configuration, pings will be sourced from the layer 3 interface specified in the drop-down menu
MR, MV Ping Tool
The MR and MV ping tool will accept the following values:
- IP address
- DNS hostname
On MR access points and MV cameras, the ping tool will source the ping from the device's management interface.
Note: For MR access points, If you ping a client that is wirelessly connected to the same AP you are sourcing the pings from, the pings will go directly between the AP and the wireless client. This holds true regardless of the VLAN configured for the SSID.

