Cisco Secure Connect - Design Overview
Overview
Cisco Secure Connect securely connects users working anywhere to any application, including private applications hosted in your data center, a private cloud, or public SaaS applications. The solution integrates both client-based and clientless remote worker access, native Cisco Meraki® SD-WAN and Cisco SD-WAN (Viptela) connectivity, and comprehensive cloud-based security capabilities into one subscription.
This section reviews some of the solution's key components. Note that certain functionality is dependent on the Secure Connect package purchased. More information about the packages can be found in the Cisco Secure Connect Data Sheet.
Cisco Validated Designs with Secure Connect can be found in the Cisco SASE with Cisco Secure Connect Design Guide.
Meraki MX Site to Site Auto VPN Topologies
There are three options for configuring the MX's role in the Auto VPN topology:
- Off: The MX device will not participate in site-to-site VPN.
- Hub (Mesh): The MX device will establish VPN tunnels to Secure Connect, and all remote Meraki VPN peers will be configured in Hub (Mesh) mode. It will also establish VPN tunnels to other MX appliances in hub-and-spoke mode, where the other MX device is configured as a hub.
- Spoke: This MX device (spoke) will establish direct tunnels only to Secure Connect. Other spokes will be reachable via their respective hubs unless blocked by site-to-site firewall rules.
Secure Internet Access
Secure Connect acts as your secure onramp to the Internet and provides the first line of defense. Internet-bound traffic from users, applications, and IoT devices in the office, along with remote users with Secure Client installed, is sent to the Secure Connect cloud, where outbound and inbound traffic is inspected.
Using multiple services to detect threats and enforce policies, Secure Connect provides a customizable approach to protecting your network from internet-based threats. The cloud-based system receives real-time threat updates from the Cisco Talos Intelligence Group, the world's largest private security threat intelligence organization.
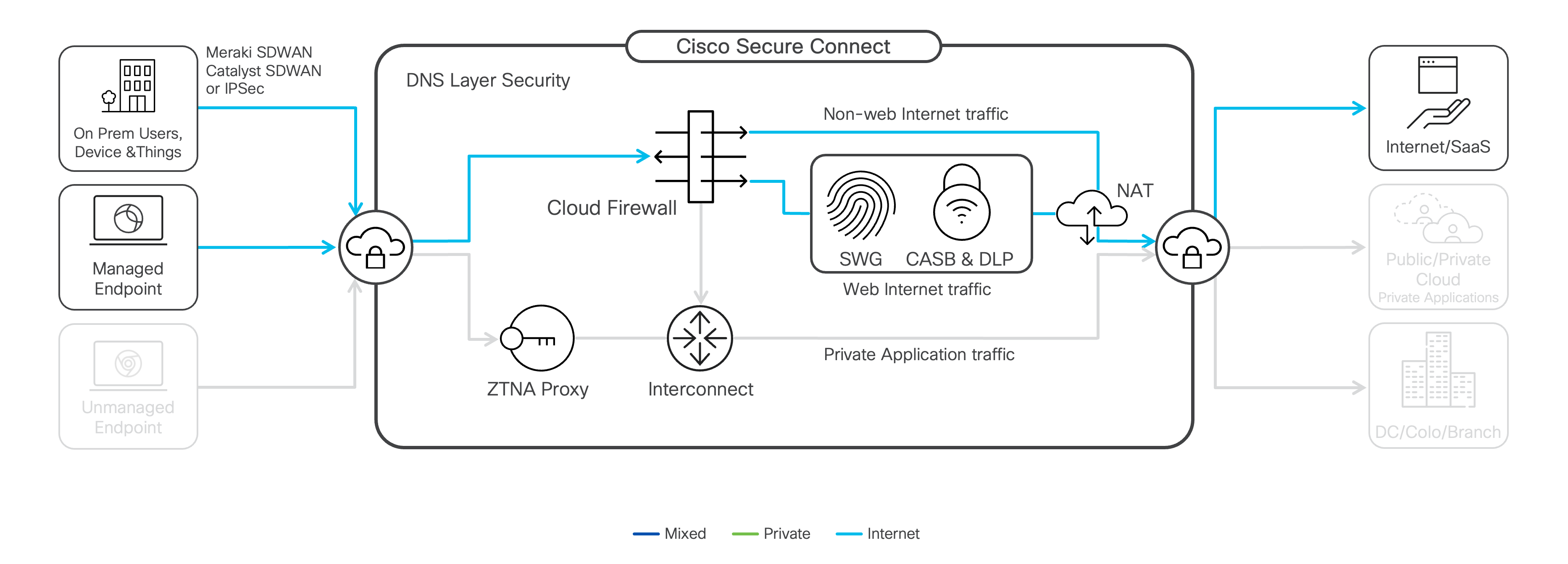
Site Interconnect
Network interconnect provides intelligent routing between sites connected to the Secure Connect network fabric. Cloud Firewall network access policies control access to private applications and resources, enforcing zero-trust policies. The cloud architecture drastically reduces the network complexity, providing a secure, high-availability network fabric, while the unified user interface minimizes the time needed for setup, monitoring, and maintenance.
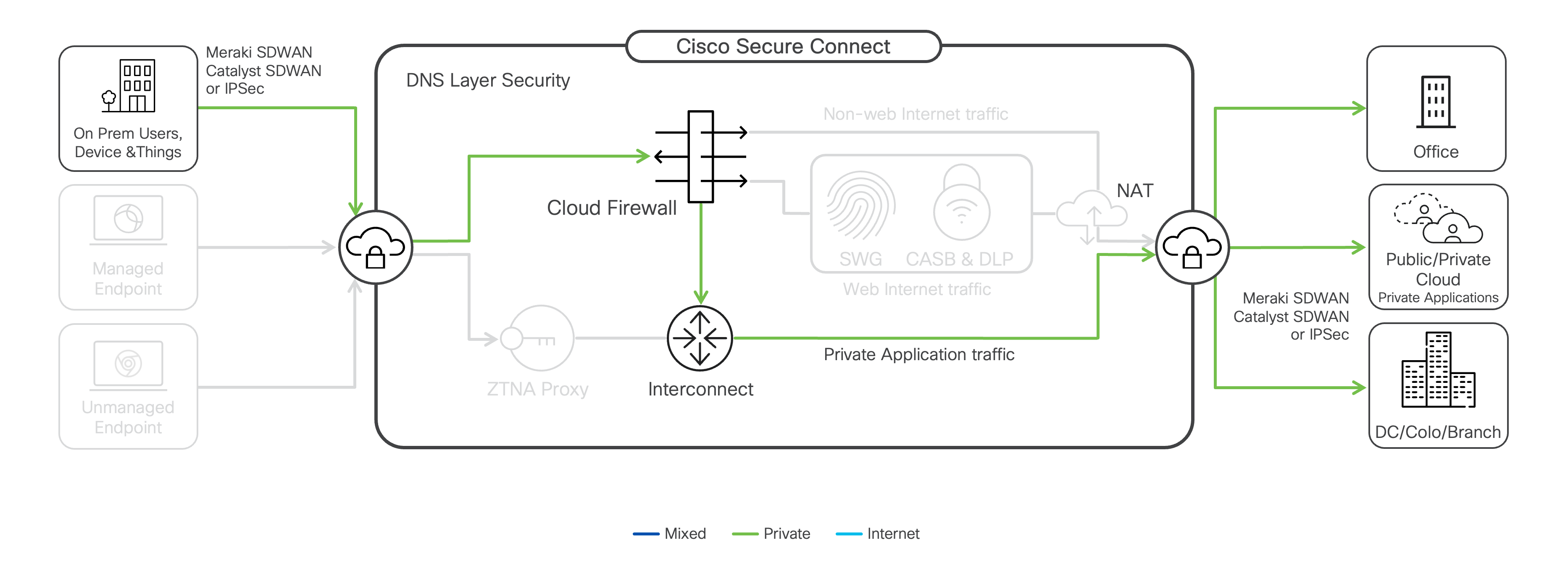
Secure Remote Access
Secure Connect provides secure access to private network destinations and applications for remote workers via client-based tunnels using the Cisco Secure Client, formerly Cisco AnyConnect, and clientless per-app access using any browser. The following explains the difference between client-based and clientless remote access solutions.
Traffic Steering
Secure Client supports traffic steering, also known as split tunneling. Traffic steering rules are either inclusion-based or exclusion-based and determine what traffic is sent (inclusion) or not sent (exclusion) through the Secure Connect tunnel.
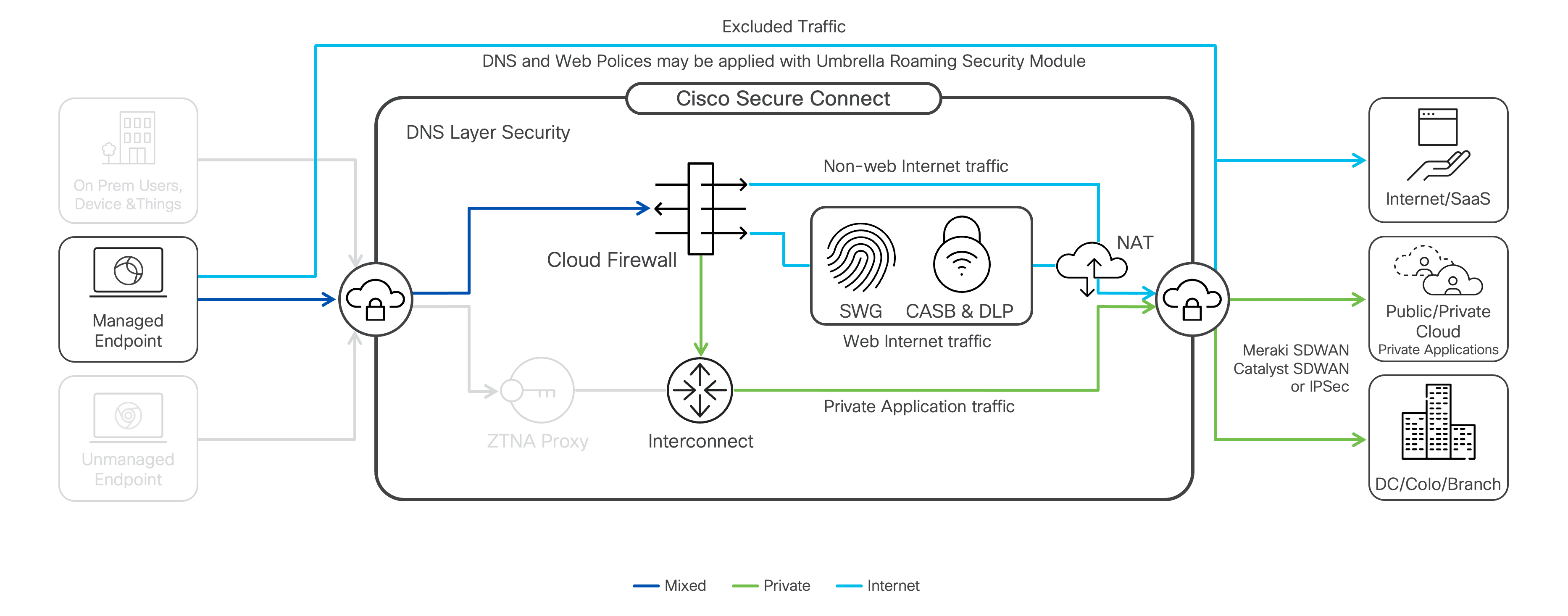
VPN-as-a-Service
With Client-based VPN Access, Secure Client, installed on the user’s device, establishes a Datagram Transport Layer Security (DTLS) tunnel to the Secure Connect cloud. Client-based access supports all ports and protocols, making it ideal for non-web-based apps or applications that require an agent or application to run on the end device.
When the tunnel is active, the user’s traffic is routed through the Cloud Firewall, where network access policies can control access to private applications and resources. In addition, endpoint posture policies can be applied to ensure only compliant devices can connect to the network.
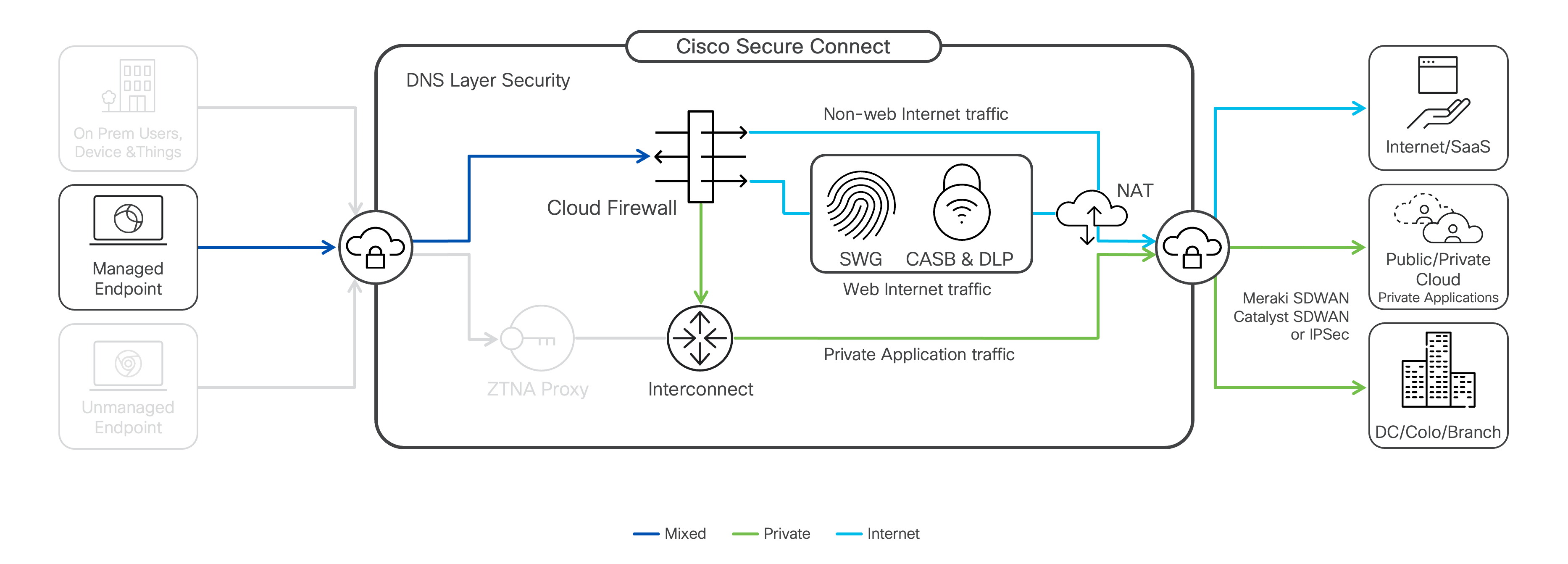
Clientless ( Browser-based) ZTNA
Browser-based) ZTNA
Clientless (Browser-based) Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) allows you to leverage a web browser for remote access to private web-based applications without requiring users to install Secure Client on their devices or create special inbound rules on your on-premises firewall. Clientless access addresses situations where installing Secure Client on a remote user’s device might not be feasible or desirable.
To access an application, the user connects to the Secure Connect ZTNA reverse proxy using a unique URL created by Secure Connect for each application. Before access is permitted to an application, the user and device are verified and validated by a Browser Access Policy (BAP) per session.
Client-based ZTNA
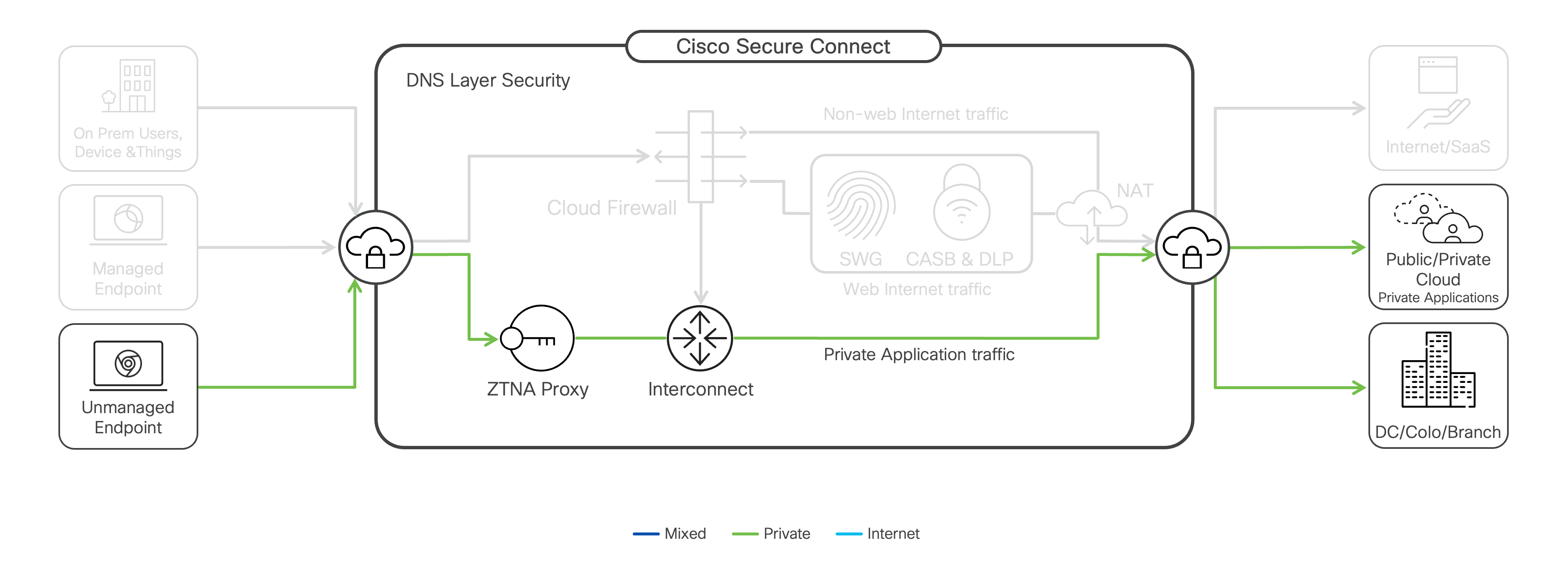
Client-based ZTNA offers a feature-rich solution powered by Cisco Secure Access, providing a seamless end-user experience that connects users to private applications and resources using any port and any protocol. User access to applications and resources is instant requiring fewer steps, delivering better remote worker experiences and stronger security. Administrators can reduce the attack surface, enforce least-privilege controls, enable posture validation, and eliminate security gaps in a distributed environment.

Note: Cisco SD-WAN sites are interconnected through the Cisco SD-WAN fabric, not the Secure Connect fabric. Cisco SD-WAN integration with Secure Connect is only for Secure Internet Access and Remote Access.

