MS DHCP Servers
Click 日本語 for Japanese
Overview
The Switching > Monitor > DHCP Servers & ARP page displays information about any DHCPv4 and DHCPv6 Servers and IPv6 Router Advertisements seen by Meraki Switches on the LAN. From this page Administrators can configure the MS switches in the network to allow or block DHCP or Router Advertisement messages from specific devices.
Learn more with this free online training course on the Meraki Learning Hub:
In an IP environment, the DHCPv4 and DHCPv6 protocols are used to assign IP addresses and other network configuration information to clients. RA (Router Advertisement) messages are used in IPv6 networks to announce the presence of routers, providing necessary information for address configuration and other network settings.
DHCP Guard and RA Guard are security features implemented on network devices to protect against unauthorized DHCPv4 and DHCPv6 servers, and rogue IPv6 router advertisements on a network. DHCP Guard and RA Guard help to ensure that clients receive this information from only trusted DHCPv4 and DHCPv6 servers and Routers that are authorized by network administrators. They do this by filtering DHCP and RA messages based on policies configured on this page, and block responses from untrusted servers, preventing potential attacks such as man-in-the-middle or rogue server attacks that could lead to network resource misallocation or traffic interception.
Email Alerts
Users can configure Email Alerts to be sent when a new DHCP server or Router Advertisement is detected on the network.
The Email Alerts can be configured from the Network-wide > Configure > Alerts page, under the Switch heading. Additionally, the Network-wide > Configure > Alerts page can be used to specify which Administrators receive these alerts.
NOTE: the Email Alerts dropdown menu on the DHCP Servers & ARP page will be deprecated in the new UI which adds support for DHCPv6 and RA Guard.
Warning: The Email Alert feature only applies to switches which are NOT bound to a configuration template
DHCP Servers
Default DHCP Servers Policy
The default policy is set to Allow DHCP Servers on the network for easy installation into an existing environment. This can be set to either Allow or Block new DHCP servers. When the default policy is set to Block DHCP Servers, the Blocked DHCP Servers section changes to Allowed DHCP Servers, and the MAC address of any servers which should be allowed to send DHCP traffic through the switches should be listed in this section.

Blocking DHCP Servers
When the default policy is set to Allow, DHCP Servers can be explicitly blocked by entering the MAC address of the server in question into the Blocked DHCP Servers box. This will prevent DHCP traffic sourced from that MAC from traversing the switches. The MAC address of the server to be blocked can be added to the list by manual entry or by Blocking a detected server from the DHCP Servers list.
Note: Meraki Switches configured as DHCP servers are always allowed to pass DHCP traffic.
Warning: Blocking a DHCP server will block that server for all VLANs and Subnets.
Allowed DHCP Servers
If the default policy is set to 'Deny DHCP Servers' the Blocked DHCP Servers box will change to the Allowed DHCP Servers box. When this change is made only DHCP Servers with a MAC Address matching one of the entries in the Allowed DHCP Servers box will be allowed to pass DHCP traffic, all other detected DHCP Servers will not be allowed to pass DHCP traffic.
Detected DHCP Servers
The DHCP Servers list displays any clients on the network that have been observed sending DHCP responses. The table can display servers that have been detected in the the Last 2 Hours, Last Day, Last Week, and Last 30 Days by selecting the appropriate time period from the dropdown menu. DHCP Servers will only be listed here if a Meraki Switch on the network has seen DHCP response traffic sourced from that client. The table displays information such as the server MAC, VLANs and Subnets of operation, time last seen, and a copy of the most recent DHCP packet to be seen from that client. The screenshot below shows two different devices acting as DHCP Servers for 3 different VLANs across 4 different Subnets.


RA Guard
Default RA Guard Policy
The default policy is set to Allow all router advertisements on the network for easy installation into an existing environment. This can be set to either Allow or Block new . When the default policy is set to Block router advertisers, the Blocked MAC List section changes to Allowed MAC list, and the MAC address of any routers which should be allowed to send router advertisements through the switches should be listed in this section.

Detected router advertisers
The Router advertisers section lists any devices on the network that have been observed sending Router Advertisements. The table can display devices that have been detected in the the Last 2 Hours, Last Day, Last Week, and Last 30 Days by selecting the appropriate time period from the dropdown menu. A device will only be listed here if a Meraki Switch on the network has seen router advertisements sourced from that device.

Warning: Blocking a device with RA Guard will block router advertisements from it in all VLANs and Subnets.
| Description | The Description field lists the description of the Client from the Network-wide > Monitor > Clients list. Clicking on the Description will take you to the Client Details page for that client, if available. If the client is another Meraki device in the Network, such as the 'Main MX' in the image above you will be taken to the Appliance Status or Details page for that device. |
| MAC | The MAC field lists the MAC address that was seen as the source of a router advertisement or a DHCP packet from the DHCP server, such as a DHCP Offer. |
| VLAN | The VLAN field shows what VLAN the DHCP server or router advertisement was detected on. If a single device is sending router advertisements or acting as a DHCP server in multiple VLANs one entry for each VLAN will be created. |
| Subnet | Shows what subnet the DHCP server or router advertisement was detected on. If a single device is sending router advertisements or acting as a DHCP server in multiple VLANs one entry for each subnet will be created. |
| IP | The source IP address of the detected router advertisement or DHCP server traffic. |
| Version | Represents the IP version of the DHCP packet sent by the server. A rhombus with a 4 in it represents IPv4 while IPv6 is represented by a hexagon with a 6 in it. For router advertisements the version is always IPv6. |
| Last Seen | The Last Seen field displays the time since a DHCP packet was seen from that server. Depending on the length of time it may be displayed in Minutes, Hours, or Days. |
| Recent Packet | Provides a link which, when clicked, brings up a pop-up window displaying the most recent router advertisement or DHCP packet to come from the server. Below is an image of an example packet as displayed after clicking the Recent Packet link.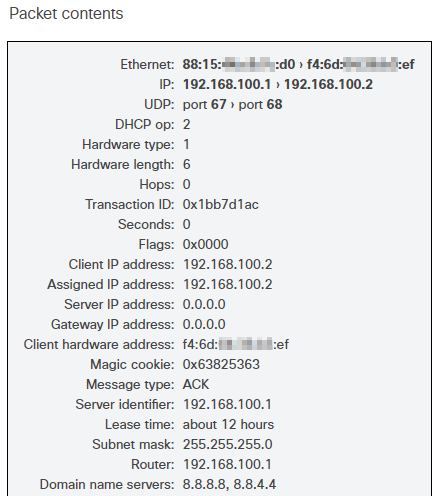 |
| Policy | The Policy field displays the policy applied to a specific DHCP Server or Router Advertiser, either 'allowed' or 'blocked.' |
| Seen By | Lists of switches in the Network that have detected a specific DHCP server. or router advertisement Clicking on the name of one of the switches will bring you to the Switch Details page for that switch. |
| Last Reply IP | Formerly Last ACK IP, this field displays the IP of the client that was last sent a DHCP ACK by the DHCP Server. |
| Last Reply Seen | Formerly Last ACK Seen, this field displays the time since the last DHCP ACK was seen for a specific server. Like the Last Seen field, the length of time may be displayed in Minutes, Hours, or Days. |
| Action | An option to Allow or Block a DHCP server or Router Advertiser, depending on the policy for that entry. |

