CRC Errors
Overview
This document provides instructions for effectively resolving cyclic redundancy check (CRC) errors that may occur within your network infrastructure. By following the guidance outlined, you can identify the root causes of CRC errors and implement appropriate solutions to restore optimal data transmission performance. CRC errors can occur due to various reasons, including electrical interference, faulty hardware, or transmission issues. They are crucial for ensuring data integrity in networks, allowing errors to be detected and possibly corrected before they cause significant problems in communication.
Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC)
CRC is used as a means of detecting errors in transmitted data.
The sending device generates a value derived from the remainder of a polynomial division of its data contents. The receiving device compares the recalculated CRC value with the one received along with the data. If the two CRC values match, it indicates that the data hasn't been corrupted during transmission.
When the receiving device detects a mismatch between the received CRC value and the recalculated CRC value, it flags a CRC error. Seeing CRC errors reported by the Meraki switch on the dashboard indicates that the data may have been altered or corrupted during transmission. 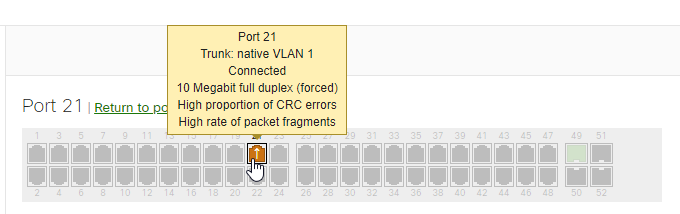
Troubleshooting CRC Errors
Please follow the flowchart below to troubleshoot CRC errors.
.png?revision=1)
The flowchart troubleshooting steps are recorded here:
- Are CRC errors incrementing?
- Yes: Move the cable to a different switch port.
Then, proceed to step 2.
- Yes: Move the cable to a different switch port.
- Do the CRC errors move to a different switch port (using the same cabling and end device)?
- No: If the CRC errors are no longer present, the issue could be with the switch port. To check, connect a different device and Ethernet cable to the original port. If CRC errors continue to increment, then the issue is most likely with the switch port.
End troubleshooting steps here. - Yes: If the issue follows the move to a new switch port, then the issue could be the cabling.
- If there is a patch between the switch and the end device, try bypassing the patch panel and connect the end device directly to the switch.
Proceed to step 3. - If there is no patch panel, change the cable to see if the CRC errors disappear.
Proceed to step 4.
- If there is a patch between the switch and the end device, try bypassing the patch panel and connect the end device directly to the switch.
- No: If the CRC errors are no longer present, the issue could be with the switch port. To check, connect a different device and Ethernet cable to the original port. If CRC errors continue to increment, then the issue is most likely with the switch port.
- Do the CRC errors continue to increment after bypassing the patch panel?
- No: the issue could be with the patch panel cable.
End troubleshooting steps here. - Yes: Change the cable to see if the CRC errors disappear.
Proceed to step 4.
- No: the issue could be with the patch panel cable.
- Do CRC errors still increment after changing the cable?
- No: the CRC errors were caused by faulty cabling.
End troubleshooting steps here. - Yes: check to make sure speed/duplex match on the switch and end device.
Proceed to step 5.
- No: the CRC errors were caused by faulty cabling.
- Does the speed/duplex match?
- No: Change the speed/duplex so that they match. If the issue is no longer present, the issue is with the client device.
- Yes: Change out the end device. If the issue is no longer present, the issue is with the client device.
End troubleshooting steps here.

