Cisco Secure Connect - Client-based ZTNA
Overview
Client-based ZTNA offers secure private access to internal network resources for devices with Cisco Secure Client. ZTNA provides more granular control than traditional remote access VPNs as it operates higher up the network stack with full visibility to the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) of your private application. This additional visibility combined with per-app connection provides greater security by limiting access to only the required network resources, adhering to Zero Trust Principles.
Client-based ZTNA works well with most modern applications that are client-initiated. Most web applications will work out of the box. Applications that can struggle with the reverse proxy architecture of ZTNA are server-initiated or client-to-client applications. For customers with private applications not supported by ZTNA, Cisco recommends using the traditional remote access VPN that is included in Cisco Secure Connect. For a deeper dive on ZTNA architecture please work with your Cisco Sales representative.

Prerequisites & Requirement
|
Requirement |
Details |
|---|---|
| Feature enablement |
2024-07-29: All new Secure Connect Complete customers will automatically be enabled with client-based ZTNA. 2024-08-26: All existing Secure Connect Complete customers can enable Client-based ZTNA by contacting Secure Connect support. If you do not have the "client-based" access method slider on the Resource & Applications edit page, your org is NOT enabled for client-based ZTNA. |
| SAML authentication must be configured | To enroll in Zero Trust Access users must enroll and authenticate with SAML via Cisco Secure Client and the Zero Trust Module. *Note: Meraki IDP is not supported for Client-based ZTNA authentication* |
| Users and Groups provisioned | Users and groups must be synced with Secure Connect to authorize access to private resources via a Zero Trust Access policy. |
| Connection details for private applications | Private Applications must be defined and enabled for Client-based Zero Trust Access. Client-initiated applications are ideal for client-based ZTNA |
| Internal DNS server (some cases) | For fully qualified domain name (FQDN) based applications, a DNS resolution must occur. If your DNS is internal only, you must specify an Internal DNS server on the FQDN-based private app. DNS resolution for private apps will come from the ZTA enforcement node in the CGNAT space 100.64.0.0/10. |
| Cisco Secure Client 5.1.5.65+ with Zero Trust Access module |
Cisco Secure Client for Windows and macOS is required for Client-based ZTNA. Software version 5.1.5.65+ is required to work with Secure Connect and client-based ZTNA. Cisco Secure Client can be downloaded directly only the Secure Connect remote access page or via the links below |
| Device Posture - Duo Desktop | Duo Desktop endpoint software is required for device posture when using client-based ZTNA. Duo Desktop is automatically installed when the ZTA module for Cisco Secure Client is installed. |
| Samsung (Android) |
Samsung devices configured with Samsung Knox running Android 14 or greater support client-based ZTNA. |
| Apple iOS |
Apple iOS devices running 17.2+ support ZTNA
|
| Network and Routing prerequisites |
ZTNA makes use of Carrier Grade Network Address Translation CGNAT IP space (100.64.0.0/10). Additional details around ZTNA network requirements |
| Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) limitation | ZTNA does not work for all applications. Most modern applications are supported. Refer to the ZTNA limitations page for the full details. |
Configuration Steps
- Private Resource & Applications Definitions
- Private Application definitions contain the connection details for the associate private app and are used in ZTNA and VPN policy
- Create Posture Profiles
- Posture profiles are optional requirements that ensure the device connecting to the private applications meets certain criteria.
- Create Zero Trust Access Policy
- Zero Trust Access policy controls access to applications enabled with ZTNA
- Deploy Zero Trust Access Module
- Windows and macOS devices require Cisco Secure Client and the Zero Trust Access module for Client-based ZTNA
- Enroll in Zero Trust Access
- Once the module is installed the client must be enrolled in ZTNA via a SAML authentication
Deploy Zero Trust Access Module
Client-based ZTNA for Windows and macOS requires the deployment of the Zero Trust Access module in the Cisco Secure Client. Remote workers need the client and module to be supported. Cisco Secure Client offers many modules and was previously called Cisco AnyConnect.
Cisco Secure Client provides security to user devices on any network from any location. User devices can connect to private resources through Zero Trust Access or VPNs, or access internet resources protected by the Cisco Secure Connect DNS-layer security and web security. Existing Cisco remote access customers running Cisco Secure Client can upgrade and add the new module to the required endpoints.
Cisco Secure Client manages the endpoint security on user devices for both Windows and macOS devices. For more information about Secure Client, see Cisco Secure Client At-a-Glance.
Install the Cisco Secure Client on any user devices in your organization. You can customize the client modules that deploy with the package. For more information about the Cisco Secure Client, see Cisco Secure Client (including AnyConnect) Administrator Guide, Release 5.1.
ZTA Module Requirements
Cisco Secure Client with the Zero Trust Access module must meet these requirements:
- Windows 10 and 11
- macOS versions 11, 12, 13, 14+
- Windows devices must support Trusted Platform Module (TPM) 2.0
- Mac devices must support Secure Enclave
Enroll in Zero Trust Access
Enrollment in Zero Trust Access is very is done by the end user in Cisco Secure Client. Cisco Secure Connection requires Cisco Secure Client version 5.1.5.56 or greater.
Enrollment Steps
- Open - Launch Cisco Secure Client
- Enroll - Find the Zero Trust Access module and click the Enroll button
- Input Enrollment Email - Input the end-user email for authentication
- Select Your Org - Select the org you wish to enroll from the provided list. Note there may only be one.
- Perform Authentication - Authenticate via the SAML prompt via the integrated Identity Provider (IDP). Note this will look different based on your IDP. Example provided of Cisco Duo.
- Enrollment - The device enrolls in ZTNA and is provisioned a certificate that is securely stored in TPM
Step 1. Open Cisco Secure Client - Windows

Step 2. Click Enroll
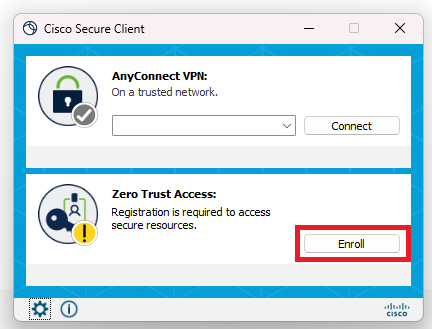
Step 3. Input Enrollment Email

Step 4. Select Your Org
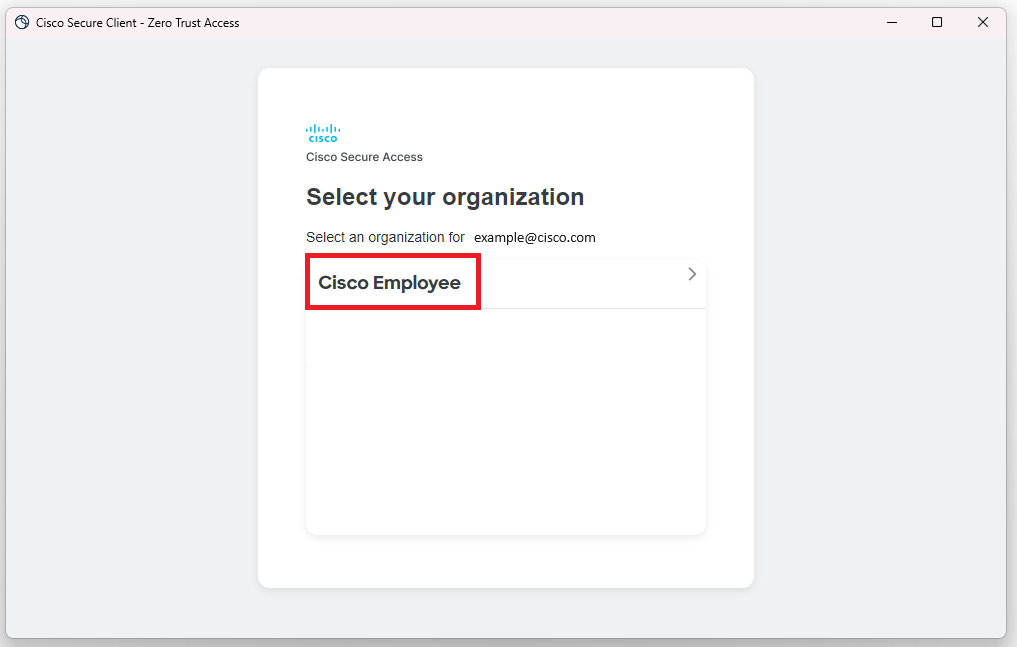
Step 5. Authentication
Note the authentication page will look different based on your organizations SSO provider.

Step 6. Enrolling

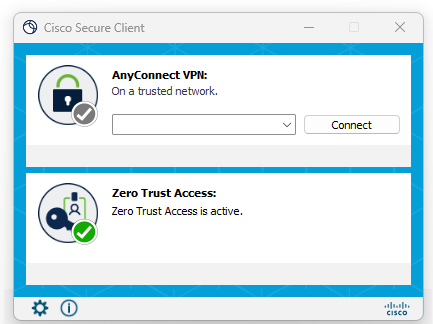
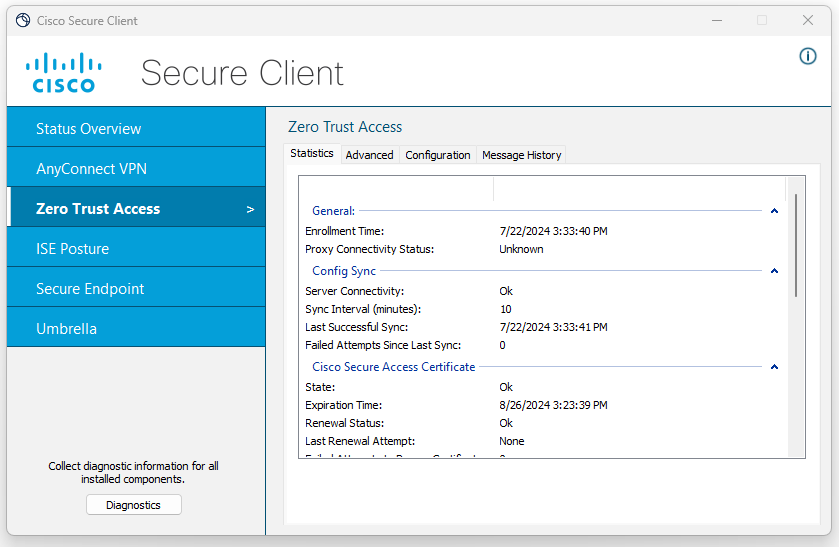
Enrolled Client
Once enrolled the Client should look similar to this.
Related Content:
Unenroll a Device from Zero Trust Access
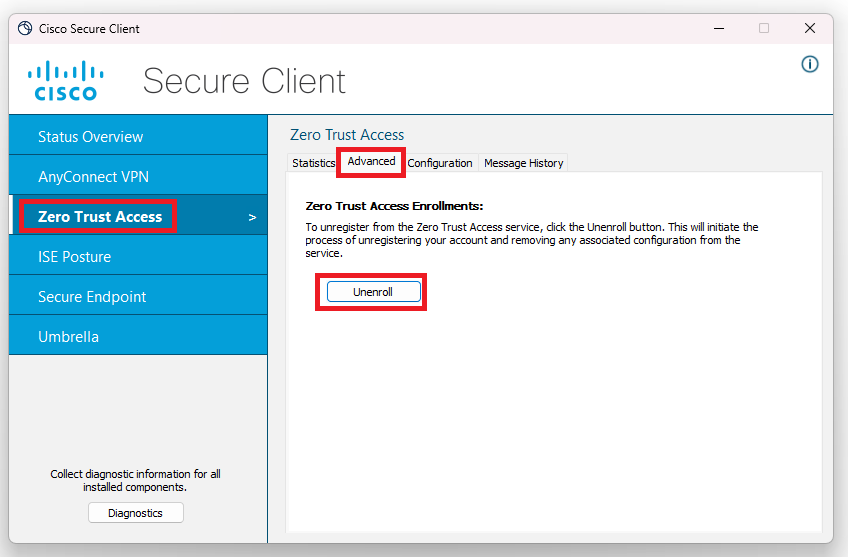
Once enrolled in client-based ZTNA, a device will automatically connect until the service is disabled or the client is unenrolled. To unenroll a ZTNA endpoint hit the unenroll button in the settings for the Zero Trust Access module.
Unenrollment in Zero Trust Access must be done in Cisco Secure Client
To unenroll a device
- Click the gear icon in Cisco Secure Client
- Navigate to Zero Trust Access -> Advanced and click Unenroll