IPv6 Support on MX Security & SD-WAN Platforms - Core Fundamentals
Note: IPv6 is an ongoing cross-product initiative for Meraki as IPv4 addresses are being exhausted and with more hosts such as IoT devices requiring addressing, IPv6 provides a new structure to accommodate a larger number of hosts.
This article describes general information on IPv6 Support on MX Security & SD-WAN Platforms. For more information on compatible devices, please see our IPv6 Device Compatibility documentation.
Overview
-
This document describes the IPv6 functionality and configuration available on the MX Security & SD-WAN Platforms. It will include information such as: supported MX and teleworker models, minimum firmware, and how to configure and use IPv6 on a network.
Note:
- MX cannot currently function in a native IPv6-only environment. It is recommended that dual-stack is implemented in order to leverage IPv6 functionality and management.
-
High-availability (HA) and template deployments are not supported at this time.
-
If a feature or functionality is not mentioned in this KB article, it is not yet supported for IPv6
Minimum Firmware
-
MX 17.5+ firmware is required for IPv6 functionality on MX Security & SD-WAN Platforms.
Supported Models
- Z3, Z3C, Z4, Z4C, MX64, MX64W, MX65, MX65W, MX67, MX67W, MX67C, MX68, MX68W, MX68CW, MX75, MX84, MX85, MX95, MX100, MX105, MX250, MX450.
- All current MX/Z models listed on our website here.
Note:
- Passthrough mode/One-Arm Concentrator mode currently only supports DHCPv6-NA, SLAAC or Static IP address assignment for IPv6 assignment on the WAN interface (including vMX-S/M/L platforms).
- For cellular support, only the MX67C and MX68CW integrated cellular models are supported.
Terminologies
-
DHCPv6 IA_NA (aka DHCPv6-NA) - Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol for IPv6 used to assign Global IPv6 addresses
-
DHCPv6-PD - Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol for IPv6 Prefix Delegation is used to assign network prefixes from an ISPs DHCPv6 server to customer’s edge routers
-
SLAAC - Stateless Address Autoconfiguration
-
PPPoE - Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet
-
Origin - The source for which an IPv6 Prefix is configured/assigned originates from and routes via
-
GUA - Global Unicast Address
-
ULA - Unique Local Address
-
Independent Prefix - Provider Independent address space
-
Prefix shortage - Refers to Prefix Starvation and this occurs when the MX detects it does not have enough prefixes from a given WAN or manual configuration to assign a /64 prefix to each IPv6 enabled VLAN
Feature set
All major functionality and configuration topics are hyperlinked and broken down in their respective documentation:
- WAN - Dual-stack (IPv4 and IPv6) WAN operations with simplicity. Currently, MX Security & SD-WAN Platforms support the following WAN features:
-
Auto (DHCP6)
-
Auto (Stateless)
-
PPPoE (Stateless)
-
PPPoE (Static)
-
Manual (Static)
-
Cellular (Stateless)
-
-
LAN - Dual-stack LAN operations complemented by WAN simplicity. Currently, MX Security & SD-WAN Platforms support the following LAN features:
-
Auto (DHCPv6-PD)
-
Manual Prefixes (Auto delegation)
-
Manual Prefixes (VLAN override)
-
Cellular (with ULA and NAT)
-
Dynamic VLAN Objects
-
Link-Local and SNMC Visibiltiy
-
Recursive DNS Server (RDNSS)
-
-
Routing - Dual-stack routing operations. Currently, MX Security & SD-WAN Platforms support the following routing features:
-
Uplink Selection
-
Dynamic routing for VPN concentrator mode
-
eBGP
-
OSPF
-
-
Static Routes
-
Global Addresses
-
Link Local Addresses
-
-
-
VPN - Meraki AutoVPN dual-stack operations. Currently, MX Security & SD-WAN Platforms support the following VPN features:
-
AutoVPN
-
Route mode
-
One-Arm / Passthrough Mode
-
-
Non-Meraki VPN
-
IPv6
-
IPv4 over IPv6
-
IPv6 over IPv4
-
-
AnyConnect VPN
-
-
-
Firewall Rules - Layer 3 dual-stack firewall operations. Currently, MX Security & SD-WAN Platforms support the following firewall features:
-
Layer 3 Inbound Firewall Rules
-
Layer 3 Outbound Firewall Rules
-
Layer 3 Cellular Failover and Inbound Cellular Firewall Rules
-
Organization-wide Layer 3 Site-to-site VPN Outbound Firewall Rule
-
- Advanced Malware Protection (AMP)
- Threat Grid
-
-
Monitoring and Reporting - Dual-stack visibility with monitoring and reporting tools. Currently, MX Security & SD-WAN Platforms support the following monitoring and reporting tools:
-
IPv6 Prefix table
-
Ping
-
Traceroute
-
DNS Lookup
-
Route Table
-
AutoVPN participants table
-
Client Tracking
-
Event Log
-
DAD
-
Addressing/VLAN updates
-
Prefix starvation
-
-
Enhanced Route Table Page
-
MX Uplink Loss and Latency
-
-
Local Status Page - Dual-stack local device management. Currently, MX Security & SD-WAN Platforms support the following local status page features:
-
LAN
- PPPoE
-
-
Upgrade and Rollback behaviours
-
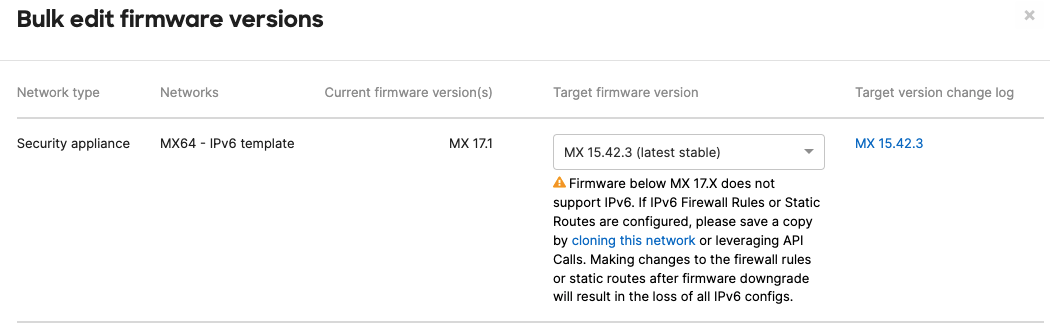
Downgrading firmware to MX 16 and prior removes all IPv6 configuration and information from the network. Hence, once the network is upgraded to MX17.3 or higher again, all previously set IPv6 configurations are lost. Prior to the downgrade, you will see the following banners and alerts:
Firmware downgrade warning:
Firewall page warning:
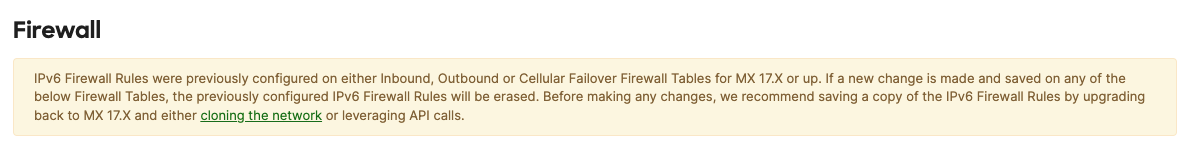
-
- API - A RESTful API to programmatically manage and monitor IPv6 networks at scale (API homepage).
-
Monitoring:
-
Return current delegated IPv6 prefixes on an appliance
-
GET /devices/{serial}/appliance/prefixes/delegated
-
- Return prefixes assigned to all IPv6 enabled VLANs on an appliance
- GET /devices/{serial}/appliance/prefixes/delegated/vlanAssignments
-
- Configuration:
- Configure static delegated prefix
- GET /networks/{networkId}/appliance/prefixes/delegated/static
- POST /networks/{networkId}/appliance/prefixes/delegated/static
- GET /networks/{networkId}/appliance/prefixes/delegated/static/{staticDelegatedPrefixId}
- PUT /networks/{networkId}/appliance/prefixes/delegated/static/{staticDelegatedPrefixId}
- DELETE /networks/{networkId}/appliance/prefixes/delegated/static/{staticDelegatedPrefixId}
- Configure IPv6 uplink
- GET /devices/{serial}/appliance/uplinks/settings
- PUT /devices/{serial}/appliance/uplinks/settings
- Configure IPv6 setting on VLAN
- GET /networks/{networkId}/appliance/vlans/{vlanId}
- POST /networks/{networkId}/appliance/vlans
- PUT /networks/{networkId}/appliance/vlans/{vlanId}
- Configure static delegated prefix
-

