Deploying Store Apps for iOS/macOS and Android
Systems Manager can be used to deploy apps to all of your managed devices through the Systems Manager > Manage > Apps page. The Meraki Dashboard integrates directly with Google Play and both the iOS and macOS App Stores, which allows you to quickly and easily configure and deploy apps to your mobile devices.
For information on deploying custom software from installer files for Windows and Mac devices, see this article. For deploying custom enterprise apps for iOS and Android, see this article.
Initial Setup
To deploy Android apps, you will first need an Android Enterprise domain, either Google or Meraki-managed, bound to your Meraki Dashboard.
To deploy iOS or macOS apps, you will first need your APNs token set up to enable communications with Apple's servers. To push out apps silently to devices, and avoid prompting the end user to sign into an Apple ID or to push apps to macOS at all, you will need to set up your Apple Volume Purchase Program (VPP) account as well, which allows you to centrally manage application licenses. See more info on silent iOS app installs here.
Adding Store Apps
Once you are ready to add apps, navigate to the Systems Manager > Manage > Apps page and select 'Add App' at the top right.

Choose the desired platform on the pop-up screen.
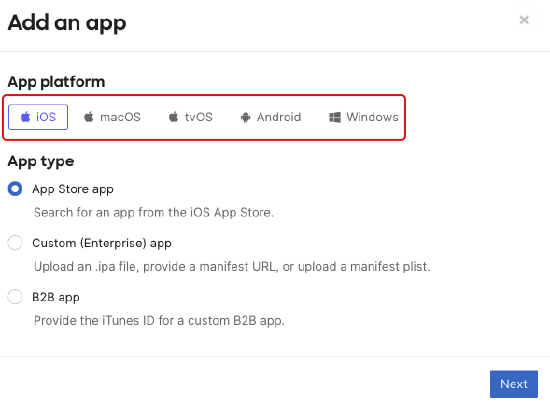
iOS / macOS
Search for your application, and click the app entry found to enter the app configuration page. In this example, we show adding an iOS app, but the steps are the same for macOS.


Android
You can now conveniently search for your Android application in the Google Play Store directly from the Dashboard. This feature allows you to quickly locate and manage your app without leaving the Dashboard interface, streamlining the process and enhancing your workflow.
Region Restricted Applications - The Google Play Store will return applications that can be installed in the same region that the administrator is accessing Dashboard from i.e. accessing Dashboard from the United States will show applications that can be installed world-wide & US-only.
Once you have found the chosen application, click "Select", this will populate the identifier and other fields below the Google Play frame.

Note: The Dashboard does not allow you to add multiple apps with the same app identifier. To check which app identifiers have already been added, navigate to the Systems Manager > Manage > Apps page, click on the wrench icon on the right, and add the "Identifier" column.
Note: "From September 2019, organizations can no longer purchase app licenses through managed Google Play. However, they can still use any licenses they already own." Please see the Android Enterprise documentation "Keep track of paid app licenses" for additional information.
Some apps address this by being free on the Play Store and incorporating licensing through the Managed App Config payload. Others negotiate terms and provide an APK or grant access to a private app hosted on Google Play.
Searching for Android apps by App ID
Some users may have difficulty finding Android apps in Systems Manager due to Internet restrictions in certain regions. To bypass these search limitations, Android apps can be located in Systems Manager using their App ID.
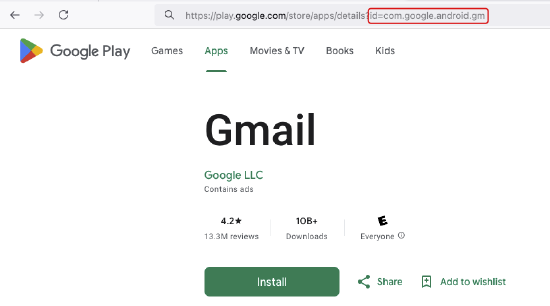
One way to find an app's package name is by searching for the app in the Google Play Store using a web browser. The package name appears at the end of the URL, as shown below.
Configuring Apps
After adding an app, you'll see an interface similar to the one below. Note that Android apps may show slightly different options until changes are saved.
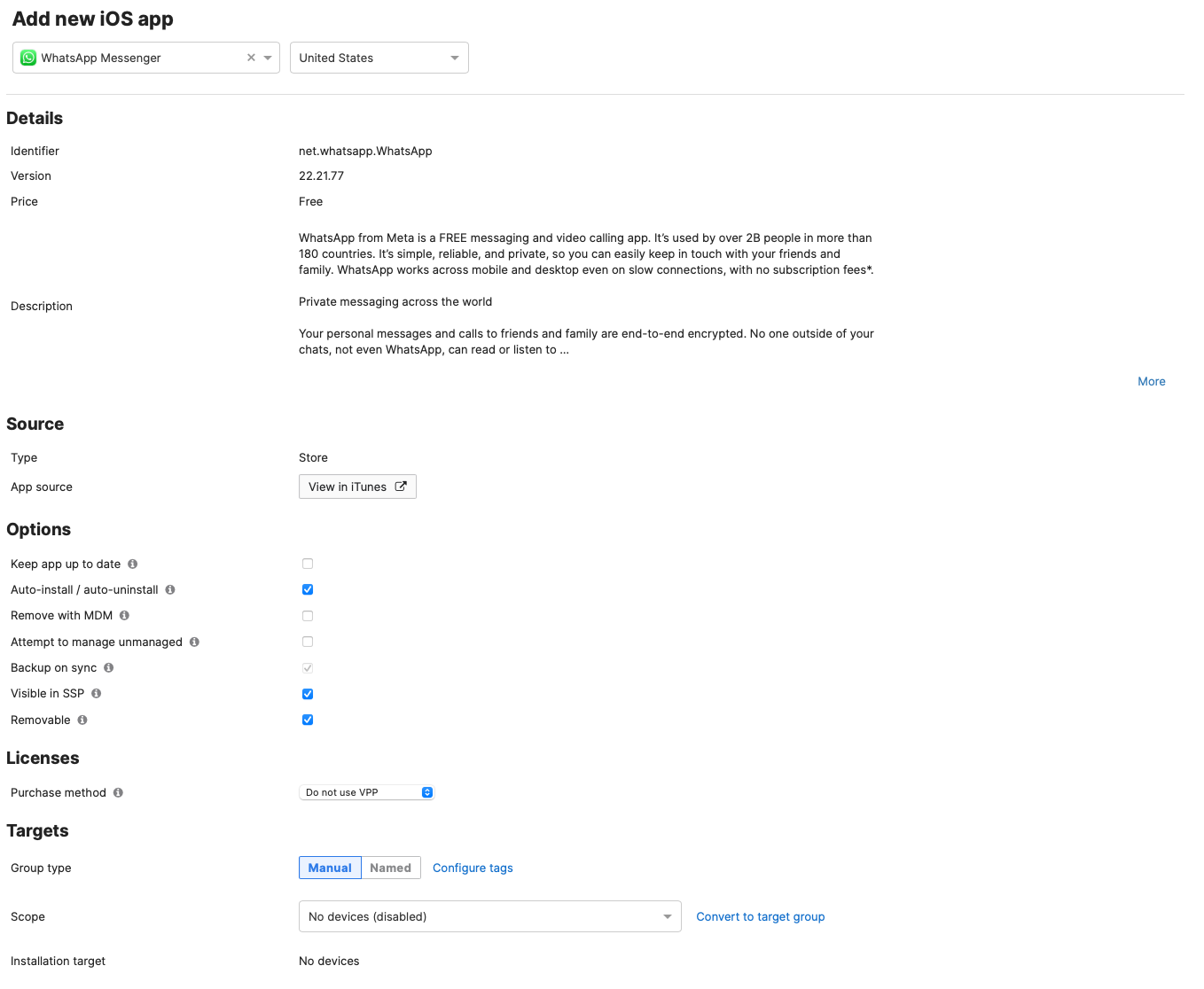
Scope
By default, this app will be pushed down to all devices of the matching operating system, but this can be narrowed down by tag. See tag scoping for more info.
License Method (iOS only)
This is used to specify if an iOS app should be configured to use one of your organizations VPP licenses, instead of prompting the user to sign into their Apple ID. You may use the drop down to select either VPP Codes, VPP User Assignment, or VPP Device Assignment. For more information about VPP, see our article here.
macOS App Store App deployment requires the use of VPP Device Assignment, and as such is always selected for this type of app.
Auto-Install / Auto-Uninstall
By default, apps will automatically attempt to install on all scoped devices once 'Save Changes' is clicked. To push out an install later, or leave the installation option up to the end user, who can access available apps through the managed Play Store or Systems Manager app, uncheck this option.
Remove with MDM
Selecting this check-box will force the app to be uninstalled when the Meraki management profile is uninstalled. This is important to have checked if you want to ensure that the apps you select are only available to those mobile devices that are managed by Systems Manager.
macOS App Store Apps cannot be removed by unscoping the app or this "remove with MDM" option. To remove macOS App Store Apps the device will need to send a command to remove the app locally such as sudo rm -r "/Application/AppName" or deploy a script / custom .pkg to do this.
Attempt to Manage Unmanaged (iOS only)
If the device you push this application to is already installed, Systems Manager will attempt to take management over the app, allowing Dashboard admins to push updates and uninstalls for that app. This is only available on iOS 9+, and will prompt the user for confirmation on unsupervised devices.
Backup on Sync (iOS only)
Deselecting this check-box will prevent app-generated data from being backed-up during a sync. This is important for administrators who want to separate personal from organizational/corporate data on an iOS device.
Pushing and Updating Apps
After configuring your app, clicking on 'save changes' will automatically push out the app install commands to devices in scope, listed at the bottom of the page. Again, ensure you have VPP app licenses available for iOS apps if applicable, and that you have approved Android apps for end users to access.
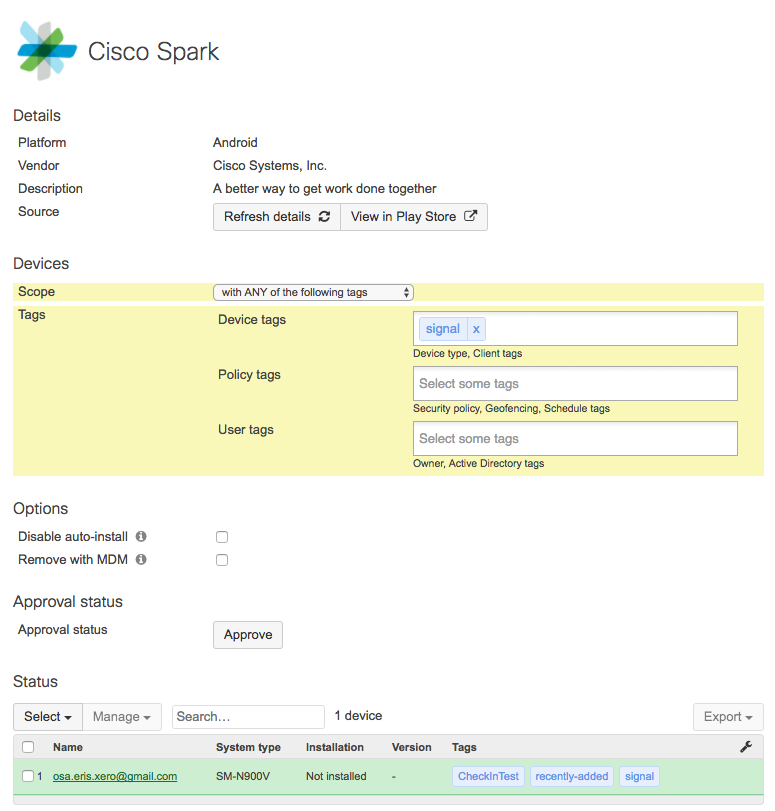
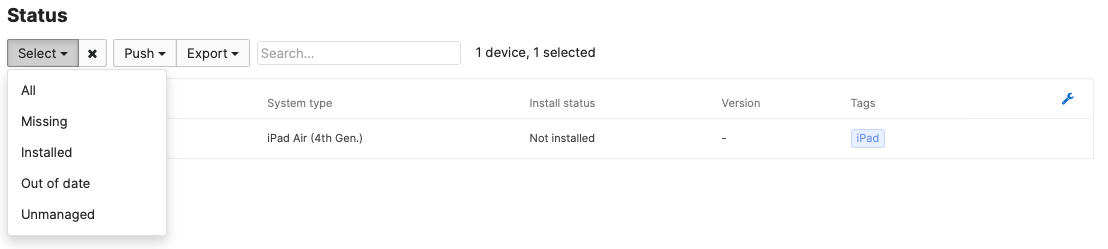
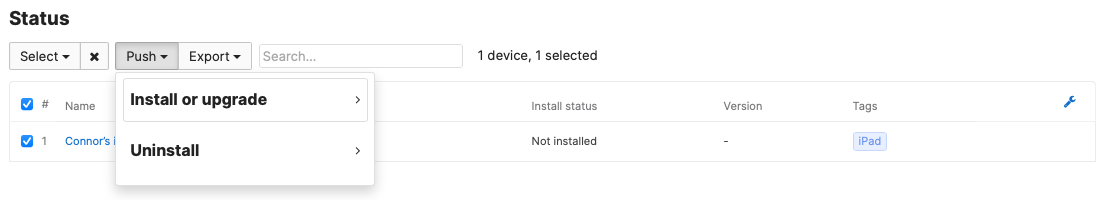
To manually re-push apps, you can use the commands under 'Status' to re-push to all scoped devices, or only devices missing the app. You can also selectively re-push the app to specific devices by checking the boxes at the bottom and clicking Push > Install or Upgrade. This can be used to manually update apps that have new versions available in the app store as well.
For more information on pushing app updates, see this article.
Google Play Store App Updates
In the Systems Manager > Settings page, administrators can create a profile to control the Google Play Store app update policy.
 There are three option administrators can choose for an individual app's update policy:
There are three option administrators can choose for an individual app's update policy:
Default - In this mode, the device needs to meet certain criteria to automatically update the app, and it will happen at some point (uncontrolled) within a 24 hours period of the new app update becoming available on the Google Play Store. The criteria for the device to update: device has an active WiFi connection to the Play Store, device is charging, device is idle, and the app to be updated is not running in the foreground.
Postpone - When using the Postpone mode, the app will not be automatically updated during 90 days after it first became out of date. After this 90-day period, the latest available version of the app is automatically installed with the default update behavior (as outlined above). After the app is updated to the latest available version, a new 90-day postponement period will begin the next time the developer publishes a new version of the app.
High Priority - When using the High priority mode, the app is updated, as soon as possible, after the developer publishes the new version and it has been reviewed by Google Play. If the device is offline then, the app will be immediately updated the next time the device is connected to the internet.
Note: In High Priority mode, if the app is in use when the update is ready to install, the app will be closed during the update, which could affect active users/devices.
More information on these Google Play Store App Update Mode policies can be found in Google's Android Enterprise documentation here.
Deploying websites to devices as apps
Websites can be deployed as Web Clips for Apple devices and Web Apps for Android devices. For more information, see this article.
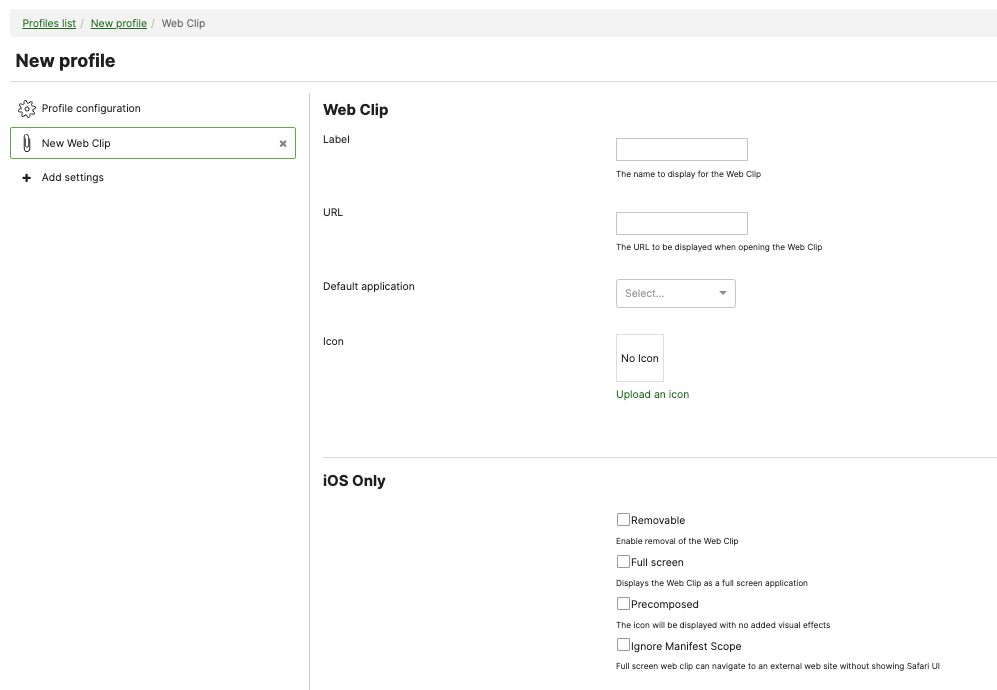
Apple Web Clips
Apple devices can have websites deployed to devices as apps with a feature called Web Clips. Web Clips can be configured as a profile in the Systems Manager > Settings page.
Android web apps
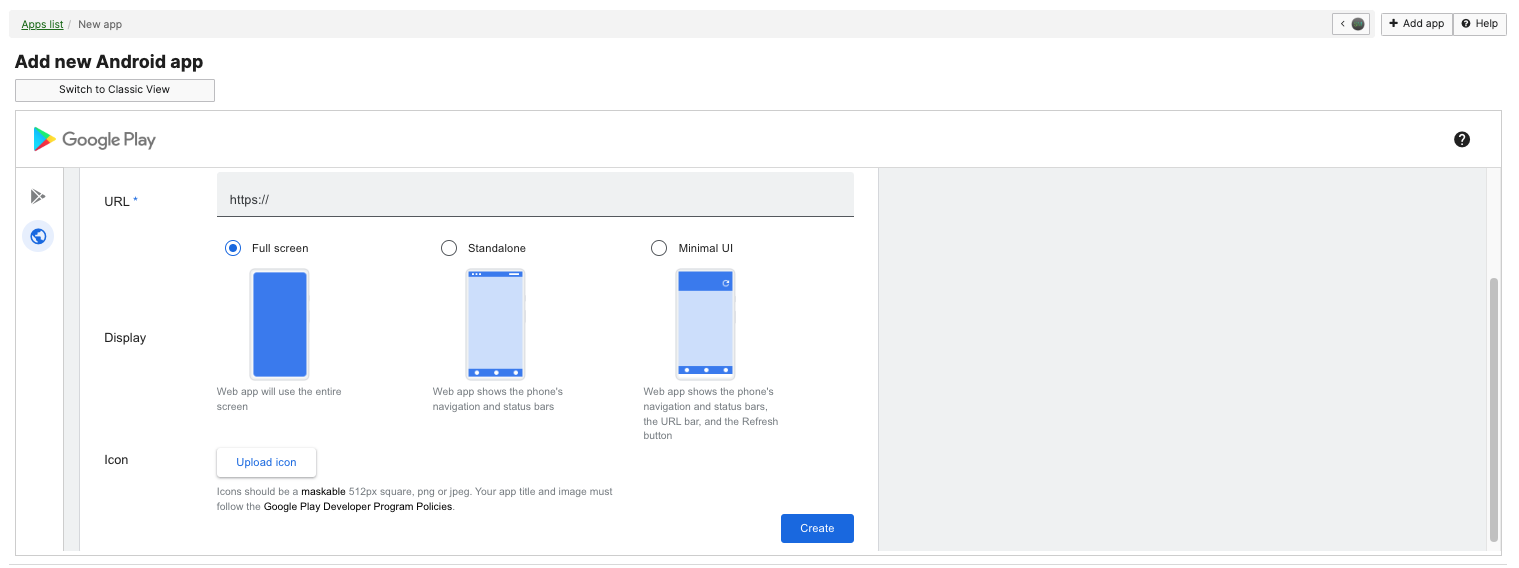
For Android devices, administrators can install web apps on managed devices. Administrators are able to configure the name, url, app icon, and display state (full screen, standalone, minimun ui, etc).