Dashboard Alerts - Configuration Issues
Overview
These are the Configuration Issues alerts, their triggers, and troubleshooting steps indicated by the alerts. Please refer to the Alerts article to learn more.
Misconfigured DNS
Triggers
Meraki devices rely on DNS to resolve dashboard URLs. If a device reports issues with its DNS configuration, typically the device is not receiving responses to DNS requests. This alert may also be phrased as "DNS is Misconfigured."
Troubleshooting Steps
To find the source of the issue, check:
- Firewall rules blocking traffic to or from the DNS servers being used or traffic to UDP port 53.
- Routing traffic to or from the DNS servers.
- Invalid responses back from the DNS server.
- Take a packet capture on an upstream device to see what traffic the device is sending and receiving.
- For larger networks, filter for the device's IP address or MAC address and download the .pcap file.
If there are no firewall rules blocking DNS traffic and there aren't issues with routing traffic, try working around the issue by changing the DNS servers to a working public resolver on the DHCP server. Have the Meraki devices request another IP or set the IP manually, and set the DNS servers to a known working public resolver.
Uplink IP Address in Conflict with Another Device
Triggers
This alert means that another device in the network is also using the same IP address as the Meraki device.
Troubleshooting Steps
To resolve this problem, ensure all devices have unique IP addresses in a network. The Network-wide > Monitor > Clients list may help pinpoint the duplicate IP addresses in use:
- Open the clients list by navigating to the client page Network-wide > Monitor > Clients.
- Find a client with an IP address that matches the one shown in the alert.
Both devices—the device showing the alert and the other device using the same IP address—will struggle to reach the internet until this problem is resolved.
Bad IPv4 Assignment Configuration
Triggers
This alert means a bad static IP or an incorrect VLAN tag with DHCP is being assigned to the Meraki device. Typically, network hardware will simply not work if you assign a bad IP address to it. Meraki devices, however, will automatically switch back to DHCP (automatic IP assignment) so that it can check in to the cloud and alert you about the problem if at all possible.
Troubleshooting Steps
- Make sure that the Gateway you have entered is correct and online.
- If the device has had a working static IP, make sure the IP address is still valid.
- Verify if the IP, Subnet mask and Gateway are correct for the subnet to which the AP is attached. Make sure there are no extra spaces in your settings (including leading, trailing, or between characters).
- The Primary DNS is valid and reachable (we recommend using Google Public DNS at 8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4).
- Check if the wrong VLAN tag is used for DHCP.
- Check the local status page - often times the local status page gives more detailed error output to help resolve the problems during troubleshooting.
- Perform packet captures to confirm ARP requests are replied to, from the upstream gateway.
- Reboot the hardware - sometimes the MAC address for the internet port can get stuck on network hardware and clear out after a set period of time. Rebooting network equipment helps speed up this process.
- Switch to DHCP. The error message will only be displayed if the Meraki device has found another working IP address. If you switch the IP assignment to DHCP instead of static IP, the device will use the current addressing. The error will go away over time. You should only specify a VLAN tag if you know what it should be.
Bad IPv6 Assignment Configuration
Triggers
This alert means a bad static IP or an incorrect VLAN tag with DHCP is being assigned to the Meraki device. Typically, network hardware will simply not work if you assign a bad IP address to it. Meraki devices, however, will automatically switch back to DHCP (automatic IP assignment) so that it can check in to the cloud and alert you about the problem if at all possible.
Troubleshooting Steps
- Make sure that the Gateway you have entered is correct and online.
- If the device has had a working static IP, make sure the IP address is still valid.
- Verify if the IP, Subnet mask and Gateway are correct for the subnet to which the AP is attached. Make sure there are no extra spaces in your settings (including leading, trailing, or between characters).
- The Primary DNS is valid and reachable (we recommend using Google Public DNS at 8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4).
- Check if the wrong VLAN tag is used for DHCP.
- Check the local status page - often times the local status page gives more detailed error output to help resolve the problems during troubleshooting.
- Perform packet captures to confirm ARP requests are replied to, from the upstream gateway.
- Reboot the hardware - sometimes the MAC address for the internet port can get stuck on network hardware and clear out after a set period of time. Rebooting network equipment helps speed up this process.
- Switch to DHCP. The error message will only be displayed if the Meraki device has found another working IP address. If you switch the IP assignment to DHCP instead of static IP, the device will use the current addressing. The error will go away over time. You should only specify a VLAN tag if you know what it should be.
Device(s) VLAN Mismatch
Triggers
A management VLAN mismatch triggers this alert. This is when there is a mismatch between operational, configured, and global management VLAN ID (see Switch Settings). This alert may also be phrased as "The device is using a DHCP IP address from VLAN X instead of using configured VLAN Y."
Troubleshooting Steps
- Make sure the device is not using a VLAN different from what is configured for its management interface.
- Make sure the device management VLAN is not configured with a different VLAN from what is configured under Switching > Configure > Switch settings. For more information, refer to Switch Settings.
Port(s) VLAN Mismatch
Triggers
This feature utilizes Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) and Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) packets from the past 3 hours to determine which switch ports are connected. If any two connected switch ports belonging to Meraki switches are in the same dashboard organization, the switch port VLAN configurations are compared.
Usually, a VLAN mismatch occurs:
- After connecting a switch that is not pre-configured to the existing Meraki switch infrastructure.
- When a network administrator changes the port VLAN settings.
If any mismatch is found in native, allowed, or access VLANs, both switches will display device-level alerts in the dashboard. The switches will continue displaying the alert until the VLAN mismatch is resolved. The alert hub will display only one alert for VLAN mismatch between two switches.
Currently, VLAN mismatch detection is supported on Meraki switches in the same organization. VLAN mismatch detection is not supported for other Meraki devices (MR, MX, and others) and non-Meraki devices.
Troubleshooting Steps
Make sure both ports allow the same VLANs. Refer to VLAN Mismatch Alerts for Meraki Switches to learn more about how to correct a VLAN mismatch error.
Guided Troubleshooting Flow
VLAN mismatch troubleshooting flow reduces time to resolution for our customers by easing manual tasks, simplifying the configuration process, and dynamically detecting errors.
Easing Manual Tasks
Guided VLAN mismatch troubleshooting flow displays switches' current configuration and allows administrators to fix the issue from the troubleshooting panel without needing to navigate to different pages on the dashboard.
Simplifying the Configuration Process
This feature allows configuring all the settings on the alert hub and in some cases, the feature also displays suggested configurations derived from the configuration of the two switches alerting on VLAN mismatch. Users can apply these suggested settings by selecting the Accept suggestion button.
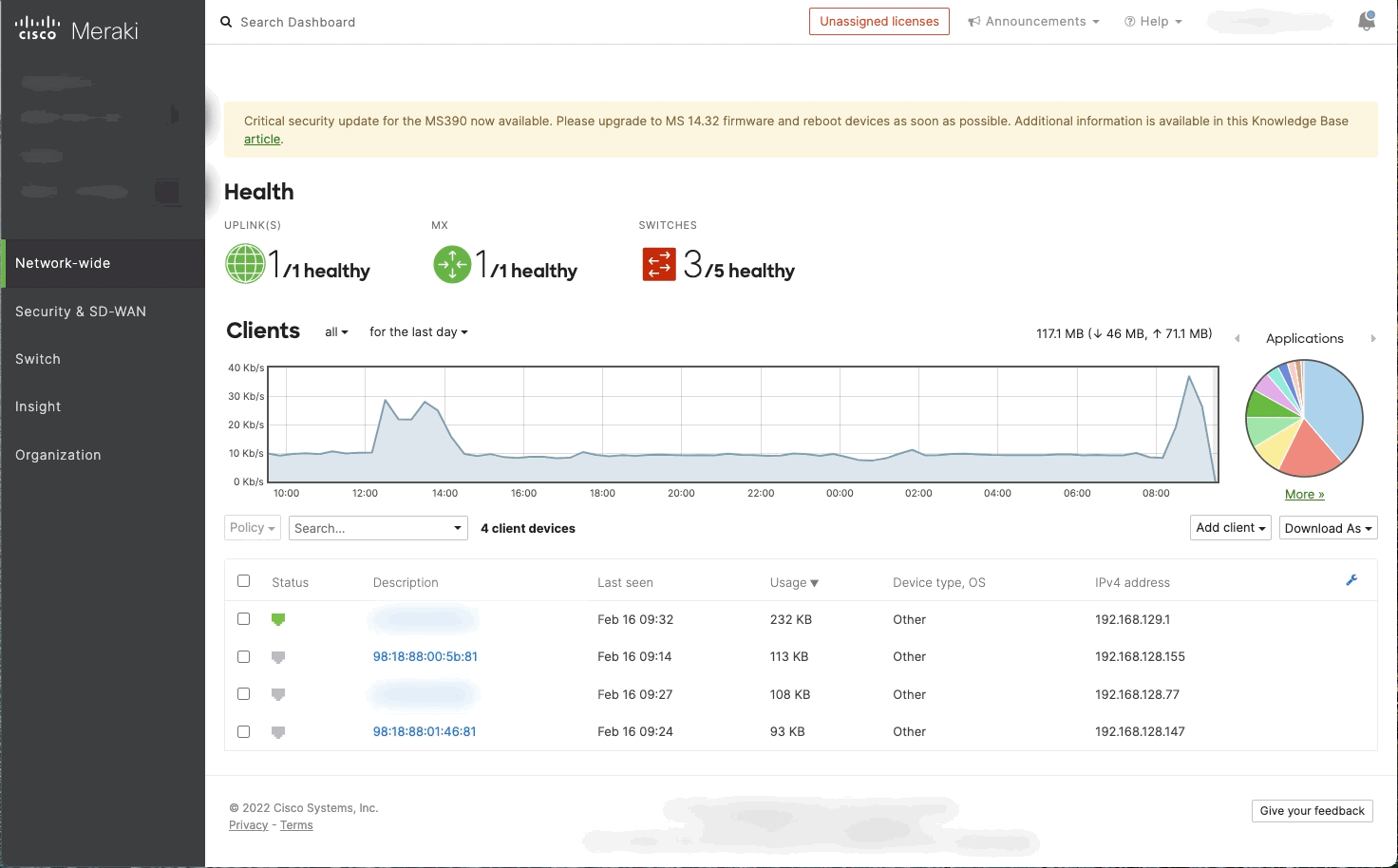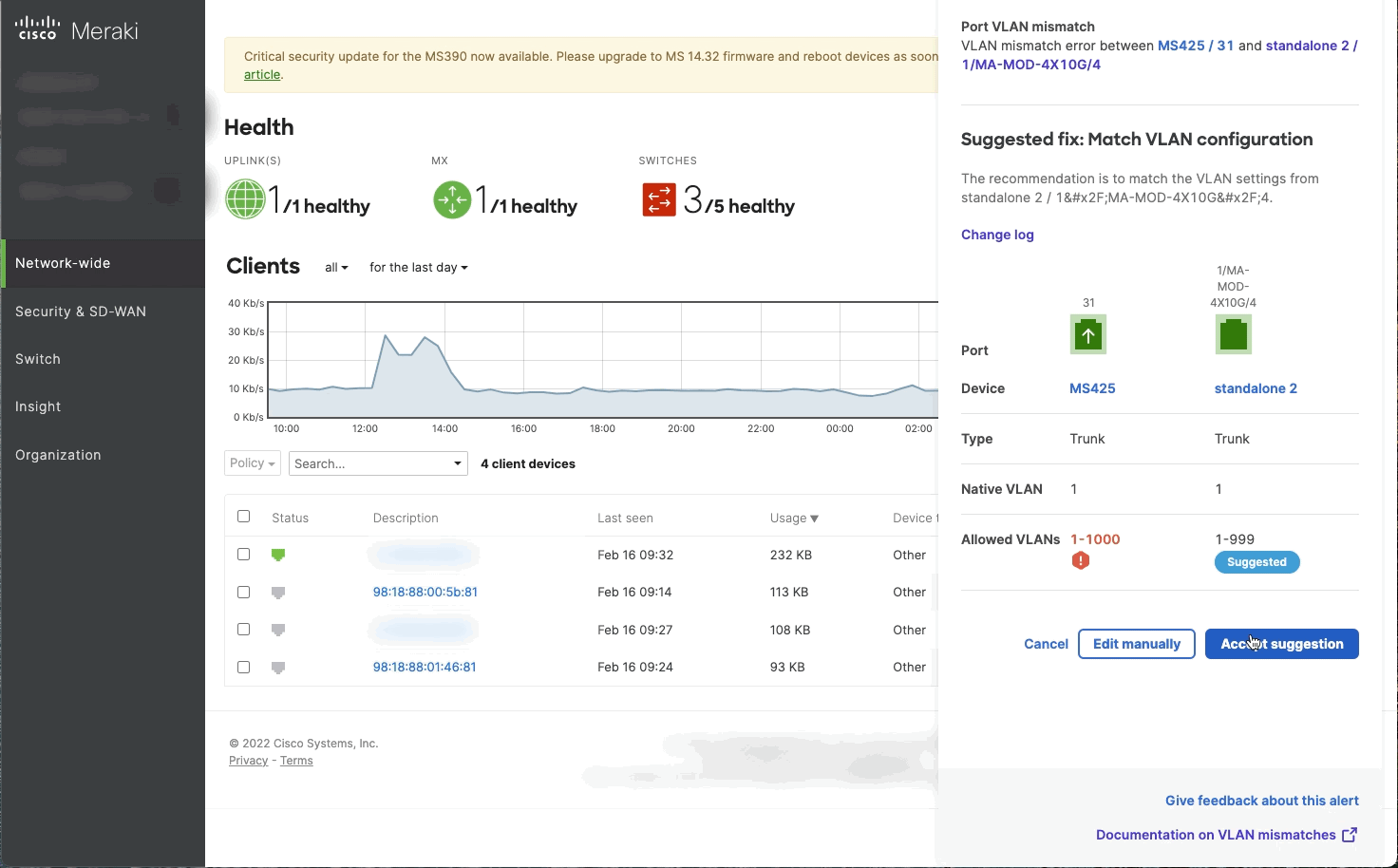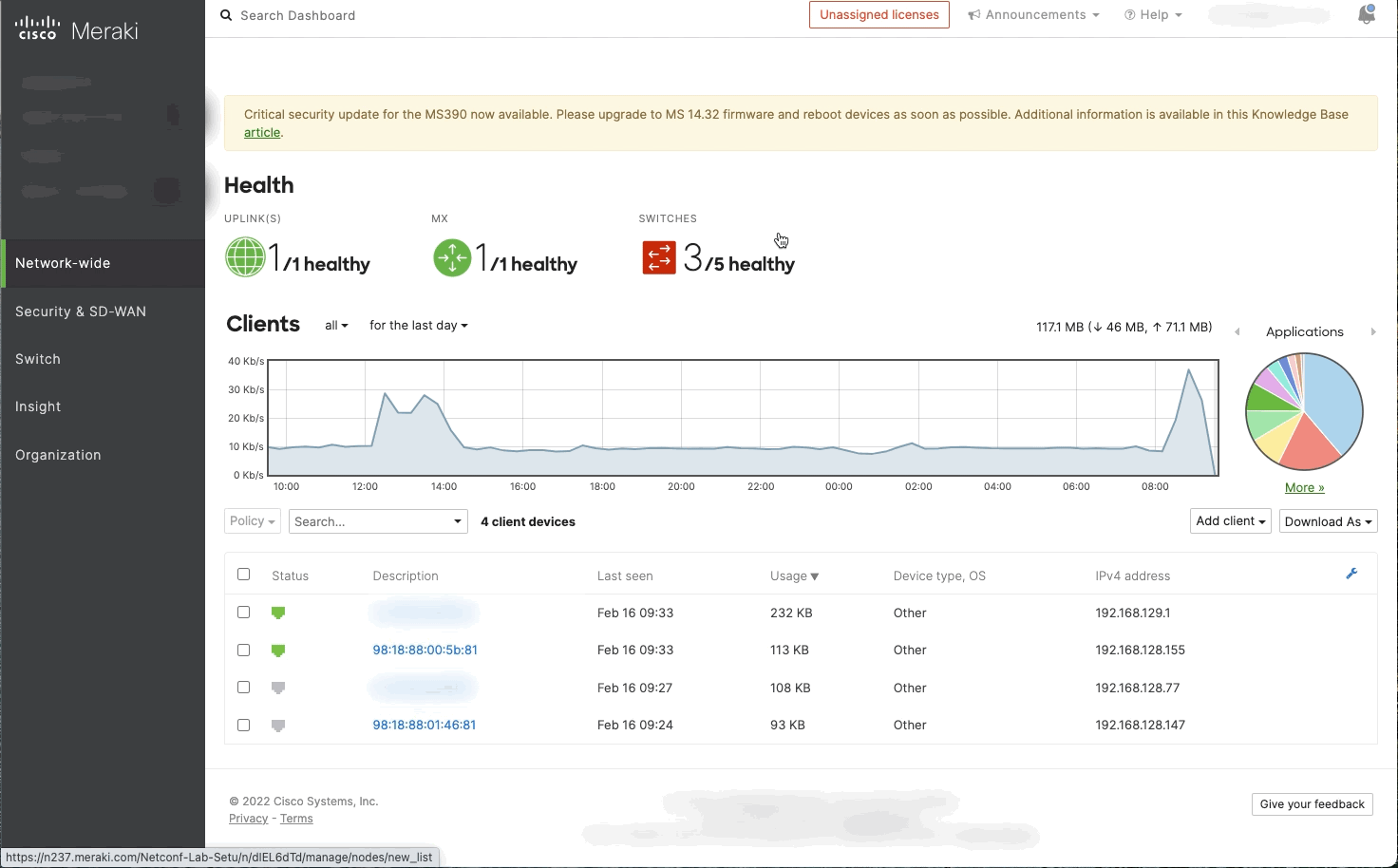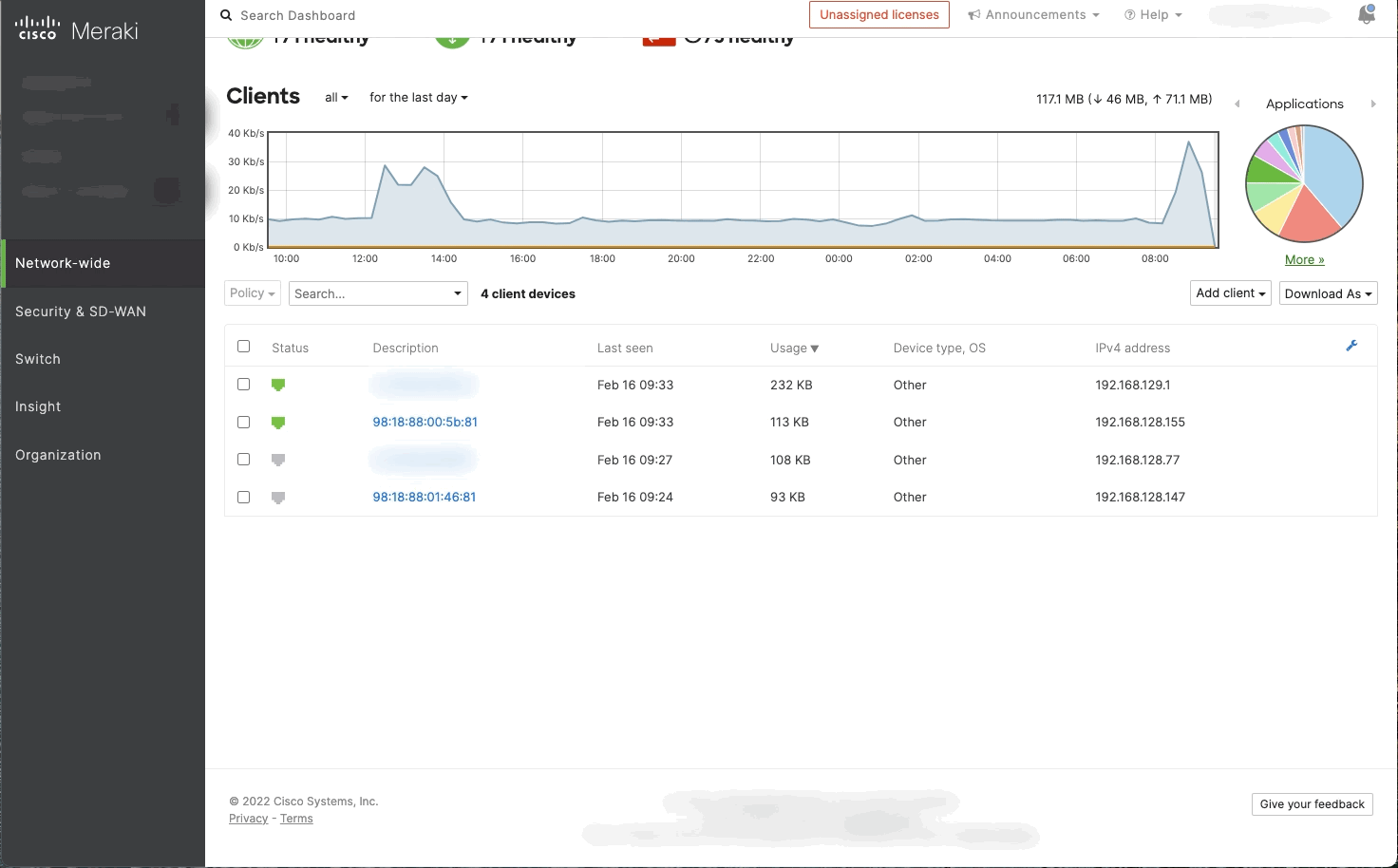
Note: Suggested configurations account for safety and security to make sure the suggested configuration does not cause any disruption for connected devices after applying it. Carefully review the suggestions and make sure it meets your organization’s security requirements.
Dynamic Error Detection
The feature auto detects and warns users if the new configuration is incorrect before saving the new configuration on the widget. The warnings make issue resolution more intuitive.
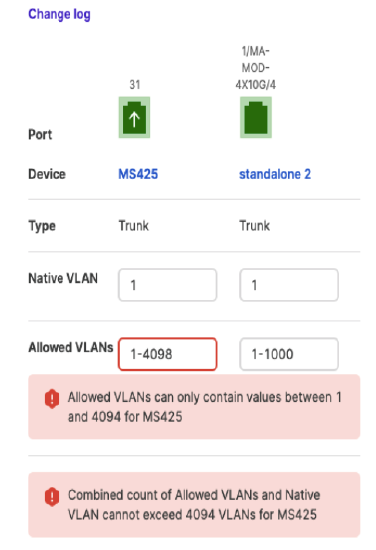
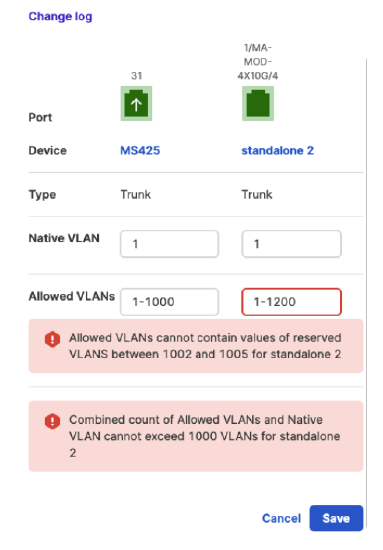
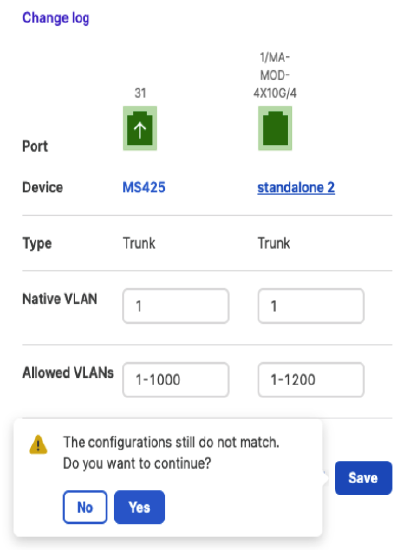
The logic behind VLAN mismatch troubleshooting flow suggested fix:
Outdated/Unreachable Configuration
Triggers
When a configuration change is made in the dashboard, but the Meraki device can't download that change. This alert may also be phrased as "Configuration is out of date".
Troubleshooting Steps
Before contacting support, try these options:
- Give the alert at least 5 minutes to resolve naturally. In this time, check to see if any changes to the network are taking hold. For example, change the password on an SSID and see if a phone can associate with the new password (refer to Access Control).
- Try rebooting the device. In some cases, this can resolve a configuration fetch issue.
- If possible, try a different connection to the internet to rule out an upstream network problem.
If the above fails, open a support case for further assistance.
Regulatory Domain Mismatch
Triggers
Access points have their regulatory body set when they are ordered. As an example, an access point (AP) purchased in the US will have the regulatory domain of the Federal Communications Commission (FCC), dictating which channels can be used on the device.
Troubleshooting Steps
- Be sure the public IP and the order region of the access point match. Check if the management traffic uses a VPN to another country. As a test, avoid using that VPN and see if the problem is resolved.
- If the above options are not possible, contact support to begin an investigation on the next steps.
Country/Region Mismatch
Triggers
Refer to the "Using Geo-IP to Automatically Update Regulatory Domain" section of MR Regulatory Domains
Troubleshooting Steps
Refer to the "Using Geo-IP to Automatically Update Regulatory Domain" section of MR Regulatory Domains
Country Detection Mismatch
Triggers
Refer to the "Using Geo-IP to Automatically Update Regulatory Domain" section of MR Regulatory Domains
Troubleshooting Steps
Refer to the "Using Geo-IP to Automatically Update Regulatory Domain" section of MR Regulatory Domains
Manual Country Mismatch
Triggers
Refer to the "Using Geo-IP to Automatically Update Regulatory Domain" section of MR Regulatory Domains
Troubleshooting Steps
Refer to the "Using Geo-IP to Automatically Update Regulatory Domain" section of MR Regulatory Domains
Switch Received High OSPF Routes
Triggers
The count of dynamically learned routes crosses the limit a switch can support.
Troubleshooting Steps
Make sure the count of routes advertised by the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) neighbors is within the limit of the Cisco Meraki switch. For more information on the number of routes supported by Cisco Meraki switches, refer to the "Supported Models "section of MS Layer 3 Switching and Routing.
Misconfigured Switch
Triggers
A switch is part of a stack configuration, but that stack configuration does not match what is actually physically connected.
Troubleshooting Steps
If the dashboard stack configuration is correct, make sure the physical stack setup matches the dashboard configuration and vice versa. Refer to Managing Stack Members and Physical Switch Stack Configuration Steps.
Unconfigured Switch
Triggers
A switch has been physically made part of a stack, but the stack has not been configured in the dashboard.
Troubleshooting Steps
If the physical stack is correct, make sure the dashboard stack configuration matches the physical setup (see Switch Stacks).
Switch Not Connected to Stack
Triggers
A switch is part of a stack configuration but is not physically part of the stack.
Troubleshooting Steps
Make sure the physical stack matches the dashboard stack configuration (see Switch Stacks).
AFC Missing Height Configuration
Triggers
The height information is missing in the AFC database where an AP is installed. This information is needed as the criteria for higher transmit power limits are heavily dependent on the location of the APs and it will be a requirement for the APs to check in to the database with their location.
Troubleshooting Steps
Complete missing height information.
AFC Request or Response Unsuccessful
Triggers
Attempts to request information from the AFC database were unsuccessful or a response was not received. If an AP is not able to check in with the AFC database, it will default to using low-power mode transmit power thus limiting the coverage from the AP.
Troubleshooting Steps
Check the AP communication to gateway and check other APs to ensure it is not widespread problem.
Unable to Fetch Configuration
Triggers
Refer to Meraki Cloud Communication Issues.
Cannot Connect to the Device via SSH or NETCONF
Triggers
This is a Configuration Source: Device error.
The triggers can be:
- Dashbboard is unable to perform NETCONF operations on the device through the Meraki tunnel, and the Meraki tunnel interfaces are UP
- Dashbboard is unable to access the device via SSH through the Meraki tunnel, and the Meraki tunnel interfaces are UP.
Troubleshooting Steps
Contact Meraki support for further troubleshooting.
Device Firmware Mismatch
Triggers
When software updates (or firmware upgrades) occur, not all of them go smoothly. If a device fails to upgrade, the dashboard will notice the difference in the version set for the device versus the version that is actually installed and running.
Troubleshooting Steps
- Wait 30 minutes. Sometimes a firmware download can take a while on a slow connection, and if it fails when the speeds are low it can take even longer.
- Reboot the hardware. This will reset any wait period before trying the software update again.
- If waiting and rebooting the hardware do not resolve the error message, contact support in the app by opening a case.
Host Overflow
Triggers
If the current number of routed clients exceeds the maximum routable client limit for the specific switch model.
Troubleshooting Steps
Refer to MS Switch FAQ for details on the maximum routable clients limit per switch model.
Line VTY Configuration Issue
Triggers
This is a Configuration Source: Device error.
The device must have 4 unused consecutive VTY slots. These VTY lines will be provisioned and secured for only the dashboard to access the device on these lines.
Troubleshooting Steps
Refer to Troubleshooting Dashboard Connectivity to Catalyst 9800 Wireless Controllers to learn how to remediate this error.
SISF Based Device Tracking Not Enabled
Triggers
SISF-based device tracking is disabled by default.
Troubleshooting Steps
You can enable it by defining a device tracking policy and attaching the policy to a specific target. Refer to Configure SISF-Based Device Tracking.
Safe Mode Active
Triggers
When the “Enable Safe Mode” option is enabled on the local status page.
Troubleshooting Steps
This feature is used to help enable troubleshooting the device and should be turned off when finished.
Missing Config Options
Triggers
The system is currently blocking serving the bad config to this device. Missing required fields for a proper config.
Troubleshooting Steps
Check and validate all required port config fields.
Device is Running an Unsupported Firmware Version
Triggers
Device is running a firmware version that is no longer supported.
Troubleshooting Steps
Update firmware to a supported level.
Device's Gateway Mismatch
Triggers
When a device’s gateway does not match the majority of other devices on the network.
Troubleshooting Steps
Check and validate gateways settings.
Radar Detected
Triggers
This is a DFS event and it has detected RADAR in the environment.
Troubleshooting Steps
DFS should hop off the channel and select a non radar sharing channel. You can also manually exclude those channels identified so as not to have an issue in the future.
Unknown Config Options
Triggers
These errors will appear as an alert on the device (just like invalid config).
Troubleshooting Steps
The details of the error will indicate which fields were not in the config inventory.
VLAN Prefix Shortage Occurred
Triggers
When Prefix Starvation occurs, which is when the MX detects it does not have enough prefixes from a given WAN or manual configuration to assign a /64 prefix to each IPv6 enabled VLAN.
Troubleshooting Steps
Check and validate IPv6 settings.
MX is Over Recommended Tunnels
Triggers
More tunnels have been defined than is recommended for the model.
Apple MDM APNS Certificate May Have Expired
Triggers
Apple MDM certificate needs attention.
Troubleshooting Steps
- Download Meraki CSR file from Organization > MDM page.
- Log in to Apple's Push Notification Portal with the same Apple ID used to create the current push certificate.
Note: If the Apple ID is not known, review "I Forgot Which Apple ID was Originally Used." Not using the original Apple ID (and therefore the original Apple Push certificate) would result in losing management of the previously enrolled devices. - Find the expiring certificate, and select Renew (do not revoke expiring certificate, nor create a new certificate).
- Upload CSR downloaded as per Step 1.
- Download renewed certificate from Apple, and upload into Dashboard.
- Enter/Confirm Apple ID used to log-in to Apple's push notification portal (highly recommended).
Apple MDM APNS Certificate Has Expired
Triggers
Apple MDM certificate needs attention.
Troubleshooting Steps
- Download Meraki CSR file from Organization > MDM page.
- Log in to Apple's Push Notification Portal with the same Apple ID used to create the current push certificate.
Note: If the Apple ID is not known, review "I Forgot Which Apple ID was Originally Used." Not using the original Apple ID (and therefore the original Apple Push certificate) would result in losing management of the previously enrolled devices. - Find the expiring certificate, and select Renew (do not revoke expiring certificate, nor create a new certificate).
- Upload CSR downloaded as per Step 1.
- Download renewed certificate from Apple, and upload into Dashboard.
- Enter/Confirm Apple ID used to log-in to Apple's push notification portal (highly recommended).
Apple MDM APNS Certificate Will Expire Soon
Triggers
Apple MDM certificate needs attention.
Troubleshooting Steps
- Download Meraki CSR file from Organization > MDM page.
- Log in to Apple's Push Notification Portal with the same Apple ID used to create the current push certificate.
Note: If the Apple ID is not known, review "I Forgot Which Apple ID was Originally Used." Not using the original Apple ID (and therefore the original Apple Push certificate) would result in losing management of the previously enrolled devices. - Find the expiring certificate, and select Renew (do not revoke expiring certificate, nor create a new certificate).
- Upload CSR downloaded as per Step 1.
- Download renewed certificate from Apple, and upload into Dashboard.
- Enter/Confirm Apple ID used to log-in to Apple's push notification portal (highly recommended).
No IMEI Detected
Triggers
During enrollments or re-enrollments, Systems Manager uses a variety of uniquely identifying values from clients to attempt to determine a device's hardware identity for pairing against it's Systems Manager identity. On mobile devices, this is usually the IMEI (International Mobile station Equipment Identity). This alert triggers when a device’s IMEI cannot be detected.
Troubleshooting Steps
It's recommended to contact the manufacturer or reseller of the device, as a missing IMEI will impact the device's ability to connect to the cellular grid.
Duplicate IMEI Detected
Triggers
If Dashboard detects a collision of these values for enrolled or enrolling devices, an alert may be displayed with a link to filter the clients list down to those devices which are suspected. These values are important for both SM and other software; on mobile devices, these values can affect the device's ability to connect to the cellular grid.
No Device Identifier Detected
Triggers
During enrollments or re-enrollments, Systems Manager uses a variety of uniquely identifying values from clients to attempt to determine a device's hardware identity for pairing against it's Systems Manager identity. On desktop machines, this is usually the BIOS UUID (Universally Unique Identifier). On mobile devices, this is usually the IMEI (International Mobile station Equipment Identity). This alert triggers when a device’s UUID or IMEI cannot be detected.
Troubleshooting Steps
It's recommended to contact the manufacturer or reseller of the device, as a missing IMEI or UUID will impact the device's ability to connect to the cellular grid.
Duplicate Device Identifier Detected
Triggers
If Dashboard detects a collision of these values for enrolled or enrolling devices, an alert may be displayed with a link to filter the clients list down to those devices which are suspected. These values are important for both SM and other software; on mobile devices, these values can affect the device's ability to connect to the cellular grid.
Endpoint Management - Enrollment Auth Disabled
Triggers
Enrollment authentication is disabled.
Bad Enable Password
Triggers
This is a Configuration Source: Device error.
If dashboard is unable to access the device's cloud console during the initial onboarding process, this may be due to the username, password or enable password provided during onboarding cannot authenticate to the device.
Troubleshooting Steps
Refer to Troubleshooting Dashboard Connectivity to Catalyst 9800 Wireless Controllers to learn how to remediate this error.
No 4 Consecutive VTY on the Device
Triggers
This is a Configuration Source: Device error.
The device must have 4 unused consecutive VTY slots. These VTY lines will be provisioned and secured for only the dashboard to access the device on these lines.
Troubleshooting Steps
Refer to Troubleshooting Dashboard Connectivity to Catalyst 9800 Wireless Controllers to learn how to remediate this error.
Configuration Error
Triggers
This is a Configuration Source: Device error.
The configuration for the device is out of date.
Troubleshooting Steps
Contact Meraki support for further troubleshooting.
Cloud is Not Able to Login to Device via Cloud Console
Triggers
This is a Configuration Source: Device error.
If dashboard is unable to access the device's cloud console during the initial onboarding process, this may be due to the username, password or enable password provided during onboarding cannot authenticate to the device.
Troubleshooting Steps
Refer to Troubleshooting Dashboard Connectivity to Catalyst 9800 Wireless Controllers to learn how to remediate this error.
Wrong Console Credentials
Triggers
This is a Configuration Source: Device error.
If dashboard is unable to access the device's cloud console during the initial onboarding process, this may be due to the username, password or enable password provided during onboarding cannot authenticate to the device.
Troubleshooting Steps
Refer to Troubleshooting Dashboard Connectivity to Catalyst 9800 Wireless Controllers to learn how to remediate this error.
SSH Error Authentication
Triggers
This is a Configuration Source: Device error.
Dashboard is unable authenticate SSH with the device using the dashboard provisioned device local meraki-user account.
Troubleshooting Steps
Refer to Troubleshooting Dashboard Connectivity to Catalyst 9800 Wireless Controllers to learn how to remediate this error.
Console Error Connection
Triggers
This is a Configuration Source: Device error.
Dashboard is unable to connect to the device's cloud console through the Meraki tunnel, and the Meraki tunnel interfaces are UP.
Troubleshooting Steps
Contact Meraki support for further troubleshooting.
SSH Error Connection
Triggers
This is a Configuration Source: Device error.
Dashboard is unable to access the device via SSH through the Meraki tunnel, and the Meraki tunnel interfaces are UP.
Troubleshooting Steps
Contact Meraki support for further troubleshooting.
NETCONF Error Connection
Triggers
This is a Configuration Source: Device error.
Dashboard is unable to perform NETCONF operations on the device through the Meraki tunnel, and the Meraki tunnel interfaces are UP.
Troubleshooting Steps
Contact Meraki support for further troubleshooting.
Console Error Authorization
Triggers
This is a Configuration Source: Device error.
To complete the onboarding configuration with the cloud console, the username provided during onboarding must have authorization for all the required onboarding configuration commands.
Troubleshooting Steps
Refer to Troubleshooting Dashboard Connectivity to Catalyst 9800 Wireless Controllers to learn how to remediate this error.
SSH Error Authorization
Triggers
This is a Configuration Source: Device error.
Dashboard is unable authorize commands via SSH with the device using the dashboard provisioned device local meraki-user account. AAA settings on the device must permit the meraki-user account to authorize the commands used for onboarding.
Troubleshooting Steps
Refer to Troubleshooting Dashboard Connectivity to Catalyst 9800 Wireless Controllers to learn how to remediate this error.
AAA New-Model Not Enabled
Triggers
This is a Configuration Source: Device error.
The device must use AAA new-model for device access control. This mode allows the dashboard to securely access the device.
Troubleshooting Steps
Refer to Troubleshooting Dashboard Connectivity to Catalyst 9800 Wireless Controllers to learn how to remediate this error.
SSH Encryption Algorithms Not Supported
Triggers
This is a Configuration Source: Device error.
The following SSH encryption algorithms are supported by the dashboard:
- aes128-gcm@openssh.com
- aes256-gcm@openssh.com
- aes128-ctr
- aes192-ctr
- aes256-ctr
Troubleshooting Steps
Refer to Troubleshooting Dashboard Connectivity to Catalyst 9800 Wireless Controllers to learn how to remediate this error.
IPv4 ACL Conflicts
Triggers
This is a Configuration Source: Device error.
Dashboard utilizes the HTTP secure server interface to read telemetry data from device. If your HTTP services are restricted by an IPv4 access control list, you must update the ACL to permit access.
Troubleshooting Steps
Refer to Troubleshooting Dashboard Connectivity to Catalyst 9800 Wireless Controllers to learn how to remediate this error.
IPv6 ACL Conflicts in HTTP Server
Triggers
This is a Configuration Source: Device error.
Dashboard utilizes the HTTP secure server interface to read telemetry data from device. If your HTTP services are restricted by an IPv6 access control list, you must update the ACL to permit access from the Meraki tunnel interface subnet FD0A:9B09:1F7:1::/64.
Troubleshooting Steps
Refer to Troubleshooting Dashboard Connectivity to Catalyst 9800 Wireless Controllers to learn how to remediate this error.
SSH Port or Rotary Conflicts with Cloud
Triggers
This is a Configuration Source: Device error.
Dashboard must provision the following command on the device in order to set the 4 configured VTY lines to be access able on port 2222.
Troubleshooting Steps
Refer to Troubleshooting Dashboard Connectivity to Catalyst 9800 Wireless Controllers to learn how to remediate this error.
AAA Authorization Conflicts in NETCONF
Triggers
This is a Configuration Source: Device error.
During onboarding, dashboard will check the device AAA default authorization method list begins with 'local.'
Troubleshooting Steps
Refer to Troubleshooting Dashboard Connectivity to Catalyst 9800 Wireless Controllers to learn how to remediate this error.
User 'meraki-tdluser' Exists on Device
Triggers
This is a Configuration Source: Device error.
If you have previously added and then removed your device from dashboard and the dashboard provisioned usernames were not removed from the configuration, dashboard will fail to configure these usernames if they already exist in the configuration.
Troubleshooting Steps
Refer to Troubleshooting Dashboard Connectivity to Catalyst 9800 Wireless Controllers to learn how to remediate this error.
User 'meraki-user' Exists on Device
Triggers
This is a Configuration Source: Device error.
If you have previously added and then removed your device from dashboard and the dashboard provisioned usernames were not removed from the configuration, dashboard will fail to configure these usernames if they already exist in the configuration.
Troubleshooting Steps
Refer to Troubleshooting Dashboard Connectivity to Catalyst 9800 Wireless Controllers to learn how to remediate this error.
NETCONF Error Authorization
Triggers
This is a Configuration Source: Device error.
Dashboard is unable to authorize NETCONF with the device using the dashboard provisioned device local meraki-user account. AAA settings on the device must permit the meraki-user account to authorize. Additional information may be available in the device log (show log). Verify there are no NETCONF aaa authorization conflicts.
Troubleshooting Steps
During onboarding, the dashboard will check the wireless controller aaa default authorization method list begins with 'local':
aaa authorization exec default local group tacacs+ group radius
lf local is NOT the first method in the list, the meraki-user user in the local username store will not be able to use NETCONF to do the required Cloud Monitoring configuration provisioning.
Option 1:
Update the default authorization exec method list to begin with local before any other server group.
Option 2:
If you can not modify the default method list you can configure the YANG interface method list to use the MERAKI method list.
Starting with IOS XE 17.9, YANG interfaces can now enable multiple authentication or authorization options with named method-lists and do not have to utilize the global default method list for AAA authentication to programmable interfaces in IOS XE such as NETCONF and RESTCONF. https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/doc...ed-method-list.
yang-interfaces aaa authorization method-list MERAKI
Contact Meraki support for further troubleshooting if needed
NETCONF Error Authentication
Triggers
This is a Configuration Source: Device error.
Dashboard is unable to authorize NETCONF with the device using the dashboard provisioned device local meraki-user account. AAA settings on the device must permit the meraki-user account to authorize. Additional information may be available in the device log (show log). Verify there are no NETCONF aaa authorization conflicts.
Troubleshooting Steps
During onboarding, the dashboard will check the wireless controller aaa default authorization method list begins with 'local':
aaa authorization exec default local group tacacs+ group radius
lf local is NOT the first method in the list, the meraki-user user in the local username store will not be able to use NETCONF to do the required Cloud Monitoring configuration provisioning.
Option 1:
Update the default authorization exec method list to begin with local before any other server group.
Option 2:
If you can not modify the default method list you can configure the YANG interface method list to use the MERAKI method list.
Starting with IOS XE 17.9, YANG interfaces can now enable multiple authentication or authorization options with named method-lists and do not have to utilize the global default method list for AAA authentication to programmable interfaces in IOS XE such as NETCONF and RESTCONF. https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/doc...ed-method-list.
yang-interfaces aaa authorization method-list MERAKI
Contact Meraki support for further troubleshooting if needed
Organization Self Signed SCEP Certificate Has Expired
Triggers
The certificate is no longer valid.
Troubleshooting Steps
To renew your Self Signed SCEP CA Certificate, you will simply need to download the CSR file available on the dashboard under Organization > MDM > SCEP CA Certificate Configuration. Once downloaded, you can sign the certificate with your Certificate Authority and re-upload it to the Dashboard. You will see an alert on Dashboard to renew your custom Third Party Signed SCEP cert if it is set to expire soon.
Refer to MDM Settings.
Organization Self Signed SCEP Certificate Will Expire Soon
Triggers
The certificate will expire soon.
Troubleshooting Steps
To renew your Self Signed SCEP CA Certificate, you will simply need to download the CSR file available on the dashboard under Organization > MDM > SCEP CA Certificate Configuration. Once downloaded, you can sign the certificate with your Certificate Authority and re-upload it to the Dashboard.
Refer to MDM Settings.
IOS XE configuration out of sync
Triggers
One or more dashboard required IOS XE configurations are missing. Dashboard will provision these configurations when IOS XE hybrid mode switch is added to a network. These configurations are required to allow the dashboard to enable Cloud-Managed Catalyst hybrid mode switches and will need to be re-applied for dashboard management.
Troubleshooting Steps
Update IOS XE with the following configurations based on the missing configuration alert.
- Access Control Lists (ACLs) for Meraki Cloud Access
ip access-list standard MERAKI_MGMT_IP_IN
20 deny any
ip access-list extended MERAKI_MGMT_IP_OUT
20 deny tcp any any
ipv6 access-list MERAKI_MGMT_IPV6_IN
sequence 10 permit tcp FD0A:9B09:1F7:1::/64 FD0A:9B09:1F7:1::/64 eq 2222
sequence 20 deny tcp any any
ipv6 access-list MERAKI_MGMT_IPV6_OUT
sequence 20 deny tcp any any
- Configuration change notification and logging for Cloud CLI
archive
log config
logging enable
notify syslog contenttype xml
- Device tracking policy on ports for client tracking
device-tracking policy MERAKI_ACCESS_TRACK
limit address-count 1000
security-level glean
tracking enable
device-tracking policy MERAKI_NO_TRACK
trusted-port
security-level glean
no protocol ndp
no protocol dhcp6
no protocol arp
no protocol dhcp4
device-tracking policy MERAKI_TRUNK_TRACK
limit address-count 32000
security-level glean
- EEM policy for Cloud CLI
event manager applet MERAKI_SHOW_RUN_EXEC
event cli pattern "show running-config" sync yes
action 1.0 if $_cli_username eq meraki-cli-ro
action 1.1 cli command enable
action 1.2 cli command $_cli_msg
action 1.3 puts $_cli_result
action 1.4 set _exit_status 0
action 2.0 else
action 2.1 set _exit_status 1
action 3.0 end
- ip flow exporter for client tracking
flow file-export default
file max-create-interval 5
file max-count 2
flow exporter MERAKI_TA1
destination local file-export default
export-protocol ipfix
option interface-table timeout 300
- ip flow exporter for traffic analysis
flow file-export default
file max-create-interval 5
file max-count 2
flow exporter MERAKI_TA2
destination local file-export default
export-protocol ipfix
option interface-table timeout 300
- ip flow monitor for client tracking
flow monitor MERAKI_TA1_V4_IN
exporter MERAKI_TA1
cache timeout inactive 300
cache timeout active 300
record MERAKI_TA1_V4_IN
flow monitor MERAKI_TA1_V4_OUT
exporter MERAKI_TA1
cache timeout inactive 300
cache timeout active 300
record MERAKI_TA1_V4_OUT
- ip flow monitor for traffic analysis
flow monitor MERAKI_TA2_IPV4
exporter MERAKI_TA2
cache timeout inactive 300
cache timeout active 300
cache entries 65536
record MERAKI_TA2_HTTP_SSL_IPV4
- ip flow record for client tracking
flow record MERAKI_TA1_V4_IN
description meraki_ta1_ingress
match application name
match interface input
match ipv4 source address
collect counter bytes long
collect counter packets long
collect datalink dot1q vlan input
collect datalink mac source address input
collect flow direction
flow record MERAKI_TA1_V4_OUT
description meraki_ta1_egress
match application name
match interface output
match ipv4 destination address
collect counter bytes long
collect counter packets long
collect datalink dot1q vlan output
collect datalink mac destination address output
collect flow direction
- ip flow record for traffic analysis
flow record MERAKI_TA2_HTTP_SSL_IPV4
match application name
match connection client ipv4 address
match connection server ipv4 address
match connection server transport port
match flow observation point
match ipv4 protocol
match ipv4 version
collect connection client counter bytes network long
collect connection client counter packets long
collect connection initiator
collect connection new-connections
collect connection server counter bytes network long
collect connection server counter packets long
collect flow direction
collect interface input
collect interface output
collect timestamp absolute first
collect timestamp absolute last
- HTTP server configuration
ip http secure-server
! Only apply the config when there is not any authentication config for http server
ip http authentication local
! Only apply the config when there is HTTP ACL rule for IPV4(The IPV4 rule blocks IPV6 traffic. It is a device bug.)
ip http access-class ipv6 MERAKI_MGMT_IPV6_IN
- device tracking policy on interfaces [xxx, xxx]
interface xxx
device-tracking attach-policy MERAKI_ACCESS_TRACK
- ip flow monitor on interfaces [xxx, xxx]
interface xxx
ip flow monitor MERAKI_TA1_V4_IN input
ip flow monitor MERAKI_TA1_V4_OUT input
- default IPv6 route with distance 2 for Meraki tunnel
ipv6 unicast-routing
- Global LLDP configuration for neighbor information
lldp run
- Telemetry subscription and receiver configurations for event logs
telemetry ietf subscription 10000
encoding encode-tdl
filter tdl-uri /services;serviceName=stkm_oper/stack_info
receiver-type pullmode
source-vrf Mgmt-vrf
stream native
update-policy periodic 6000
receiver name meraki_stack_info
telemetry ietf subscription 10002
encoding encode-tdl
filter tdl-uri /services;serviceName=iosevent/syslog_msg
receiver-type pullmode
stream native
update-policy on-change
receiver name meraki_syslog_msg
telemetry receiver pullmode meraki_stack_info
size 1000000
telemetry receiver pullmode meraki_syslog_msg
size 50000000
- Local users (meraki-cli-ro or merakicli-rw) for Cloud CLI
username meraki-cli-ro view MERAKI-MONITOR secret 9 xxx
username meraki-cli-rw privilege 15 view MERAKI-CONFIG secret 9 xxx
ip ssh pubkey-chain
username meraki-cli-ro
key-hash {KEY_HASH}
username meraki-cli-rw
key-hash {KEY_HASH}
Contact Meraki support if the IP SSH key configuration needs to be configured on your IOS XE device.
parser view MERAKI-CONFIG inclusive
secret 9 xxx
commands configure exclude all parser
commands configure exclude all archive
commands configure exclude all ntp
commands configure exclude all timezone
commands configure exclude all clock
commands exec exclude all clock
commands exec exclude all show memory
commands exec exclude all show tech-support
parser view MERAKI-MONITOR
secret 9 xxx
commands exec include traceroute
commands exec include ping
commands exec include terminal width
commands exec include terminal length
commands exec include terminal
commands exec exclude all show memory
commands exec exclude all show tech-support
commands exec include all show
- Syslog SNMP traps for event logs
logging snmp-trap 0 4
logging history informational
snmp-server enable traps syslog
- SNMP traps for config change notification
Contact Meraki support for this configuration to be re-applied.
- Log level configuration for syslog-events
logging syslog-events informational
Configuration is out of date
Triggers
Device's configuration has not yet synchronized with the changes made in the Meraki dashboard. This can occur due to delays in applying updates, network connectivity issues, or high load on the Meraki shard.
Troubleshooting Steps
-
Check Network Connectivity Ensure that the device has stable internet access. Poor connectivity can delay configuration updates.
-
Monitor Bandwidth Utilization High bandwidth usage during configuration changes can slow down synchronization. Check your network's utilization and reduce load if necessary.
-
Wait for Synchronization In most cases, changes should apply within 1-5 minutes. However, occasional delays of up to 10-20 minutes may occur due to shard load or other factors.
-
Reboot the Device If a device remains out of sync for an extended period, rebooting it may force it to fetch the latest configuration from the dashboard.
-
Contact Support If delays persist beyond normal expectations and a reboot does not resolve it, reach out to support. They can check for shard-related issues or maintenance tasks that might be causing delays.
Meraki Shelluser Conflict
Triggers
One or more of the required IOS XE internal usernames already exists in the IOS XE configuration.
Troubleshooting Steps
Username meraki-cli-ro or meraki-cli-rw already exists on the device. Please remove it manually from the IOS XE running configuration.
IPv6 ACL conflicts in NETCONF Server
Triggers
Dashboard utilizes the NETCONF to provision wireless controllers. If your NETCONF-YANG services are restricted by an IPv6 access control list, you must update the ACL to permit access from the Meraki Tunnel interface subnet FD0A:9B09:1F7:1::/64
Troubleshooting Steps
Refer to Troubleshooting Dashboard Connectivity to Catalyst 9800 Wireless Controllers to learn how to remediate this error.
DNA License Required
Triggers
Typically occurs when a Cisco device or feature requires a valid Cisco DNA license to operate, but the license is either missing, expired, or not properly applied. This error can arise due to several causes:
- The device does not have the appropriate Cisco DNA subscription license installed or activated. Cisco DNA licenses are mandatory for certain platforms and features, such as Catalyst 8300/8200 series edge platforms, which require Cisco DNA subscription licenses to enable traditional and advanced IOS-XE features.
-
License compliance issues can occur if the device is not properly synchronized with Cisco Smart Software Management (CSSM). Devices in highly secured networks with limited internet access may fail to sync, causing license errors. Specific License Reservation (SLR) or Permanent License Reservation (PLR) can be used in such cases to reserve licenses without continuous CSSM connectivity.
-
Communication failures between the device and Cisco Smart Licensing servers (CSSM or CSLU) can cause authorization failures. This may be due to network reachability issues, DNS resolution problems, or incorrect license server URLs.
-
System clock inaccuracies or lack of synchronization with NTP servers can cause signature or timestamp mismatches, leading to license authorization failures.
Troubleshooting Steps
-
Verify License Type and Validity
- Confirm you have the correct Cisco DNA license type (e.g., DNA Advantage, DNA Essentials, or DNA Premier) for your device and use case.
- Check if the license is active and not expired, especially for subscription-based DNA-stack add-on licenses which have term limits (3, 5, or 7 years).
- Ensure that the license tier supports your device throughput and features; for example, Tier 3 or higher tiers are not supported with Network Essentials and DNA Essentials licenses
-
Set Up and Register Licenses in Cisco DNA Center
- Access Cisco DNA Center with appropriate admin permissions.
- Configure Cisco Smart Account credentials and link your Smart Account(s) in DNA Center under System > Settings.
- Register devices and assign licenses via the License Manager tool in Cisco DNA Center.
- For devices running IOS XE 17.3.2 or later, use the Smart License Compliance Reporting workflow for license registration
-
Check Device Connectivity and Communication
- Ensure devices can reach Cisco Smart Software Manager (CSSM) portals (tools.cisco.com) for license validation.
- Verify network connectivity and firewall rules allow required ports and URLs for license communication.
- Confirm devices are present and reachable in Cisco DNA Center inventory with assigned sites.
- Check that the system clock is accurate and synchronized with an NTP server
-
Troubleshoot License Errors and Status
- Use Cisco DNA Center License Manager to view license status and compliance reports.
- For migrated devices (e.g., from Meraki to DNA management mode), ensure proper license availability and controller connectivity; devices may enter a "looking for controller" state if licenses or controllers are missing
SSH compression algorithms not supported
Triggers
Occurs when your SSH client and the SSH server you're trying to connect to cannot agree on a common compression algorithm to use for the session. SSH connections involve a negotiation process where both sides propose a list of supported algorithms (including key exchange, encryption, message authentication code, and compression). If no mutually supported compression algorithm is found, the connection fails.
Troubleshooting Steps
- Enable Compression on the Client Side
-
Check and Configure Compression on the Server Side
-
Update SSH Client and Server Software. Outdated SSH software is a common cause of algorithm negotiation failures, as newer, more secure algorithms are introduced and older, less secure ones are deprecated. Updating your SSH client and server to the latest stable versions is often the most robust and recommended long-term solution.
-
Use Verbose Mode for Debugging. To get more detailed information about the algorithm negotiation process and pinpoint the exact mismatch, use the verbose option (-v) with your ssh command: ssh -v username@your_server_ip. You can add more v's (e.g., -vvv) for even more detailed output.
SSH host key algorithms not supported
Triggers
Indicates that your SSH client and the SSH server you are trying to connect to cannot agree on a mutually supported cryptographic algorithm for authenticating the server's identity. This often occurs when one side (usually the client) has been updated to deprecate older, less secure algorithms, while the other side (often an older server or device) still relies on them.
Troubleshooting Steps
- Identify Supported Algorithms
-
Modify SSH Client Configuration. If the server supports an algorithm that your client has deprecated (e.g., ssh-rsa), you can temporarily enable it for a specific connection or permanently configure your client. You can specify the desired host key algorithm directly in the ssh command using the -o option. For example, to enable ssh-rsa: ssh -oHostKeyAlgorithms=+ssh-rsa user@your_server_ip
-
For a more permanent solution, you can add an entry to your SSH client configuration file, usually ~/.ssh/config. This allows you to apply the settings only to specific hosts.
-
Security Considerations
-
Prioritize Updates: The best long-term solution is to update both your SSH client and server software to their latest versions. This ensures support for the most secure and efficient algorithms.
-
Avoid Weak Algorithms: Enabling older algorithms like ssh-rsa (which uses SHA-1 for signing) should be a last resort and only for connecting to legacy systems that cannot be updated. SHA-1 is cryptographically weak and vulnerable to collision attacks.
-
Scoped Configuration: If you enable weaker algorithms, always restrict them to specific Host entries in your client's ~/.ssh/config or Match blocks in the server's sshd_config to minimize security exposure
-
SSH KEX algorithms not supported
Triggers
Occurs when your SSH client and the SSH server cannot agree on a common key exchange (KEX) algorithm to establish a secure connection. This often happens due to outdated SSH client or server software, or strict security configurations that disable older, less secure algorithms.
Troubleshooting Steps
- Identify Supported KEX Algorithms. The first step is to determine which KEX algorithms are supported by both your SSH client and the SSH server you are trying to connect to.
-
The most recommended solution is to update both your SSH client and the SSH server to their latest versions. This ensures you have access to the most secure and widely supported algorithms.
-
If updating is not immediately possible, or if specific security configurations are in place, you might need to manually enable or prioritize compatible algorithms.
-
You can specify a KEX algorithm (client side) to use for a single SSH connection using the -o KexAlgorithms=<algorithm> option. Example: ssh -o KexAlgorithms=<algorithm name> user@your_server_ip
SSH MAC algorithms not supported
Triggers
Indicates that your SSH client and the SSH server you are trying to connect to do not have any common Message Authentication Code (MAC) algorithms enabled. MAC algorithms are crucial for ensuring the integrity and authenticity of data exchanged during an SSH session, preventing tampering and ensuring the data has not been altered.
Troubleshooting Steps
- Identify Supported MAC Algorithms. You can list the MAC algorithms supported by your SSH client using the ssh -Q mac command.
-
Understand MAC Algorithm Security
-
Recommended/Secure MAC Algorithms:
- hmac-sha2-256
- hmac-sha2-512
- hmac-sha2-256-etm@openssh.com (Encrypt-then-MAC)
- hmac-sha2-512-etm@openssh.com (Encrypt-then-MAC)
- umac-128-etm@openssh.com
-
Weak/Deprecated MAC Algorithms (avoid if possible):
- hmac-md5
- hmac-md5-96
- hmac-sha1 (while still widely supported, SHA-2 variants are preferred)
- hmac-sha1-96
-
- Once you've identified a common, secure MAC algorithm, you can configure either your client to use it.
- Temporary (for a single connection): You can specify the MAC algorithm directly in the ssh command using the -m or -oMACs option. Example: ssh -oMACs=hmac-sha2-512,hmac-sha2-256 user@your_server_ip
- Permanent (for your user): Edit your SSH client configuration file, typically ~/.ssh/config. Add or modify the MACs directive for the specific host or globally.
SSH public key algorithms not supported
Triggers
Ttypically indicates a mismatch or incompatibility between the SSH client and the SSH server regarding the cryptographic algorithms they are configured to use for key exchange, host key authentication, ciphers, or message authentication codes (MACs).
Troubleshooting Steps
-
Verify SSH Public Key Algorithms Configuration. Ensure that the SSH server is configured to support the required public key algorithms. On Cisco devices, you can check and configure the SSH server settings using the sshconfig command.
-
Verify if SSH client keys are present using the command show ssh client key. If keys are missing, generate them and push the public key to the remote server using the appropriate CLI commands such as push ssh-key <hostname> user <username>. Also, confirm that the remote server supports public key authentication
-
Update RSA Key Size if Using Cisco IOS XE. If you are using Cisco IOS XE Release 17.11.1 or later, RSA keys smaller than 2048 bits are not supported by default. Check the RSA key modulus size with show ip ssh | include Modulus. If the key size is less than 2048 bits, generate a new RSA key pair with at least 2048 bits using:
-
crypto key generate rsa modulus 2048 label strong-ssh-key
ip ssh rsa keypair-name strong-ssh-key
-
-
Configure SSH Algorithms Explicitly. On Cisco IOS devices, you can explicitly configure the SSH server and client algorithms for encryption, MAC, host key, and key exchange to ensure compatibility
-
Consider SSH Client Compatibility. Some newer SSH clients may consider certain algorithms like ssh-rsa unsafe and block connections. Ensure that the client and server support mutually compatible algorithms.
WLC Add Standby
Triggers
Wireless controller standby was not added to the network. There was an error adding the standby chassis to the network
Troubleshooting Steps
The device already exists in the Meraki dashboard. To fix this issue, remove the standby from the network it is currently in. Once deleted, the standby will automatically be added to the intended network. The Meraki dashboard will continue to retry adding these devices in the background. If the standby WLC continues to fail to add to the network contact Meraki support.
WLC AP Onboard
Triggers
One or more access points associated to the WLC the failed to onboard.
Troubleshooting Steps
The Meraki dashboard will continue to retry adding these devices in the background. If the AP's continue to fail please contact Meraki support.
Dashboard Config Generation Failure
Triggers
An error occurring when the system is unable to successfully generate or apply the configuration for Dashboard. This can happen due to various reasons such as network connectivity issues, delays in applying updates, or internal system errors during the configuration process.
Troubleshooting Steps
-
Check Network Connectivity. Ensure the Meraki device has stable internet access. Poor connectivity can delay or prevent configuration updates from being applied, causing this error.
-
Monitor Bandwidth Utilization. High bandwidth usage during configuration changes can slow down synchronization. Check your network's utilization and reduce load if necessary.
-
Wait for Synchronization. Configuration changes typically apply within 1-5 minutes. However, delays of up to 10-20 minutes may occur due to high load on the Meraki shard or other factors. Allow some time for the changes to propagate.
-
Reboot the Device. If the device remains out of sync for an extended period, rebooting it may force it to fetch the latest configuration from the dashboard.
-
Verify for Configuration Conflicts. Check for any internal username conflicts on IOS XE devices (e.g., usernames like meraki-cli-ro or meraki-cli-rw), which should be removed manually from the device configuration. For wireless controllers, ensure AAA settings permit the Meraki user account to authenticate and authorize commands properly.
-
Check for IPv6 ACL Conflicts. If using NETCONF provisioning, ensure IPv6 ACLs permit access from the Meraki Tunnel interface subnet FD0A:9B09:1F7:1::/64.
-
Review Firmware Compatibility. Ensure devices are running firmware versions compatible with the features in use, such as Open Roaming or vMX firmware requirements.
-
Try Different Internet Connection. If possible, connect the device through a different internet connection to rule out upstream network issues.
Device Config Failure
Triggers
Indicates that the Meraki Dashboard was unable to successfully apply or generate the intended configuration on the device.
Troubleshooting Steps
-
Verify Device Connectivity:
-
Check if the device is powered on and connected properly.
-
Confirm the device is reachable from the Meraki Dashboard.
-
Review device LED status and run cable tests if needed.
-
-
Check Credentials:
-
Ensure the username, password, and enable password used during onboarding are correct.
-
Incorrect credentials can cause the dashboard to fail accessing the device for configuration.
-
-
Review Configuration Parameters:
-
Validate access policies, Radius server IPs, ports, and secret keys if 802.1X is used.
-
Remove or disable unused or dummy Radius server entries.
-
-
Check Dashboard Alerts and Logs:
-
Look for specific error messages related to configuration failures.
-
Review event logs under Network-wide > Event Log in the Meraki Dashboard.
-
-
Device Registration and Licensing:
-
For virtual devices like C9800-CL wireless controllers, ensure the device is properly registered and claimed in the Meraki Dashboard.
-
Verify licenses are valid and applied correctly.
-
-
Restart or Reboot Device:
-
Power cycle the device to clear transient issues.
-
OpenRoaming Firmware Incompatible
Triggers
Open Roaming is enabled on firmware that does not support this feature
Troubleshooting Steps
Upgrade the network devices to a firmware version that supports Open Roaming. Wireless networks in Dashboard needs to be configured for firmware version 28.5 or above. This is the minimum firmware requirement for the feature to work.
WPA3 Warning
Triggers
This device has disabled the 6 GHz frequency band because there are no active SSIDs using WPA3 encryption.
Troubleshooting Steps
Ensure that all SSIDs enabled for 6 GHz are configured for WPA3
Line VTY Conflict
Triggers
Occurs when there is a conflict or issue with the virtual terminal lines (VTYs) on a Cisco device. VTY lines are used for remote access sessions such as Telnet or SSH.
Troubleshooting Steps
-
Check current VTY line usage:
-
Use the command show users or show line to see active sessions and which VTY lines are occupied.
-
-
Clear stale or hung VTY sessions:
-
Use clear line <line_number> to free up VTY lines that are stuck or idle.
-
-
Configure idle timeout:
-
Set an exec-timeout on VTY lines to automatically disconnect idle sessions
-
-
Verify transport protocols:
-
Ensure VTY lines allow the desired protocols (SSH, Telnet) using the transport input command
-
-
Review and adjust access control:
-
Check for any access-class or access-list applied to VTY lines that might restrict access improperly.
-
-
Increase the number of VTY lines if needed:
-
Some devices allow increasing the number of VTY lines, e.g., line vty 0 15 to allow more simultaneous sessions.
-
-
Reboot device if necessary:
-
If conflicts persist and cannot be cleared, a device reboot may clear stuck sessions.
-
Switchport Allowed VLANs Missing
Triggers
Occurs when a trunk port on a switch does not have the correct VLANs allowed on it, which can cause connectivity problems for devices relying on those VLANs.
Troubleshooting Steps
By ensuring the trunk port is correctly configured with the appropriate allowed VLANs, and that the VLANs themselves are active and consistent across the network, the "Switchport Allowed VLANs Missing" issue can be resolved.
-
Verify trunk mode on the port
-
Check allowed VLANs on the trunk
-
Ensure VLANs exist and are active
-
Check native VLAN settings
-
Review VTP status and VLAN propagation
-
Clear and reset trunk port if needed
-
Check for errDisable state or port shutdown
Switch Required VLANs Missing
Triggers
Indicates that certain VLANs expected or required on a switch are not configured or active, which can cause connectivity or segmentation problems.
Troubleshooting Steps
-
Verify VLAN existence and status:
-
Use commands like show vlan brief to confirm required VLANs are present and active.
-
Create missing VLANs if necessary.
-
-
Check VLAN interface state:
-
Ensure VLAN interfaces are not administratively down.
-
-
Verify trunk port VLAN allowed list:
-
Confirm trunk ports allow the required VLANs.
-
Configure allowed VLANs explicitly if missing.
-
-
Avoid overlapping VLAN pools without proper domain and EPG association (for ACI environments):
-
Associate overlapping VLANs to different Attachment Access Entity Profiles (AAEPs) and Endpoint Groups (EPGs).
-
Enable EPG VLAN validation to prevent conflicts.
-
-
Use VLAN filtering carefully:
-
Ensure VLAN filters include all required VLANs.
-
-
Reapply or reset VLAN configurations if needed.
vMX Incompatible Firmware
Triggers
A vMX that is running 'on-prem' on a Cisco Enterprise Network Function Virtualization Infrastructure Software (NFVIS) appliance and has it's network firmware set to a version of MX firmware below MX 19.2.
Troubleshooting Steps
Upgrade the configured network firmware version to be above MX 19.2 on the Organization > Firmware Upgrades page.
Port-Channel Mixed Speed Ports Issue
Triggers
Meraki dashboard indicates that the ports configured as members of a port-channel (EtherChannel) have different link speeds. This situation can cause issues because all ports in a port-channel must operate at the same speed and duplex settings to function correctly.
Troubleshooting Steps
- Verify the speed and duplex settings on all ports that are part of the port-channel.
- Ensure all ports in the port-channel are configured to the same speed (e.g., all 1 Gbps or all 10 Gbps).
- Check the physical connections and cables to confirm they support the intended speeds.
- Adjust switch port configurations to match speeds or remove mismatched ports from the port-channel.
- Use the Meraki Dashboard to monitor port speeds under Switching > Monitor > Switch ports.
Device Onboarding In Progress
Triggers
Meraki dashboard typically indicates that a device is in the process of being registered and configured within the Meraki cloud management system. This onboarding process involves several key steps and prerequisites to ensure successful device registration and management
Troubleshooting Steps
- Devices should have internet connectivity to reach the Meraki cloud.
- DHCP should provide IP address, gateway, and DNS information to the device's WAN uplink for automatic registration.
- Proper firewall rules must be configured upstream to allow the device to communicate with Meraki cloud services.
- A Meraki dashboard account and organization must be created to manage devices.
- Devices must be added to the organization's inventory using order or serial numbers.
- Required licenses must be added to the dashboard, either automatically via order numbers or manually using claim keys.
- The dashboard shows real-time onboarding status as devices connect to the cloud and download configurations.
- Zero-touch provisioning allows devices to automatically download their configurations when powered on and connected to the network.
Switch Using Reserved VLAN(s)
Triggers
VLAN configuration issues involving VLANs that are reserved by the switch platform and should not be used for carrying traffic. Reserved VLANs are VLAN IDs within the valid 802.1Q range (1-4094) that the switch platform does not use for traffic. For Cisco Catalyst switches managed by Meraki, the reserved VLANs include VLANs 1002-1005 and 4093-4094.
Troubleshooting Steps
To resolve this alert, review the VLAN configuration on the affected switch, remove any reserved VLANs from active or allowed VLAN lists, and use VLAN Profiles and the VLAN Database feature to manage VLANs consistently across switches.
Session modules conflict in HTTP Server
Triggers
Dashboard uses TDL to receive telemetry from the connected device. This requires the use of HTTPS communication within the encrypted tunnel. The NG_WEBUI module is required for the HTTPS server on the switch to function as expected. This alert indicates that the NG_WEBUI module is currently disabled.
Troubleshooting Steps
Verify the configuration line containing ip http secure-active-session-modules. If this is set to none or uses a custom list without NG_WEBUI, communication with the device is limited and will not operate as expected.
To resolve, add NG_WEBUI to the custom module list or remove the ip http secure-active-session-modules line to revert to default behavior.

