Creating and Applying Group Policies
Group policies define a list of rules, restrictions, and other settings that can be applied to devices in order to change how they are treated by the network. Group policies can be used on wireless and security appliance networks and can be applied through several manual and automated methods. This article will describe the options available, how to create policies, and how those policies are applied to clients.
Learn more with these free online training courses on the Meraki Learning Hub:
Note: There is a limit of 3,000 clients that can have a group policy manually applied per network.
This limit does not apply for manually applied SSID polices and automatically applied policies (device-type group policies, SM Sentry group policies, RADIUS/802.1X login group policies, iPSK group policies).
Note: Cisco Meraki recommends as a best practice to create no more than 100 group policies per network.
Creating Group Policies
Available Options
The following table describes the rules, restrictions, and other settings that can be controlled via group policy on each platform. Only features that are available for the network will be displayed when configuring a group policy.
| MR Access Points | MX or Z Appliance with Enterprise License | MX with Advanced Security License | MS Switches | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scheduling | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | |
| Per-client bandwidth limit | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | |
| VLAN tagging | ✔ | |||
| Splash page authorization | ✔ | |||
| Layer 3 firewall rules | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Layer 7 firewall rules | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | |
| Traffic shaping rules | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | |
| Security filtering | ✔ | |||
| Content filtering | ✔ |
Note: If using a group policy with content filtering, please reference our documentation regarding content filtering rule priority to understand how certain filtering rules supersede each other.
Note: Source IP addresses on layer 3 firewall rules are only configurable on WAN Appliance when active directory integration is enabled.
Note: If you are using group policy on MS switches, please refer to our documentation on MS Group Policy Access Control Lists for additional details, including supported hardware and software.
Creating a Group Policy
- Navigate to Network-wide > Configure > Group policies.
- Click Add a group to create a new policy.

- Provide a Name for the group policy. Generally, this will describe its purpose or the users it will be applied to.
Ex. "Guests," "Throttled users," "Executives," etc. - Modify the available options as desired. Unless changed, all options will use the existing network settings.
- When done, click Save Changes.
The group policy listed will now be displayed on the Group policies page and made available for use. Remember that a group policy has no effect until it is applied.
Example Group Policies
The following examples outline two common use cases and how group policies can be used to provide a custom network experience.
Guests on a WAN Appliance
The following example is meant to demonstrate how a group policy could be configured on a security appliance network to limit the access and speed of guest clients. This policy would accomplish the following:
- Limit client bandwidth to 2Mbps up/down
- Deny access to the internal network (which uses the 10.0.0.0/8 address space)
- Block all peer-to-peer sharing applications
- All other settings would be inherited from network defaults (such as security and content filtering settings)

Bandwidth limit cannot be set lower than 20 kbps.
It is not possible to enter multiple comma-separated ports in group policy custom layer 3 firewall rules. Ports must be in the range of 1-65535, or "any."
Executive Users on Wireless
This example demonstrates how a group policy could be used on a wireless network to provide executive users with more freedom and special treatment over other users. This policy would accomplish the following:
- Remove bandwidth restrictions
- Remove layer 3/7 firewall rules
- Provide QoS tagging for voice and video-conferencing traffic.
- Remove the splash page requirement
- All other settings would be inherited from network defaults

Applying Group Policies
Group policies can be applied to client devices in a variety of ways, depending on the platform being used. The table below illustrates which options are available for each platform. The rest of this section explains how to use each method.
Note: Only one policy can be active on a client at a time.
Note: When doing a Configuration Sync to multiple target SSIDs, disable group policy assignment by device type before doing the sync.
| MR Access Points | MX or Z Appliance with Enterprise License | MX with Advanced Security License | MS Switches | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| By client | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | |
| By device type | ✔ | |||
| By VLAN | ✔ | ✔ | ||
| By sentry policy | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | |
| By active directory group | ✔ | |||
| By RADIUS attribute | ✔ | ✔ | ||
| By identity PSK | ✔ |
Note: A group policy will only be enforced by the appropriate Meraki device that is has been applied on. For example:
- A group policy applied 'By device type' will be enforced by the MR access point.
- A group policy applied 'By VLAN' will be enforced by the MX security appliance.
- A group policy applied 'By client' will be enforced by both the MR and MX, depending on the settings configured.
- For example, if there is an option to bypass splash enabled, the MR will enforce this. If there are only firewall rules configured, both the MR and MX will enforce these rules.
By Client
Group policies can be manually applied to clients from the Network-wide > Monitor > Clients page.
- Check the box next to the desired client(s) in the list.
- Click the Edit Policy button at the top of the list.
- Select Group policy and then choose the specific policy in the drop-down.
- Click Save.
Alternatively, on wireless and combined networks, different group policies can be applied depending on the SSID the client is associated to. This is applied from the same page as the previous steps.
- Check the box next to the desired client(s) in the list.
- Click the Policy button at the top of the list.
- Select Different policies by [connection or] SSID.
- For each SSID, select the desired group policy, built-in policy, or leave as normal.
- Click Apply policy.
Policies can also be applied to individual clients by clicking on the client in the clients list and then choosing a Device policy under the Policy section.
By Device Type
In wireless networks, group policies can be automatically applied to devices by type when they first connect to an SSID and make an HTTP request.
- Navigate to Wireless > Configure > Access control.
- Select the desired SSID.
- Set Assign group policies by device type to "Enabled."
- Click Add group policy for a device type.
- Select the desired Device type and the Group policy that should be applied to it.
- Repeat steps 4-5 as needed to assign policies to all desired devices.
- Click Save changes.
Keep in mind that this only occurs when a device first connects to the SSID and persists until it is manually overridden. Thus, some previously connected clients may need to have policies manually assigned. It is also possible for a client to be misclassified based on the initial HTTP request, depending on how it is generated by the device. If this occurs, manually assign the desired policy.

Please refer to the documentation for more information on applying group policies by device type.
By VLAN
On security appliance networks, group policies can be automatically applied to all devices that connect to a particular VLAN. From the Security & SD-WAN > Configure > Addressing & VLANs page:
- Ensure that VLANs is "Enabled."
- Click on the desired Local VLAN.
- Select the desired Group policy.
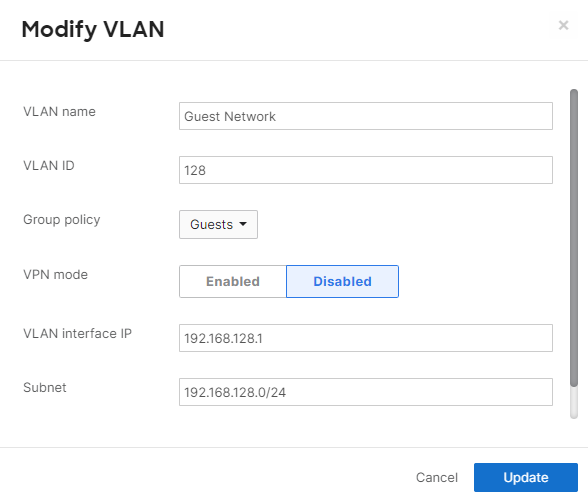
- Click Update.
- Click Save Changes.
Any clients that are placed in this VLAN will now be given the desired Group policy.
Note: Since the policy is applied on a per-VLAN basis, clients affected by this configuration will not contribute to the 'Affecting' counter for that policy displayed under Network-wide > Configure > Group policies page.
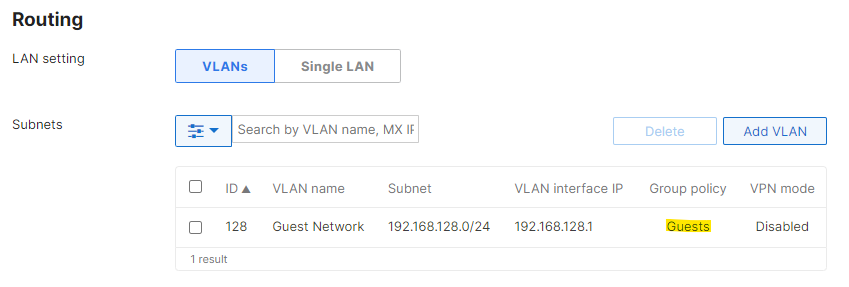
When a group policy is applied to a VLAN, that policy becomes the new "network default" for any other group policies applied to clients in that VLAN. Since this policy is the new "network default," the client devices will still show a "normal" policy applied under Network-wide > Monitor > Clients.
For example, a group policy named "Guest Network" with more restrictive layer 3 firewall rules than the network-wide configuration is applied to the guest VLAN, and a second group policy "Low Bandwidth" has a custom bandwidth limit, but is set to Use network firewall & shaping rules. If the Low Bandwidth group policy is applied to a client on the guest VLAN, the client will use the layer 3 firewall rules configured on the Guest Network group policy, not the network-wide layer 3 firewall rules configured on the Security & SD-WAN > Configure > Firewall page.
By Active Directory Group
Security appliance networks with Advanced Security licensing can use Active Directory groups to assign policies to clients. Refer to the article on configuring AD-based group policy for more information.
By RADIUS Attribute
Wireless networks that are using RADIUS to authenticate clients can be configured to assign group policies via RADIUS attributes. Refer to the article on configuring group policies with RADIUS attributes for more information.
By Identity PSK (IPSK)
Identity PSK or IPSK comes in two variants, IPSK with RADIUS and IPSK without RADIUS. Identity PSK with RADIUS authentication acts as a standard WPA2 PSK SSID to clients, while authenticating clients to a central server based on their MAC address. IPSK without RADIUS allows a network administrator to use multiple PSKs per SSID without the use of a RADIUS server. Further, the feature allows you to assign group policies in the dashboard based on the PSK used by the client device to authenticate to the Wi-Fi network. Please refer to the article IPSK with RADIUS Authentication and/or IPSK Authentication without RADIUS.
Scheduling
Group policies can be scheduled using the Schedule option. This allows the policy to only be active (or inactive) during the times specified.
When enabled, elements of the policy that are subject to schedule will be indicated with a small clock icon, as shown below. Options without this icon will always be in effect, regardless of time.

Warning: When scheduling a policy applied to a VLAN, traffic on the LAN will briefly drop as the configuration is applied. This will occur at the start and end of the schedule. Please take this into consideration when scheduling your group policy.
e.g., If production starts at 08:00, schedule the group policy to start earlier to ensure client connectivity is uninterrupted.
Scheduling Examples
8:00 am-5:00 pm weekdays (business hours)
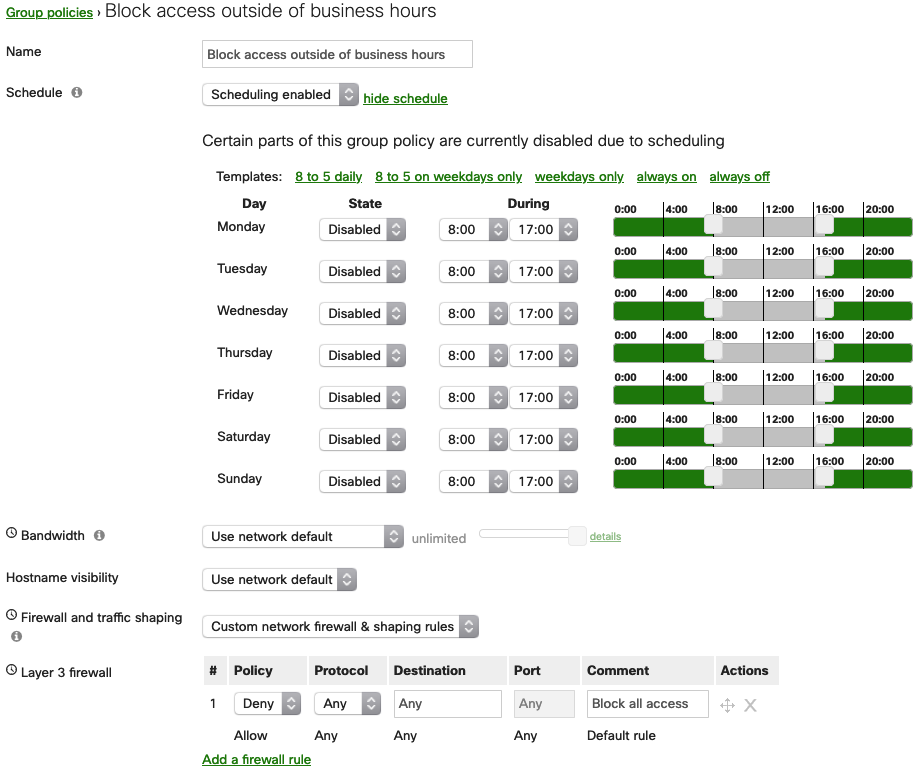
In the example below, a policy has been scheduled to only be active from 8:00 am-5:00 pm on weekdays:

From one day to the next
If it is required to have a policy applied from one day to another, the example below can be followed. Note that the policy is being disabled from 8:00 am-5:00 pm and on layer 3 firewall section, all traffic is being blocked. This means that:
- The policy will be disabled from 8:00 am-5:00 pm, not enforcing the configured the layer 3 firewall, allowing the traffic
- The policy will be enabled from 5:00 pm-8:00 am (next day), enforcing the configured the layer 3 firewall, blocking the traffic