AnyConnect on the MX Appliance
Click 日本語 for Japanese
Overview
A new AnyConnect Settings page in now available, and can be enabled on the dashboard by navigating to Organization > Configure > Early Access

The Cisco AnyConnect Secure Mobility Client consistently raises the bar by making the remote-access experience easy for end users. It helps enable a highly secure connectivity experience across a broad set of PC and mobile devices. This document provides information on the AnyConnect integration on Meraki appliances and instructions for configuring AnyConnect on the Meraki dashboard.
Learn more with these free online training courses on the Meraki Learning Hub:
AnyConnect Client Download and Deployment
AnyConnect Authentication Methods
AnyConnect Troubleshooting Guide
AnyConnect Load Sharing
AnyConnect Licensing on the MX Appliance
AnyConnect on ASA vs MX
Secure Connect (AnyConnect) Cisco TAC Support
Using the Cisco Secure Client Diagnostics Reporting Tool (DART)
FAQ
Feature
The AnyConnect VPN server on the MX uses Transport Layer Security (TLS) & Datagram Transport Layer Security (DTLS) for tunneling and requires AnyConnect VPN client version 4.8 or higher on either Windows, macOS, Linux, or mobile devices to terminate remote access connections successfully. The AnyConnect client negotiates a tunnel with the AnyConnect server and gives you the ability to access resources or networks on or connected to the AnyConnect server (MX). Unlike the AnyConnect implementation on the Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA), with support for other features like host scan, web launch, etc, the MX security appliance supports Secure Socket Layer (SSL), VPN, and other AnyConnect modules that do not require additional configuration on the MX. For more details, see AnyConnect on ASA vs. MX.
The MX supports Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP)/Internet Protocol Security (IPsec) Client VPN and AnyConnect VPN simultaneously.
AnyConnect can be used in place of L2TP/IPSec Client VPN configurations on operating systems that no longer support L2TP VPN services as it is a TLS & DTLS application based VPN.
AnyConnect is currently not supported on template bound networks.
AnyConnect VPN traffic can be routed through Site-to-Site VPN (both AutoVPN and Non-Meraki VPN).
Use Cases
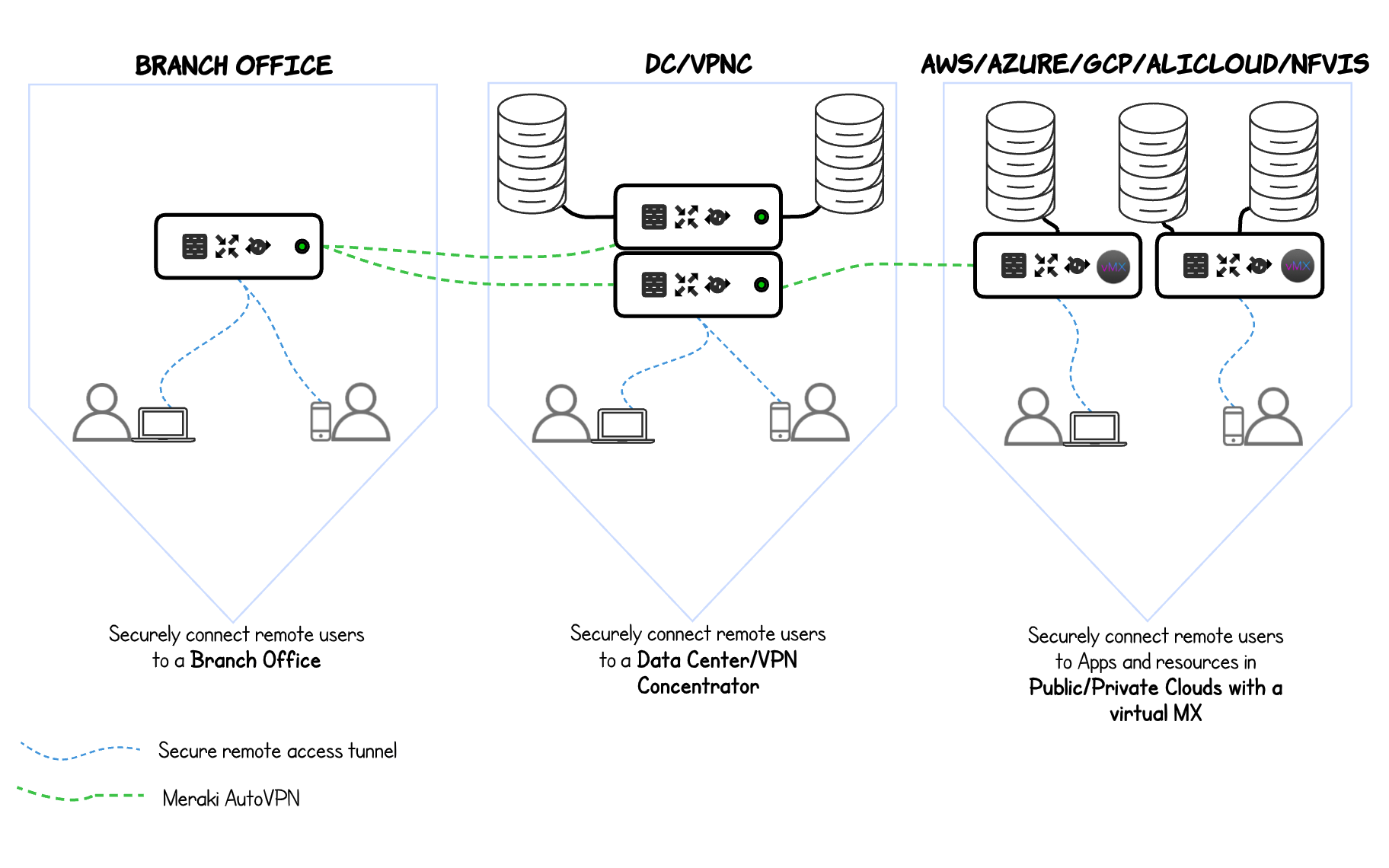
AnyConnect can be used to securely connect remote users to Branch Offices, Datacenter or Public Cloud environments. Using AnyConnect with the Meraki MX Appliance for remote access can enable users secure and seamless connectivity between different locations. Remote users can connect to a Branch office and transverse the Secure Software Defined Wide Area Network (SD-WAN) AutoVPN tunnel to access recourses in the Amazon Web Services (AWS)/Azure, etc., or other locations within the SD-WAN fabric.
Caveats
There are certain caveats to keep in mind before enabling AnyConnect:
-
Supported MX models: MX600, MX450, MX400, MX250, MX105, MX100, MX95, MX85, MX84, MX75, MX68(W,CW), MX67(C,W), MX65(W)*, MX64(W)*, Z3(C), Z4(C), vMX
*MX65(W) and MX64(W) only supports AnyConnect when running on firmware 17.6+
Not supported: MX90, 80, 60, Z1 (The AnyConnect Settings page will not be visible on dashboard for these models)
-
Either NAT Exceptions (No NAT) on MX Security Appliances or AnyConnect can be enabled per WAN uplink
-
IPsec and AnyConnect share the same configured RADIUS and Active directory servers
-
AnyConnect does not currently support cellular uplink (integrated or USB modem)
Note:
Stateless high availability and WAN failover are supported with AnyConnect on the MX. This means, when HA or WAN failover occurs, active user sessions will be disconnected and users will need to reconnect to the new active WAN link or the new primary MX. If you have two uplinks, its recommended to use the unique DDNS names of WAN1 and WAN2 as primary and backup servers in the AnyConnect connection profile.
How to Enable AnyConnect on Your Dashboard
Having reviewed the caveats, upgrade your MX security appliance to the required firmware version.
-
To enable AnyConnect, ensure that your network firmware version meets the minimum requirement. For MX64(W) and MX65(W), the firmware version must be 17.6+, and for all other supported models, the latest MX-16 firmware. Upgrades can be managed by navigating to Organization > Monitor > Firmware upgrades. For more details on firmware upgrades see Managing Firmware Upgrades
Server Settings
To enable AnyConnect VPN, select Enabled from the Cisco Secure Client Settings radio button on the Security & SD-WAN > Configure > Client VPN > Cisco Secure Client Settings tab. The following AnyConnect VPN options can be configured:
|
Hostname: This is used by Client VPN users to connect to the MX. This hostname is a Dynamic DNS (DDNS) host record that resolves to the Public IP address of the MX. The DDNS hostname is a prerequisite for publicly trusted certificate enrollment. You can change this hostname by following instructions on the Dynamic DNS (DDNS) article. For an alternative to DDNS enrolled certificates, see Custom hostname certificates section in this article. Profile update: This specifies the AnyConnect VPN configuration profile that gets pushed to the user on authentication. |
|
|
Cisco Secure Client VPN subnet: This specifies the address pool used for authenticated clients. IPv6 prefix (MX 18.104+): This specifies IPv6 prefix for AnyConnect to support IPv6 to both terminate a client VPN tunnel as well as IPv6 traffic inside the tunnel. More information can be found in IPv6 Support on MX Security & SD-WAN Platforms - VPN document in Configuring IPv6 for AnyConnect section. DNS nameservers: This specifies the Domain Name System (DNS) settings assigned to the client. DNS suffix: This specifies the default domain name or DNS suffix passed to the AnyConnect client to append to DNS queries that omit the domain field. This domain name only applies to tunnelled packets. Client routing: This is used to specify full or split-tunnel rules pushed to the AnyConnect client device. You can send all traffic through VPN, all traffic except traffic going to specific destinations, or only send traffic going to specific destinations. Dynamic client routing: This is used to specify full or split-tunnel rules pushed to the AnyConnect client device by hostname. For more details see Dynamic Client routing section in this article. |
|
|
Authentication Type: This is used to specify authentication with Meraki Cloud, SAML, RADIUS, or Active Directory. Certificate Authentication: This is used to configure the trusted Certificate Authority (CA) file that is used to authenticate client devices. This configuration is only required if you need to authenticate client devices with a certificate. Only certificates PEM format (*.pem) are supported at this time. RADIUS servers: This is used to specify the RADIUS host IP address, RADIUS port that the MX Security Appliance will use to communicate to the server, and the RADIUS shared secret. RADIUS message-authenticator verification: This is used to enable a RADIUS attribute that ensures integrity and authenticity of a message. Group policy with RADIUS filter-ID: This is used to enable dashboard group policy application using the filter passed by the RADIUS server. RADIUS timeout: This is used to modify the RADIUS time-out for two-factor authentication and authentication server failover. Default Group Policy: This is used to apply a default group policy to all connecting AnyConnect clients. For more details see Group Policies section in this article. |
|
Server Certificates
The AnyConnect server on the MX uses TLS 1.2 for tunnel negotiation, and TLS 1.3 on MX 19.1+, hence it needs a server identity certificate. The MX supports three certificate options:
Option 1: Auto-generated certificate with DDNS hostname
This is the default option. With this option, the MX Appliance will enroll in a public trusted certificate using the DDNS hostname of the Meraki network. This publicly trusted certificate renews automatically. The DDNS hostname is not easy to remember, hence, it is highly recommended to use an AnyConnect profile to create a DDNS alias to simplify user interaction. For more information see, how to create a profile. Dashboard administrators do not have to worry about interacting with public CAs to get a signed certificate.

DDNS hostname is configurable on MX Appliances in Passthrough/VPN Concentrator mode when AnyConnect is enabled.
Automatic certificate generation is not supported for networks hosted on dashboard.meraki.cn or dashboard.meraki.ca or dashboard.meraki.in
If the MX is in High Availability (HA) mode with a virtual IP and behind a NAT device, we recommend using the custom certificates feature to enable you manage your certificates and DNS records. The automatic DDNS hostname certificates may not suffice.
Option 2: Custom hostname certificates
- Requires MX firmware version 16.16+.
- Custom hostname certificates do not renew automatically. Administrators will need to renew certificates manually in addition to managing their DNS record (to enable their hostname resolve to the MX IP on the Internet).
- Custom hostname certificates are supported in High Availability mode. Adminstrators are required to download Certificate Signing Requests (CSRs) and upload certificates for both Primary and Spare MX Appliances with the custom certificates Primary | Spare tab only visible when the MX Appliance is in High Availability mode. Each MX device in HA needs to have its' own CSR generated with a different Common Name (CN).
- Wildcard certificates are not supported.
- Changing the Server Certificate Generation Method back to the default option of Auto-Generated from Custom will cause the MX to delete the current uploaded custom certificate.
Warning: A factory reset or device replacement (RMA) will generate a new private key for that MX. As such, a new CSR will need to be generated, signed and the resulting certificates will need to be re-added under Security & SD-WAN > Configure > Client VPN > AnyConnect.
Note: Utilizing a custom hostname certificate will replace the auto generated DDNS hostname on the MX.
Administrators can generate a CSR, that can be signed by a public CA. The signed certificate should be uploaded to the MX Appliance via the dashboard. This option allows administrators to use a preferred hostname. For example, vpn.abc.com

Step 1. Generate CSR

Step 2. Get the CSR signed by a public CA of your choice
Step 3. Upload the signed certificate and CA chain from your CA*

*Note: A chain certificate must establish a full chain of trust back to a root CA, including any intermediate certificates that sit between the device and root certs. Such certificates are self-signed by the CA providing them, as the following example demonstrates:
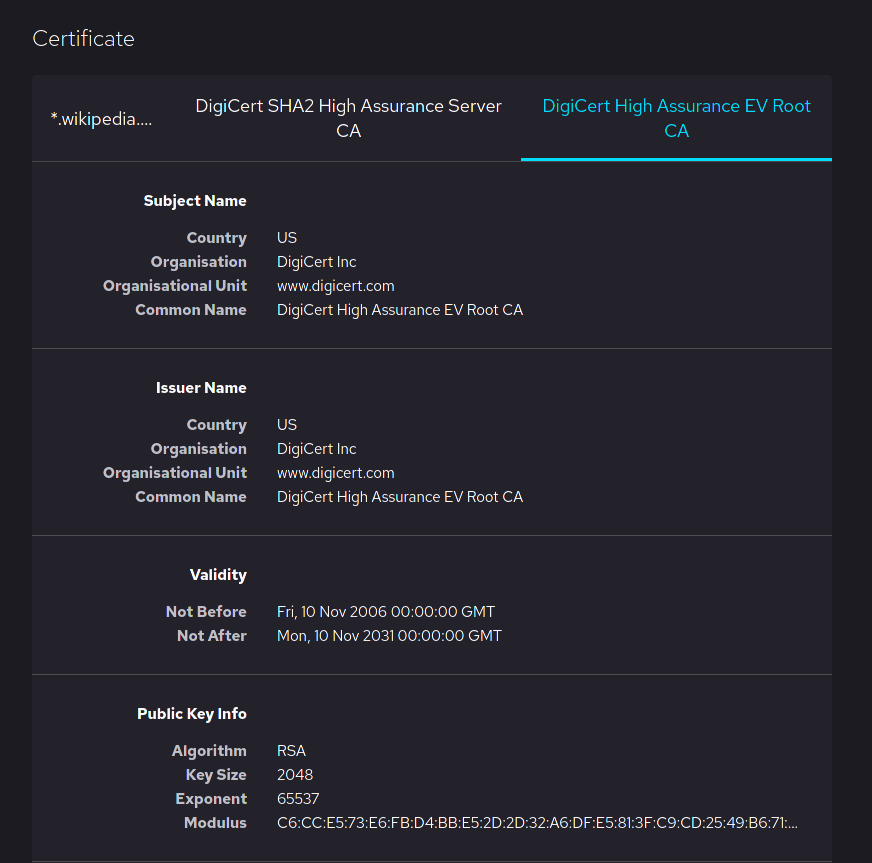
Image courtesy of Mozilla Software Foundation and Wikipedia
Note that both the Subject Common Name and Issuer Common name are equal.
An incomplete or invalid chain of trust will result in the error "Failed verifying Device Cert with Cert Chain" being seen on dashboard when you go to upload the certificates.
Questions on how to obtain such a certificate should be brought up to whatever entity is providing the ones in question. For more details regarding certificate chains, see the following DigiCert Article.
Option 3: Self-signed certificates:
Only available for testing purposes.
Note on Certificates
Starting in June 2026, Public Certificate Authorities will no longer issue TLS certificates that contain both the serverAuth EKU and the clientAuth EKU in the same certificate. Browsers such as Chrome will prevent the use of the Client Authentication purpose in the Extended Key Usage (EKU) extension on server certificates. This restriction does not impact Cisco Secure Client (formerly AnyConnect), as it does not leverage the Chrome browser for certificate-based authentication. However, users configured for SAML authentication with external browser workflows may be affected if the external browser is Chrome and certificate-based authentication is required. For more information on these changes for Chrome, please refer to this link https://googlechrome.github.io/chromerootprogram/
Authentication Methods
AnyConnect supports authentication with either SAML, RADIUS, Active Directory, Meraki Cloud and Certificate authentication. For more details on authentication configuration, refer to AnyConnect Authentication Methods.
Client Routing

- Send all traffic through VPN: This is the same as full tunneling. All traffic from the client is sent over the VPN tunnel.
- Send all traffic except traffic going to these destinations: This is the same as full tunnel with exclusions, when configured, the client will send all traffic over the VPN except traffic destined for the configured subnet. This option is not supported on Android devices.
- Only send traffic going to these destinations: This is the same as spilt tunneling, when configured, the client will only send traffic destined for the configured subnet over the VPN. Every other traffic sent over the local network.
When selecting "Only send traffic going to these destinations" or "Send all traffic execpt traffic going to these destinations" at least one IP must be entered otherwise the following error will be presented:
"The AnyConnect traffic destination (Client Routing) must contain at least one valid subnet in CIDR format."
Dynamic Client Routing
Dynamic Client Routing is only supported on MX16.5+ firmware
Dynamic Client Routing is only supported on Windows and Mac platforms. It is not supported Linux or any mobile platforms.
Dynamic split tunneling/client routing allows for the specification of traffic that should be included or excluded in the VPN tunnel based on domain name rather than IP/Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) notation. This is critical for services that do not have dedicated or fixed IP addresses. Dynamic split tunneling can be used with or without the regular split tunneling feature.
Please note that every hostname configured is treated as a wildcard. For example, cisco.com is treated as *.cisco.com. Wildcards, for example, *.cisco.com cannot be configured on the dashboard. For the end user, routes are populated when a user tries to access the specified hostname.

When selecting "Only send traffic going to these destination" or "Send all traffic except traffic going to these hostnames" at least one FQDN should be entered otherwise the following error message will be presented:
"The AnyConnect traffic destination (Dynamic Client Routing) must contain at least one valid destination."
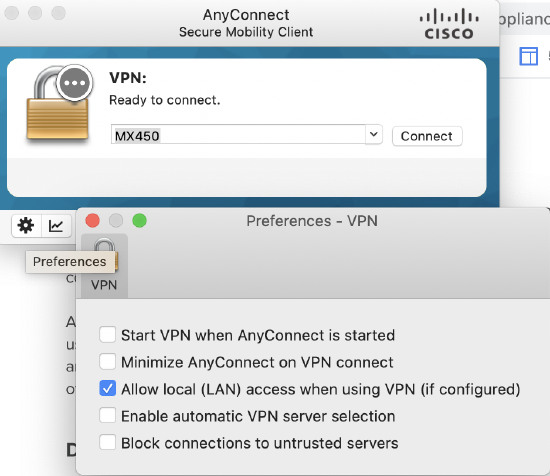
Local LAN access
Local LAN access may be desired when full-tunneling is configured (Send all traffic through VPN), but users still require the ability to communicate with their local network. For example, a client that is allowed local LAN access while connected to the MX in full tunnel mode is able to print to a local printer at home, while other traffic flows through the tunnel.
To enable local LAN access, two things need to be done. Local LAN access will not work if both conditions are not satisfied.
1. Configure the MX: Select "Send all traffic except traffic going to these destinations" option on the dashboard and configure a 0.0.0.0/32 route. This will cause the AnyConnect client to automatically exclude traffic destined for the user's local network from going over the tunnel.

2. Configure the Client: Enable Allow local LAN Access on the AnyConnect Client. This can be enabled manually or via the AnyConnect profile.
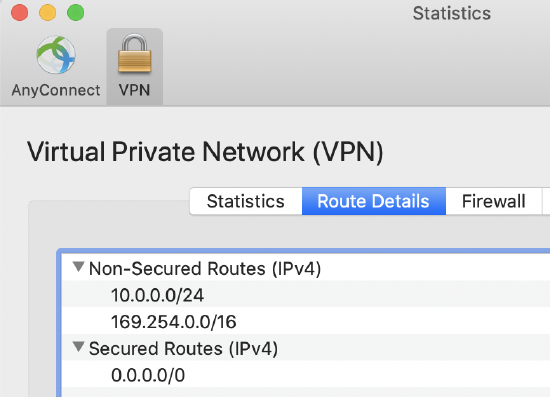
After connection, the user should see their local network subnet added as a non secure routes (destinations that should be accessed locally not via the VPN tunnel)
Session Timeout
The client session timeout can be configured using one of the predefined values (8 hours, 1 day, 7 days). Or, you can use the custom option and specify up to a maximum of 256 hours.

Group Policies
The need for access control over remote access connections cannot be over-emphasized. While some administrators use multiple address pools to segment users, others use VLAN tagging to existing subnets. From a Client VPN standpoint, multiple subnets or separate VLANs do not provide access control in itself. What segments users from talking to each other or other network resources is the presence and the enforcement of access rules. For example, if users are in different VLANs and access policies are not enforced somewhere, users could access anything.
AnyConnect on the MX does not support multiple VLANs or address pools for Client VPN users. However, the MX supports the application and enforcement of policies to AnyConnect users on authentication. It is also important to note that, from a Client VPN standpoint on the MX, having users on the same subnet does not mean they are in the same VLAN. Users are assigned a /32 address (one address) from the pool configured on dashboard. Group Policies can then be used to limit users on the same AnyConnect subnet from talking to each other or other resources on the network.
Default Group Policy
Administrators can apply a global group policy to all users connecting through AnyConnect by selecting a configured policy from the default Group Policy drop-down menu. Group policies can be configured via Network-wide > Configure > Group policies. Refer to Creating and Applying Group Policies for more details.

Note: If a default group policy set and group policy with Filter-ID is also enabled, the Filter-ID policy passed by the RADIUS server will take precedence over the default group policy.
Group Policies with RADIUS Filter-ID
AnyConnect supports the application of dashboard-configured group policies to AnyConnect users when authenticating with RADIUS. This is achieved using the RADIUS Filter-ID attribute. To set this up on your MX:
-
Create group policies under Network-wide > Configure > Group Policies. Specify rules within the policy. Multiple group policies can be mapped to different user groups on the RADIUS server. In this example, we are matching CONTRACTOR policy to CONTRACTOR user group.


-
Enable the Filter-ID option on the dashboard. This option is only configurable if you are authenticating with a RADIUS server.

-
Configure the RADIUS server to send an attribute in its accept message containing the name of a group policy configured in dashboard (as a String). Commonly, the Filter-ID attribute will be used for this purpose. The screenshot below shows a network policy in Windows Network Policy Server (NPS), configured to pass the name of a dashboard group policy ("CONTRACTOR") within the Filter-ID attribute:
.png?revision=1&size=bestfit&width=752&height=395)
The RADIUS server is configured with the group policy "CONTRACTOR" defined on dashboard. When a user in the group successfully authenticates, the "CONTRACTOR" group policy name for the authenticated user will be sent in the RADIUS accept message, allowing the MX to apply the requested policy to the user. The group policy name sent by the RADIUS server must match verbatim what is configured on the dashboard for policies to apply correctly. Currently, policies do not show up on Network-wide > Monitor > Clients list page if you have only a security appliance in your dashboard network, however, If you have a combined network, the policy will show under the 802.1X policy column.
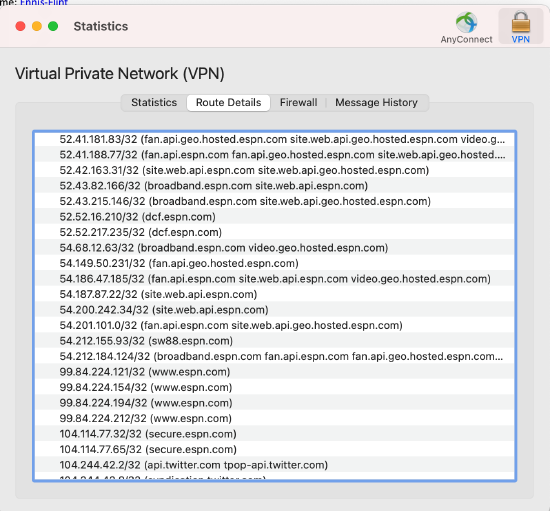
Client VPN Connections
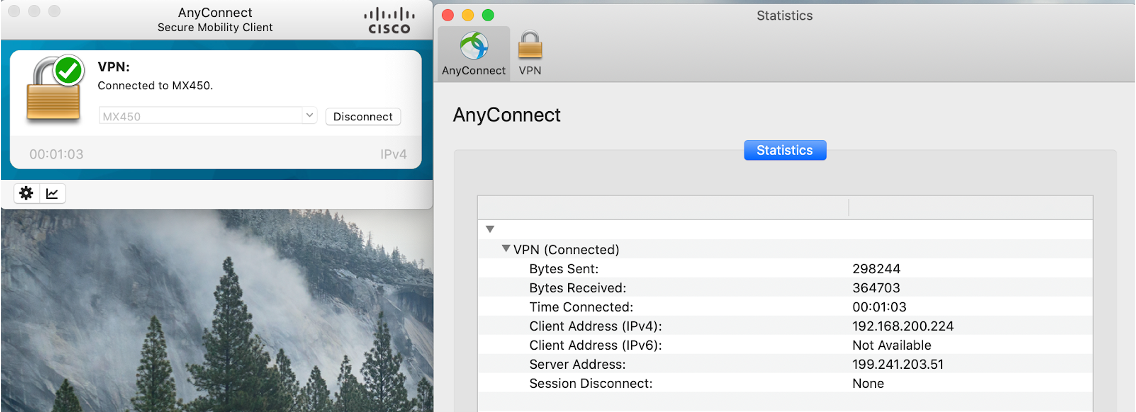
Client view:
You can see client stats and connection details by clicking on the graph in the bottom-left corner of the client.
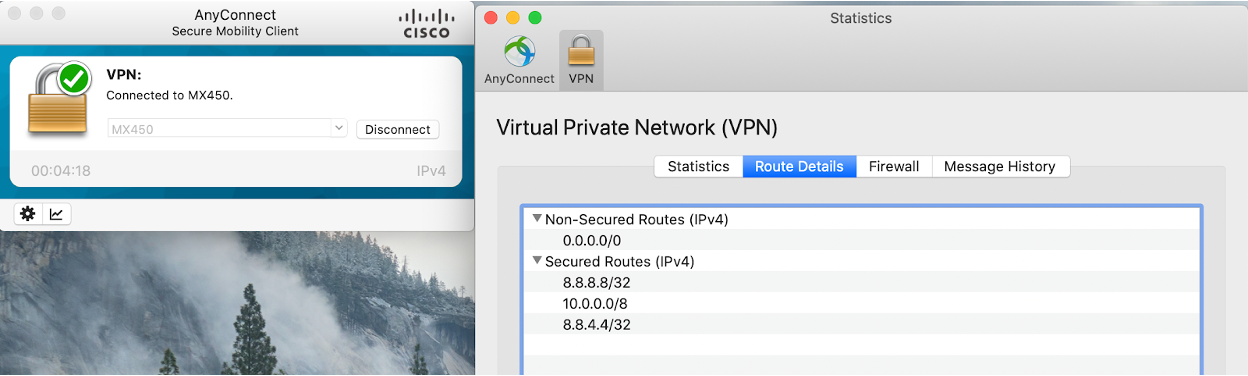
Clients can also see available routes on the Route Details tab. Secure routes are accessible by the client over the VPN while nonsecure routes are not accessible by the client over the VPN. Nonsecure routes are visible when split-tunneling is configured.
Connection logs can be found under the Message History tab.
Dashboard view:
After configuring client VPN, to see how many users are connected to your network, navigate to Network-wide > Monitor > Clients. All AnyConnect clients will be seen with the AnyConnect icon. You can filter by client VPN using the search menu.
Note: The MAC address seen on the client list is is not the actual MAC address of the AnyConnect client. Instead, the displayed address is pseudo-randomly generated, using the provided username as its base. For example, each time someone connects using the name xyz.test@example.com, an entry will show up as active on the clients list with the same given MAC address.
In the event that multiple devices are connected simultaneously with the same set of credentials, the data seen on the list will reflect the most recently connected device.
Depending on your operating system the output of ipconfig/ifconfig may show a default gateway of 0.0.0.0 and subnet mask of 255.255.255.255. This is expected behavior and does not affect the functionality of AnyConnect.
Event Logging
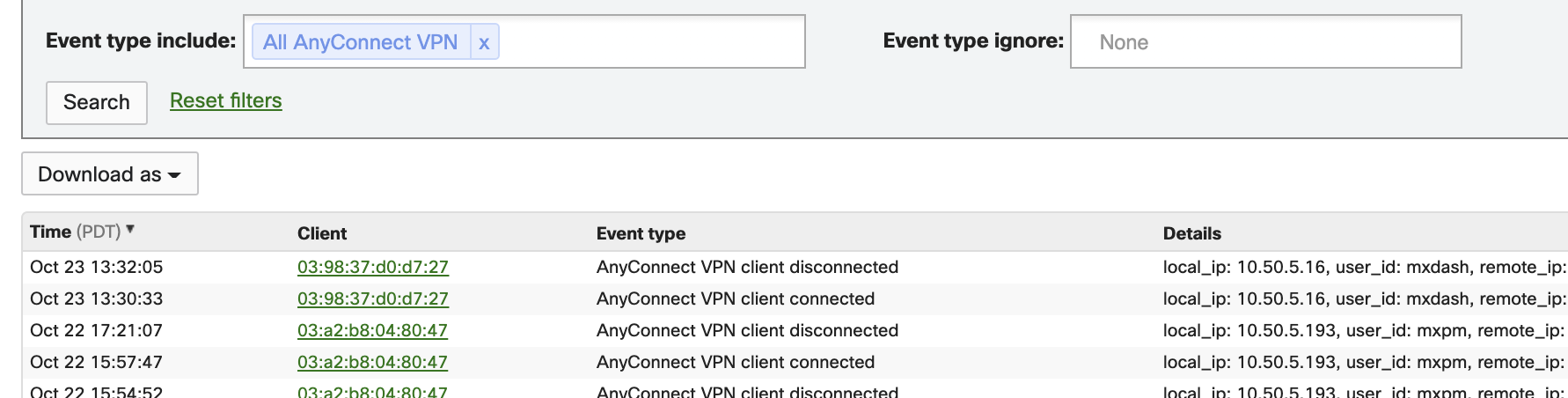
To see all available events, navigate to Network-wide > Monitor > Event Log and filter the Event type include field by AnyConnect.
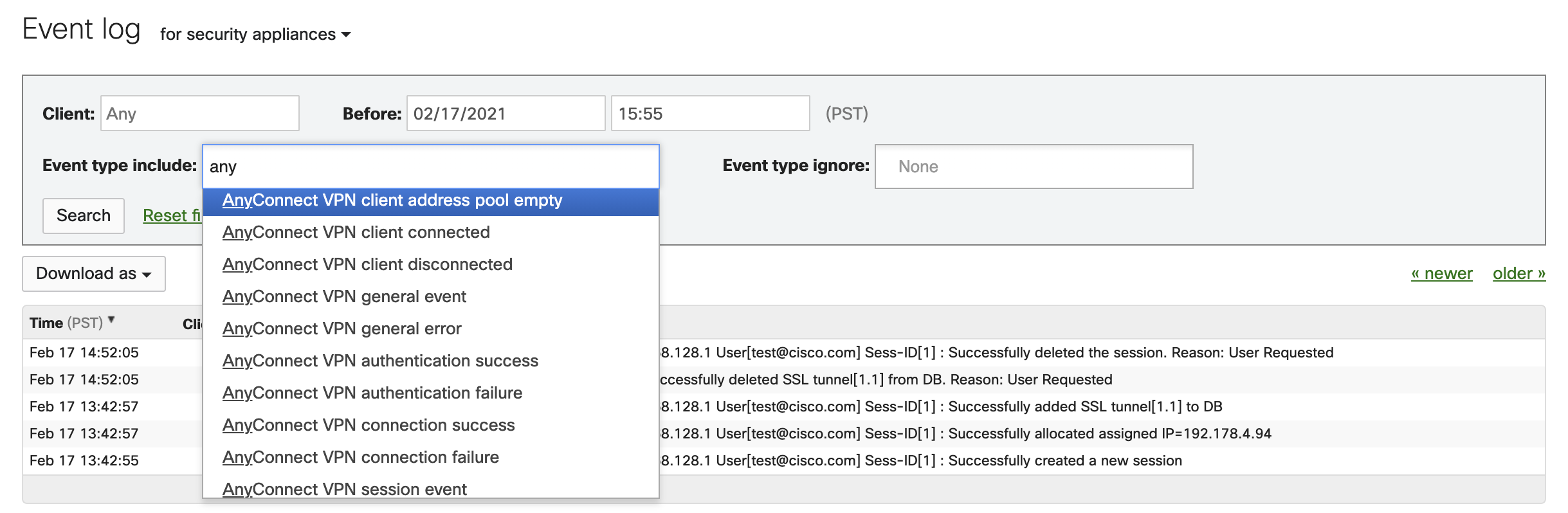
To see log-on and log-off events, go to Network-Wide > Monitor > Event log and filter by VPN client connected and VPN client disconnected.
Number of Supported Sessions per MX Model
Below is the number of sessions allowed per MX model. When the limit is reached, new sessions will not be formed.
|
Model |
Max sessions |
|---|---|
| MX450 | 1,500 |
| MX250 | 1,000 |
| MX105 | 750 |
| MX100 | 250 |
| MX95 | 500 |
| MX85 | 250 |
| MX84 | 100 |
| MX75 | 250 |
| MX67/68 | 100 |
| MX64/65 | 50 |
| Z3 | 5 |
| vMX S/M/L | 100/250/500 |
| vMX100 | 250 |
| MX600 | 1000 |
| MX400 | 750 |
FAQ
-
Who signs the Meraki facilitated publicly trusted certificates?
A publicly trusted Certificate Authority. -
Can I use my own hostname or publicly trusted certificate on the MX as a server certificate?
Yes, see Custom hostname certificates -
How will AnyConnect be licensed on the Meraki MX?
See AnyConnect licensing on the MX -
Can I use AnyConnect profiles?
Yes, see the AnyConnect Profiles section. Only VPN profiles can be pushed via the MX. Others profiles, like Umbrella profiles, etc will not be pushed via the MX. -
Can I configure different split-tunnel rules/VLANs/IP address pools for different sets of users?
No, not at the moment. However, you can use group policies when authenticating with RADIUS to apply access policies to a user or groups of users on authentication. -
Can I do certificate-based authentication?
Yes, as a combination with username and password. See the certificate-based authentication section. Certificate-only authentication is currently in beta see Certificate-only authentication for more details. -
Where can I download the AnyConnect client?
On the AnyConnect Settings page on dashboard in the Client Connection section or on cisco.com -
What are the current caveats/known issues with the AnyConnect feature & firmware?
See caveats section -
Which features are supported? Any plans to support Umbrella, posture scan, 802.1x, etc?
VPN Only. Other AnyConnect modules that do not require additional server support can be used as well, for example, DART, Umbrella. This module must be deployed and configured separately as the MX does not support web launch, client software deployment, or update at this time. See AnyConnect on ASA vs. MX for more details. -
Can I use IKEv2 on AnyConnect to connect to the MX Appliance?
No, AnyConnect only supports TLS 1.2 ( TLS 1.3 on 19.1+ firmware) and DTLS 1.2 connections on the MX. -
Can I run L2TP/IPsec Client VPN and AnyConnect VPN simultaneously on the MX?
Yes. -
Can I connect to the inside interface of the MX with AnyConnect? For example, connect to the MX from the LAN side?
No, only inbound connections on the WAN side are supported at this time. -
When will AnyConnect General Availability (GA)?
AnyConnect GA'd on the MX 16.16+ firmware released in March 2022. - Does Cisco AnyConnect custom server certificate support the use of a wildcard certificate? Example, XXX.mycompany.com vs wildcard certificate *.mycompany.com
Wildcard certificates are not supported.